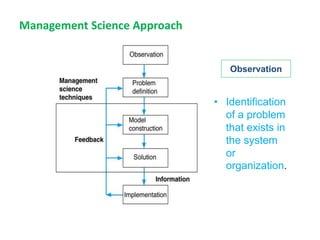
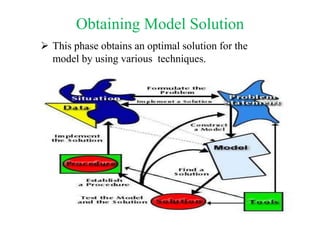
1) Operations research is a quantitative approach to decision making based on the scientific method of problem solving. It involves modeling real-life situations as mathematical problems to arrive at optimal or near-optimal solutions.
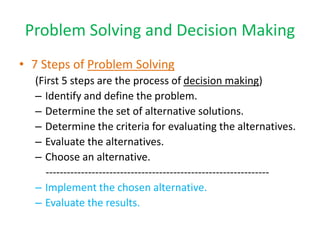
2) The key steps in operations research problem solving are defining the problem, determining alternative solutions, evaluating alternatives using criteria, choosing the best alternative, implementing the chosen alternative, and evaluating the results.
3) Common techniques used in operations research include linear programming, transportation modeling, assignment modeling, and simulation methods like PERT/CPM. These techniques help optimize objectives while satisfying constraints.