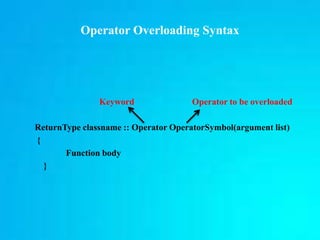
Operator overloading allows operators like + and - to be used with user-defined types in C++. Certain operators like = and [] must be overloaded as member functions, while others like friends and non-members can also be overloaded. Unary operators operate on a single operand, while binary operators require two operands. Overloaded operators are implemented via member functions, non-member functions, or friend functions depending on whether the left operand is of the class type. Strings can also be manipulated using overloaded operators by defining a string class with a character pointer and length.
![OPERATOR
OVERLOADING IN C++
PRESENTED BY
M.RAMYA
M.Sc[CS&IT]
NSCAS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operatoroverloading-170904143009/85/Operator-overloading-1-320.jpg)


![Operator that must be overloaded as members
• Assignment operator - =
• Subscript operator – [ ]
• Function call operator – ()
• Indirect member access operator - ->
• Indirect pointer to member access operator - ->*](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operatoroverloading-170904143009/85/Operator-overloading-4-320.jpg)