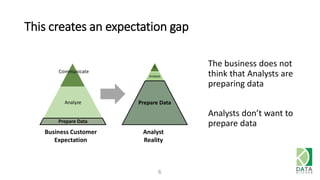
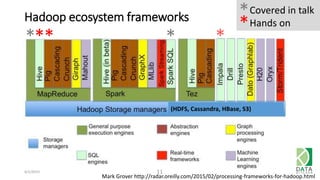
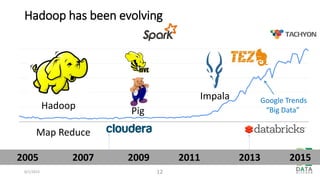
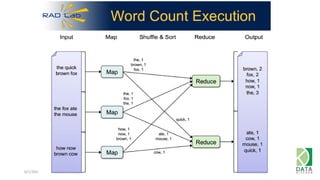
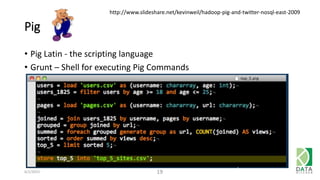
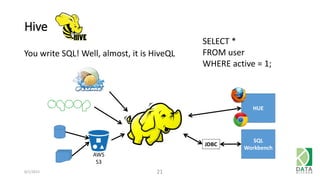
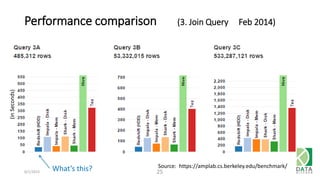
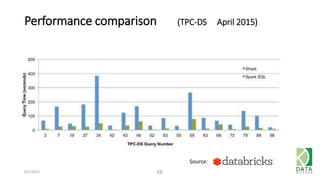
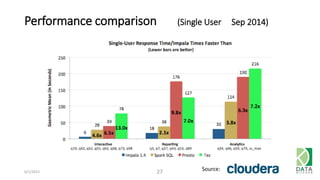
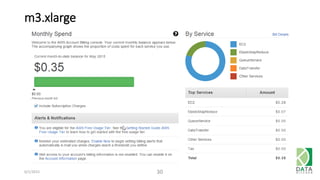
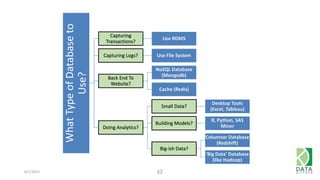
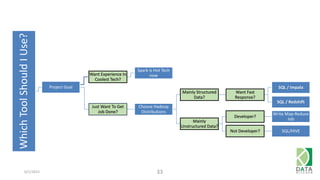
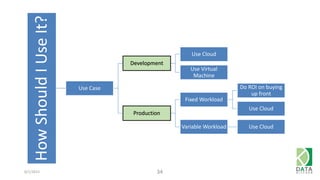
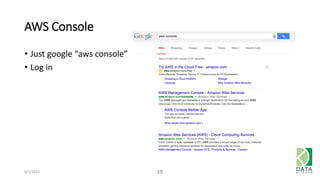
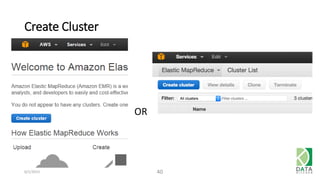
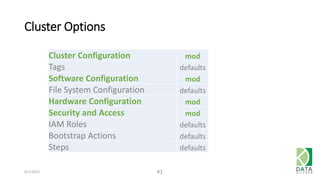
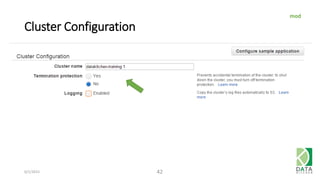
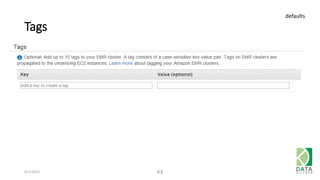
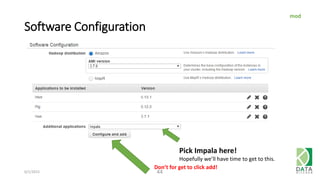
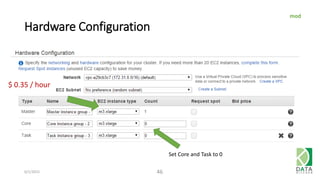
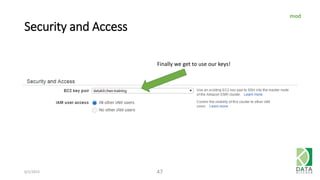
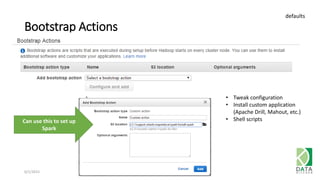
