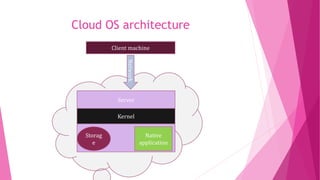
The document discusses cloud operating systems. A cloud OS runs applications and stores data on remote servers that can be accessed from any internet-connected device. This is different than traditional desktop computing which stores programs and files locally. A cloud OS has several advantages like lower costs, automatic updates, universal access, and unlimited storage. However, it requires an internet connection and performance may be reduced without fast speeds. The document provides examples of cloud OSs, describes their architecture which involves clients connecting to a remote server over the network, and covers applications, demonstrations, storage features, advantages and disadvantages of cloud OSs.