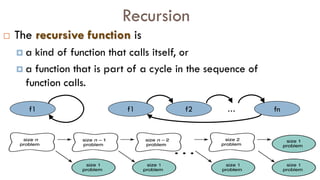
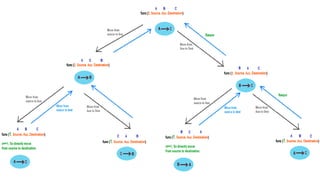
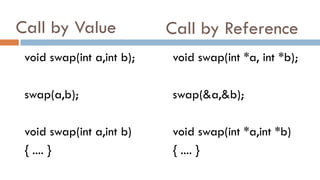
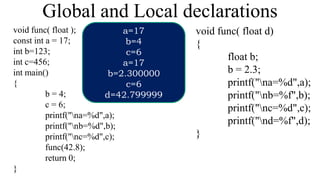
The document discusses call by value vs call by reference in functions, and different storage classes in C including auto, extern, register, and static. It provides examples of each storage class and how they determine the scope and lifetime of variables. It also discusses recursion and provides examples of recursive functions to calculate factorial, sum of natural numbers, Fibonacci series, and solve the Towers of Hanoi problem.











![Syntax : auto [data_type] [variable_name];
Example : auto int a;
void main()
{
auto int i=10;
{
auto int i=20;
printf("nt %d",i);
}
printf("nnt %d",i);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppspost-220308050120/85/C-Programming-Storage-classes-Recursion-14-320.jpg)

![Syntax : extern [data_type] [variable_name];
Example : extern int a;
Program:
extern int i=10;
void main()
{
int i=20;
void show(void);
printf("nt %d",i);
show();
}
void show(void)
{
printf("nnt %d",i);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppspost-220308050120/85/C-Programming-Storage-classes-Recursion-16-320.jpg)


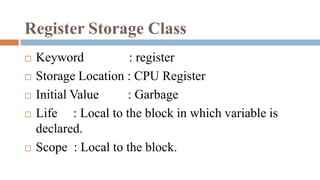
![Syntax : register [data_type] [variable_name];
Example : register int a;
void main()
{
register int i=10;
{
register int i=20;
printf("nt %d",i);
}
printf("nnt %d",i);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppspost-220308050120/85/C-Programming-Storage-classes-Recursion-20-320.jpg)
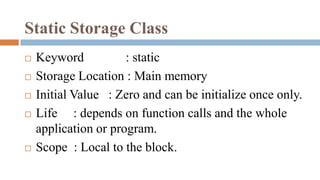
![Syntax : static [data_type] [variable_name];
Example : static int a;
void main()
{
int i;
void incre(void);
for (i=0; i<3; i++)
incre();
}
void incre(void)
{
int avar=1;
static int svar=1;
avar++;
svar++;
printf(“Auto var value : %d",avar);
printf("Static var value : %d",svar);
}
OUTPUT
Auto var value : 2
Static var value : 2
Auto var value : 2
Static var value : 3
Auto var value : 2
Static var value : 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppspost-220308050120/85/C-Programming-Storage-classes-Recursion-22-320.jpg)