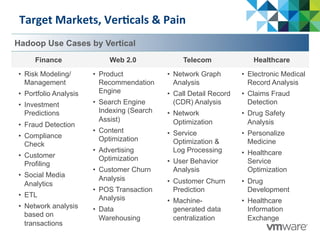
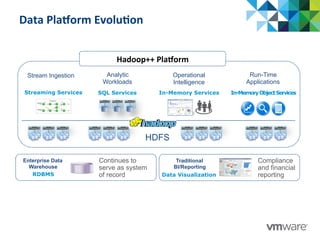
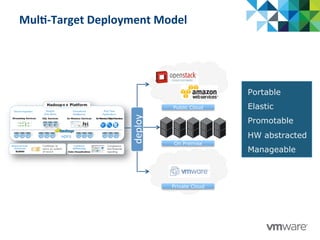
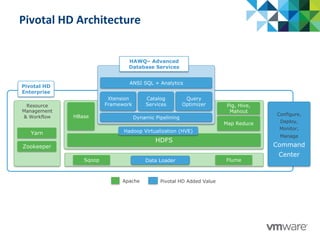
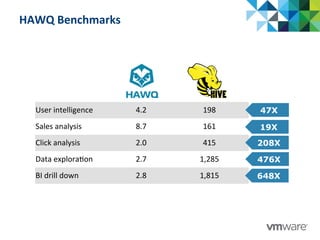
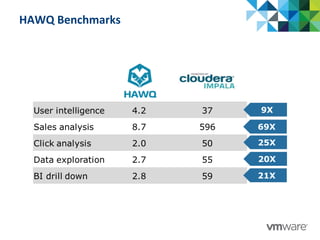
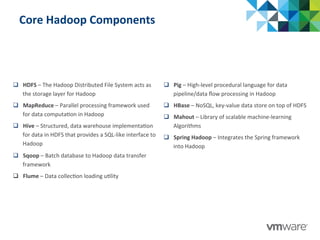
This document discusses Pivotal's vision and products for big data and Hadoop. It introduces Hadoop as an open source framework for distributed storage and processing of large datasets. Pivotal Hadoop is presented as providing an enterprise-grade Hadoop distribution with additional capabilities like SQL query processing, data management tools, and stream processing. Key components of Pivotal Hadoop include the HAWQ database for interactive SQL queries on Hadoop data and tools for data loading, analytics, and administration. Real-world use cases and benchmarks are shown to demonstrate how Pivotal Hadoop can enable both interactive analysis and massive-scale data processing.


















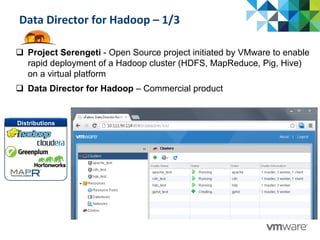
![Data
Director
for
Hadoop
–
2/3
More comprehensive feature-set than the Web
console, and provides a greater degree of control of
the system
CLI console
serengeti> cluster create --name dcsep
serengeti> cluster list
name: dcsep, distro: apache, status: RUNNING
NAME ROLES INSTANCE CPU MEM(MB) TYPE
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
master [hadoop_namenode, hadoop_jobtracker] 1 6 2048 LOCAL 10
data [hadoop_datanode] 1 2 1024 LOCAL 10
compute [hadoop_tasktracker] 8 2 1024 LOCAL 10
client [hadoop_client, pig, hive] 1 1 3748 LOCAL 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08a-vmware-hadoop-150124114220-conversion-gate02/85/VMUGIT-UC-2013-08a-VMware-Hadoop-30-320.jpg)