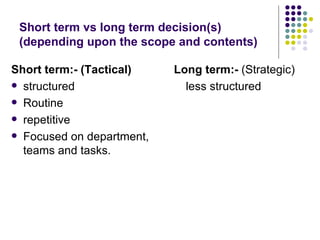
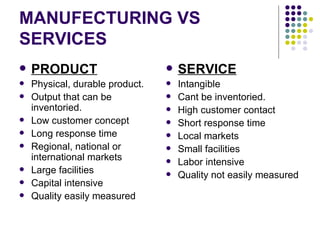
Operations management involves directing and controlling processes that transform inputs into products and services. A process takes inputs, transforms them through processing functions, adds value, and produces outputs. There are two types of customers - external customers who are end users or intermediaries, and internal customers who rely on outputs from earlier processes. Nested processes involve initiating a process within another process. Operations management principles state that all parts of an organization must design and operate processes to deal with quality, technology, and staffing issues. Decisions can be either strategic and long-term, or tactical and short-term.