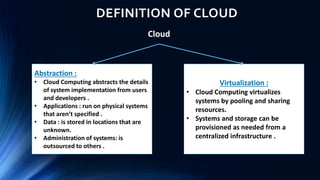
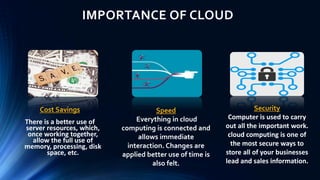
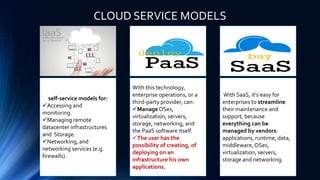
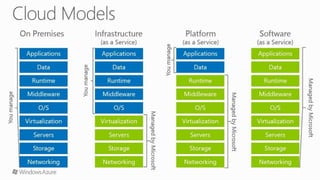
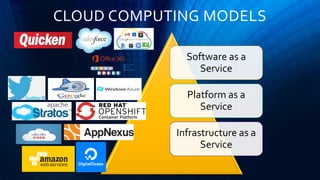
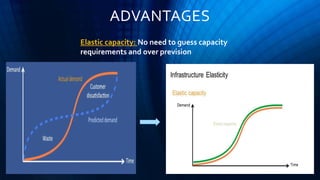
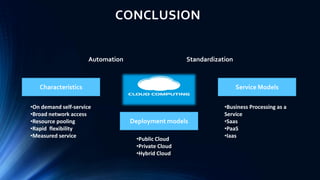
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to shared computing resources like networks, servers, storage, applications and services available over the internet. It allows users to access applications from anywhere using a web browser. Cloud computing offers advantages like cost savings, speed, security, unlimited storage and access to data from anywhere. While cloud services like AWS have become very popular, cloud computing also presents risks like security vulnerabilities and inconsistent performance on shared infrastructure. The growth of cloud computing is impacting IT jobs by creating new roles while reducing needs for some traditional IT positions.