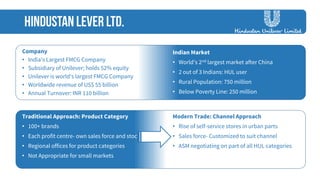
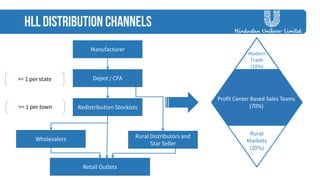
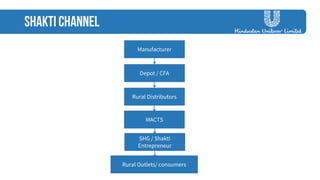
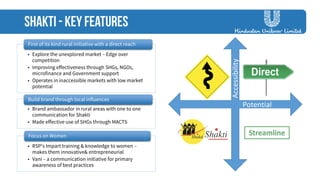
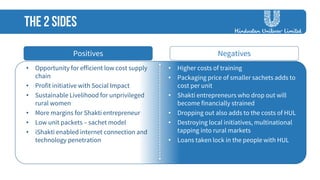
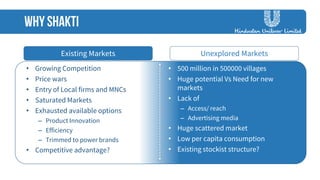
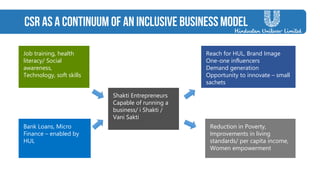
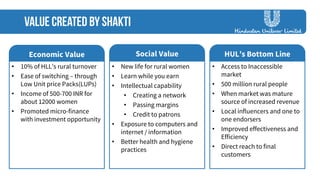
The document discusses strategies employed by India's largest FMCG company, HUL, to penetrate rural markets with a focus on women empowerment through Shakti entrepreneurs and low-cost supply chain innovations. It highlights the challenges faced, including competition and market saturation, while emphasizing the economic and social value generated through the initiative. Key initiatives include training programs, micro-finance support, and local influencer engagement to establish brand presence in over 500,000 villages.