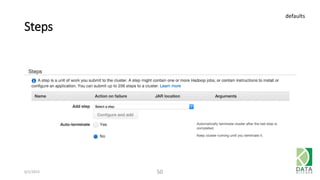
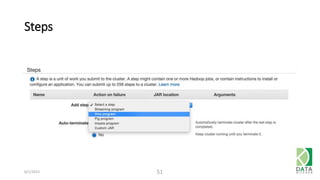
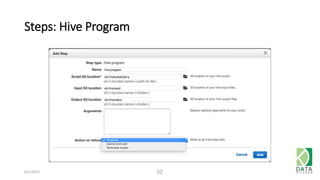
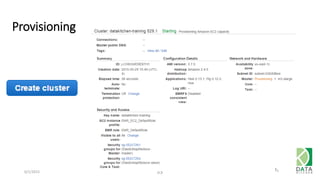
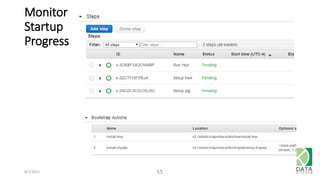
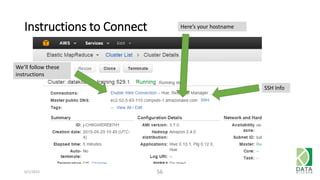
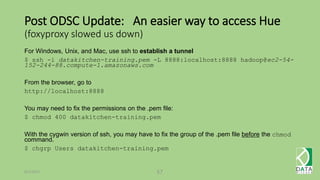
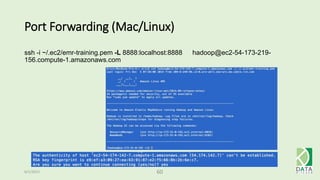
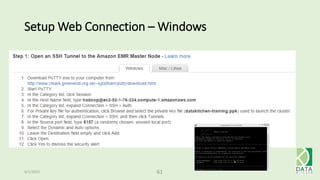
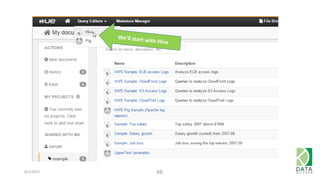
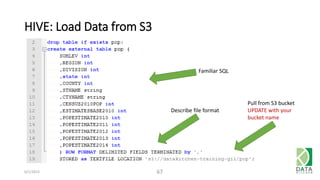
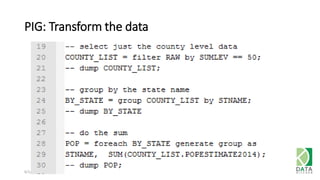
The document provides an overview of Hadoop and its associated frameworks for processing large-scale data. It discusses the roles of various tools like MapReduce, Pig, and Hive, as well as how to leverage AWS EMR for big data applications. The presentation emphasizes the evolution of the Hadoop ecosystem and its suitability for big data tasks, alongside practical use cases and setup instructions.