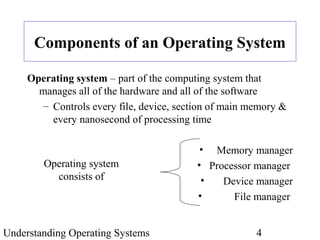
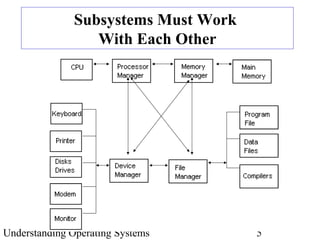
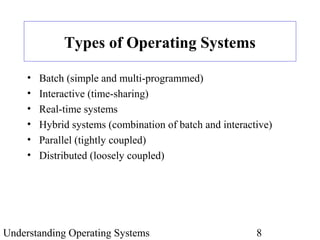
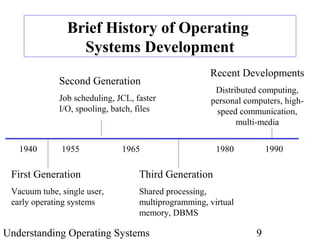
The document provides an overview of the textbook "Understanding Operating Systems" by Flynn & McHoes. It discusses 12 chapters that are split into two parts - the first part covers operating system theory, including memory management, processor management, process management, and other topics. The second part discusses specific operating systems in practice like MS-DOS, Windows 2000, UNIX/Linux, OpenVMS Alpha and IBM OS/390. It also includes introductory sections on operating system components, the role of hardware and software, a brief history of operating system development, and definitions of key terms.