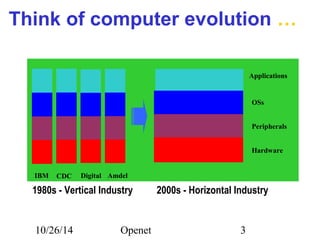
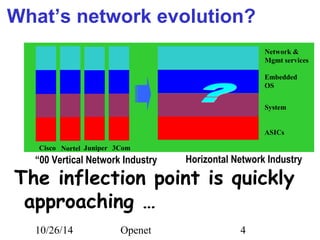
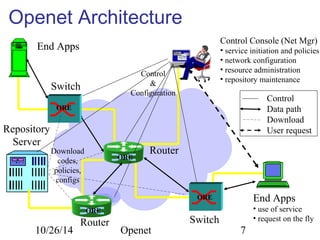
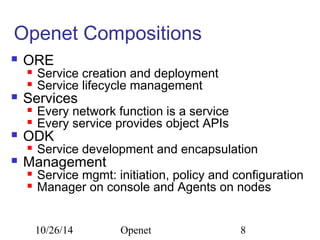
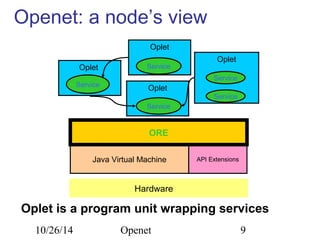
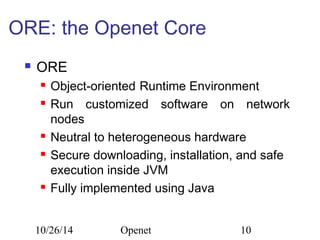
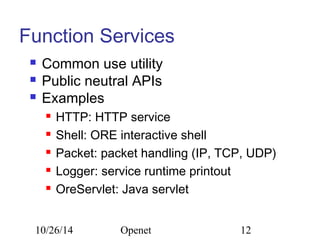
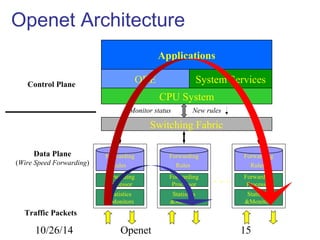
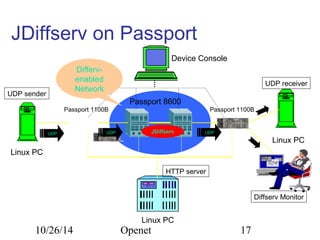
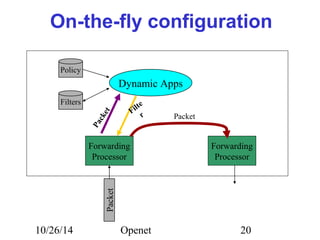
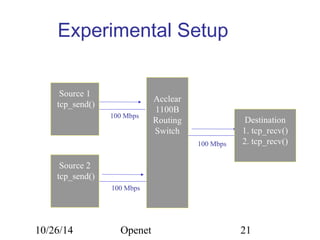
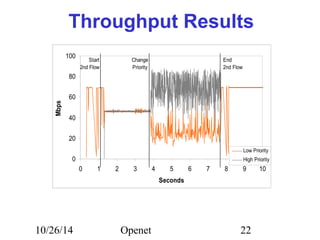
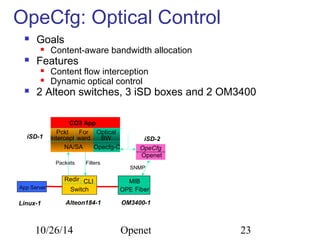
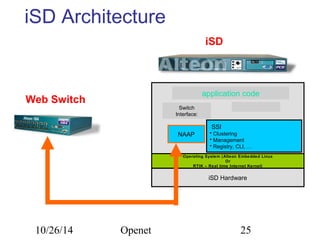
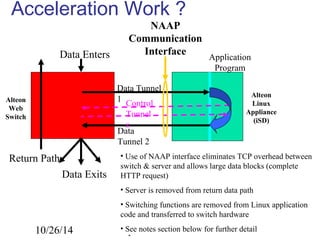
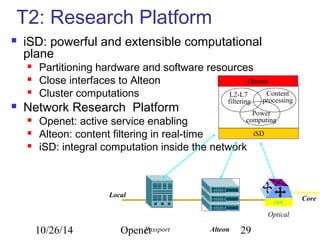
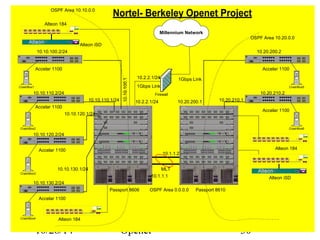
The document discusses Openet, a programmable networking platform that aims to enable open networking and enhance network management and performance through programmability. It outlines the evolution of network technologies, challenges in current systems, and the architecture of Openet, including its applications and features. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of flexibility and accessibility in network devices to better meet diverse client needs.