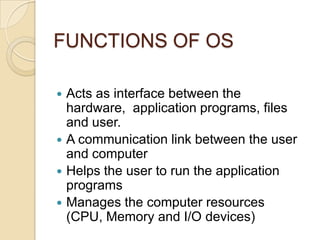
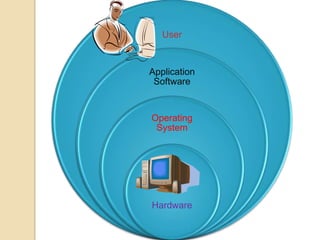
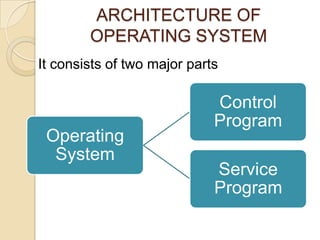
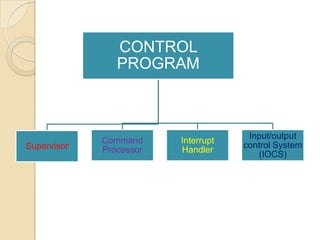
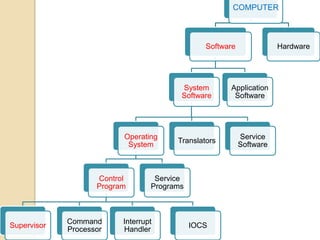
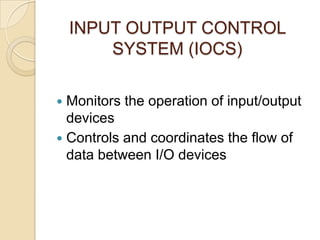
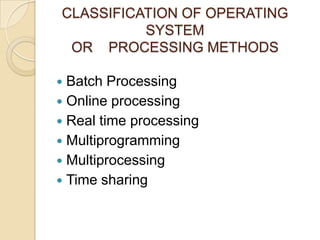
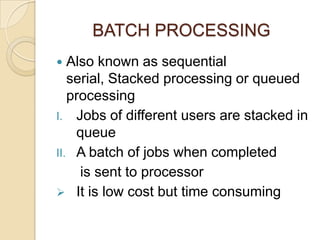
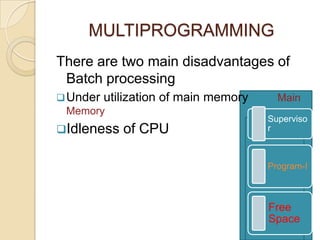
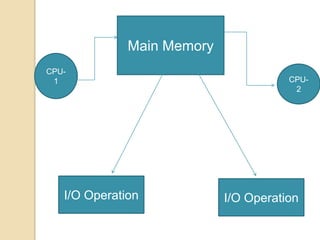
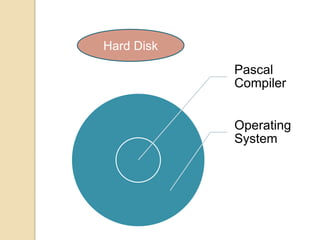
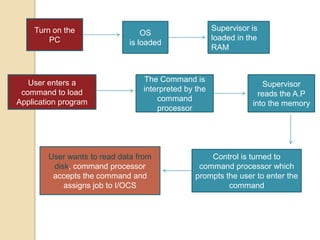
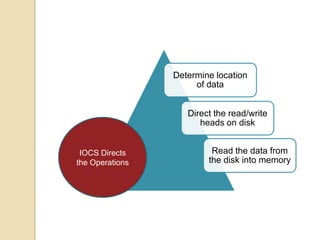
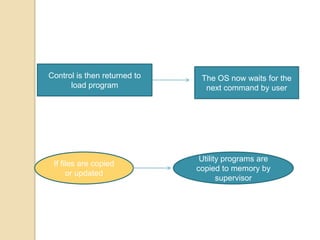
An operating system is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs. It acts as an interface between users and applications and the underlying hardware. Key functions of operating systems include running application programs, managing memory and disk storage, handling input/output devices, and providing a user interface. Common examples of operating systems include Windows, Linux, macOS, and iOS.