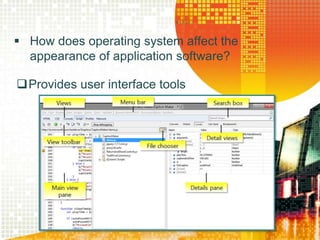
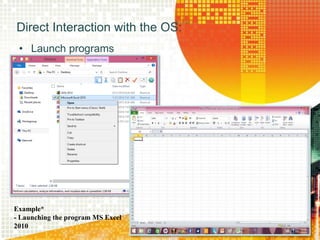
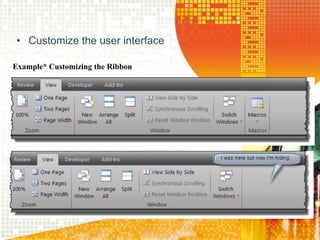
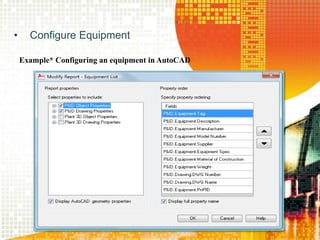
An operating system acts as an interface between the user and computer hardware, managing resources like the processor, RAM, storage, and peripherals. It provides a graphical user interface to allow users to point and click icons and windows on screen. Operating systems can be single-user and found on devices like PCs, servers, and mainframes stored on a hard disk, or multi-user and network operating systems that allow file sharing and multitasking between multiple users on a network. Common examples are Windows, Mac OS, Linux, and IBM's OS/360.