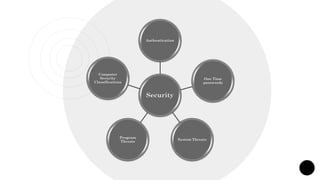
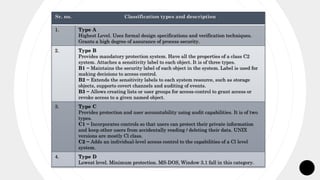
The document presents a comprehensive overview of operating systems and application security, emphasizing the importance of proper authentication and various program and system threats such as viruses and worms. It details different authentication methods, security classification types as per the U.S. Department of Defense, and acknowledges contributions from teachers, family, and friends in creating the presentation. Additionally, it highlights the impact of malicious programs on system performance and outlines security measures necessary for protecting computer resources.