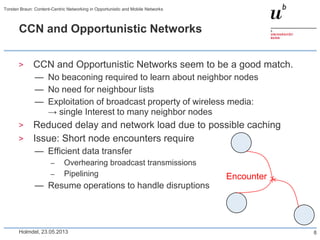
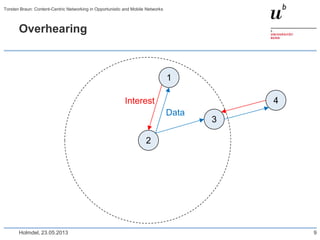
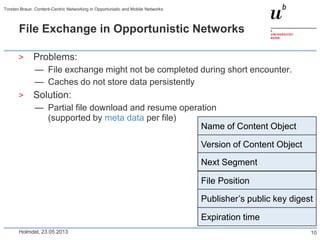
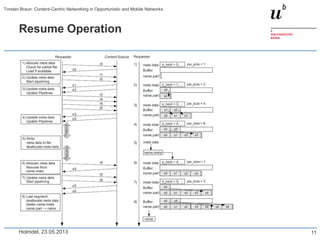
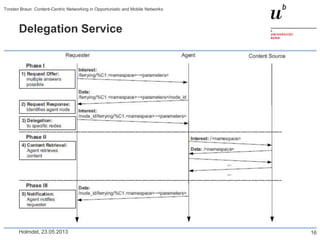
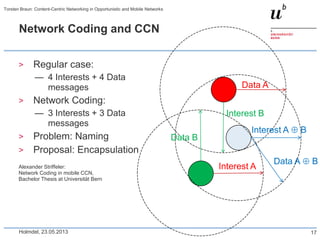
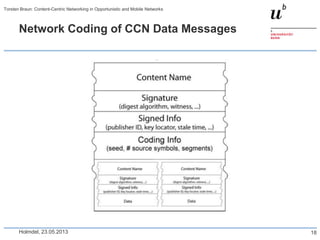
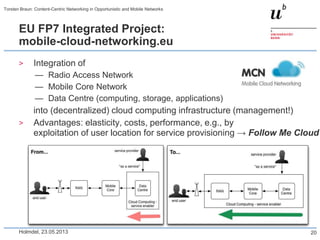
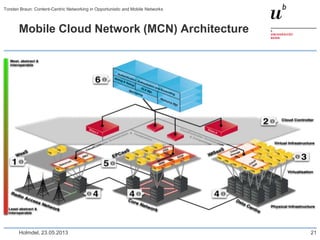
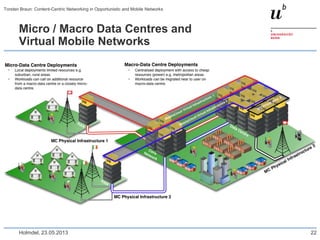
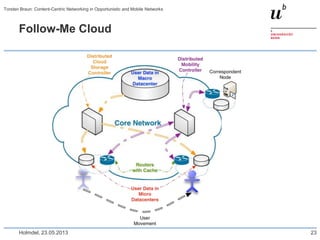
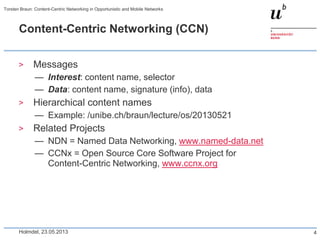
Torsten Braun presented on using content-centric networking (CCN) in opportunistic and mobile networks. CCN is well-suited for these environments as it does not require neighbor discovery and can take advantage of wireless broadcast. However, short encounters require efficient transfer methods like overhearing, pipelining, and resume operations to handle disruptions. CCN also supports receiver mobility but source mobility presents challenges. The EU FP7 mobile cloud networking project is investigating using CCN for caching mobile user cloud data.


![SCN Prototype Evaluation
Holmdel, 23.05.2013
Torsten Braun: Content-Centric Networking in Opportunistic and Mobile Networks
7
user1 ccnd1
client1
user2 ccnd2
client2 ccndr
conversion
service &
repository
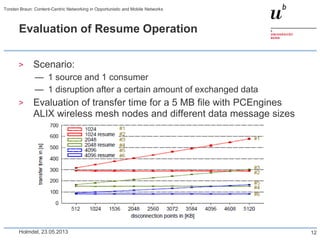
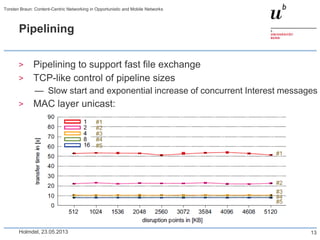
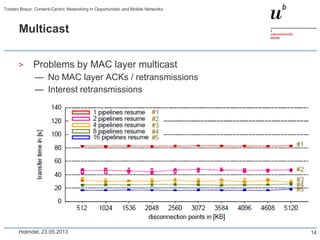
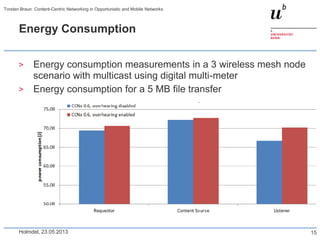
CCN router
ccndp
publisher
1/8
2/7
11/12
3
5
6
4
13/14
18/19
10
15
9
16
17/20
186 31 4
0
50
100
150
200
1-8 9-16 17-20
time [s]
1-8: Client 1 retrieves bit map image (36 MB)
9-16: Client 2 retrieves JPEG image (6 MB)
17-20: Client 1 retrieves JPEG image
Torsten Braun, Andreas Mauthe, Vasilios Siris:
Service-Centric Networking Extensions,
28th ACM Symposium on Applied Computing,
Coimbra, Portugal, March 18 - 22, 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/torstenbelllabs2013-130523224603-phpapp01/85/Content-Centric-Networking-in-Opportunistic-and-Mobile-Networks-7-320.jpg)