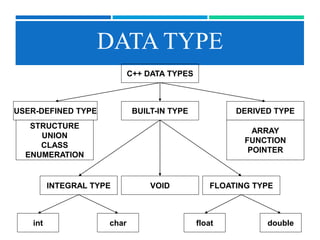
The document discusses various data types in C++ including built-in, user-defined, and derived types. Structures and unions allow grouping of dissimilar element types. Classes define custom data types that can then be used to create objects. Enumerated types attach numeric values to named constants. Arrays define a collection of elements of the same type in sequence. Functions contain blocks of code to perform tasks. Pointers store memory addresses.








![DERIVED TYPE
ARRAYS:
An array is a fixed sequence collection of
elements of same data type that share a
common name.
General syntax to declare is
data_type name[size];
General syntax to initialize is
for(i=0;i<=10;i++)
cin>>a[i];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypesinc-170219034138/85/Data-types-in-c-18-320.jpg)




