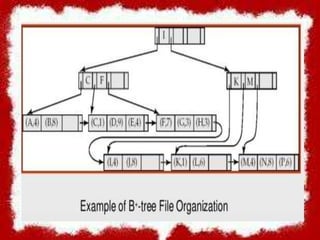
B+ tree is a data structure used to store (key, value) pairs in a tree-like structure for fast retrieval. It has a root node, intermediary nodes that point to leaf nodes but do not store data, and leaf nodes that store the actual records. Leaf nodes must contain a minimum and maximum number of values, and non-leaf nodes a minimum and maximum number of child nodes. B+ trees allow fast traversal and search via balanced structure and sorted nodes. Records are inserted and deleted by searching the tree to the appropriate leaf node and updating pointers and values.
![B+ TREE
PRESENTED BY
M.RAMYA
Msc[CS&IT]
NADAR SARASWATHI COLLEGE OF ARTS &SCIENCE,
VADAPUDUPATTI , THENI.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/btree-180126072907/85/B-tree-1-320.jpg)



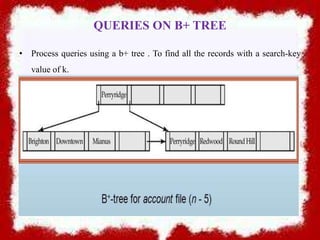
![• Leaf nodes must have between 2 and 4 values([(n-1)/2)] and n-
1 , with n=5).
• Non-leaf nodes other than root must have between 3 and 5
children([(n/2)]and n with n=5).
• Root must have at least 2 children.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/btree-180126072907/85/B-tree-6-320.jpg)