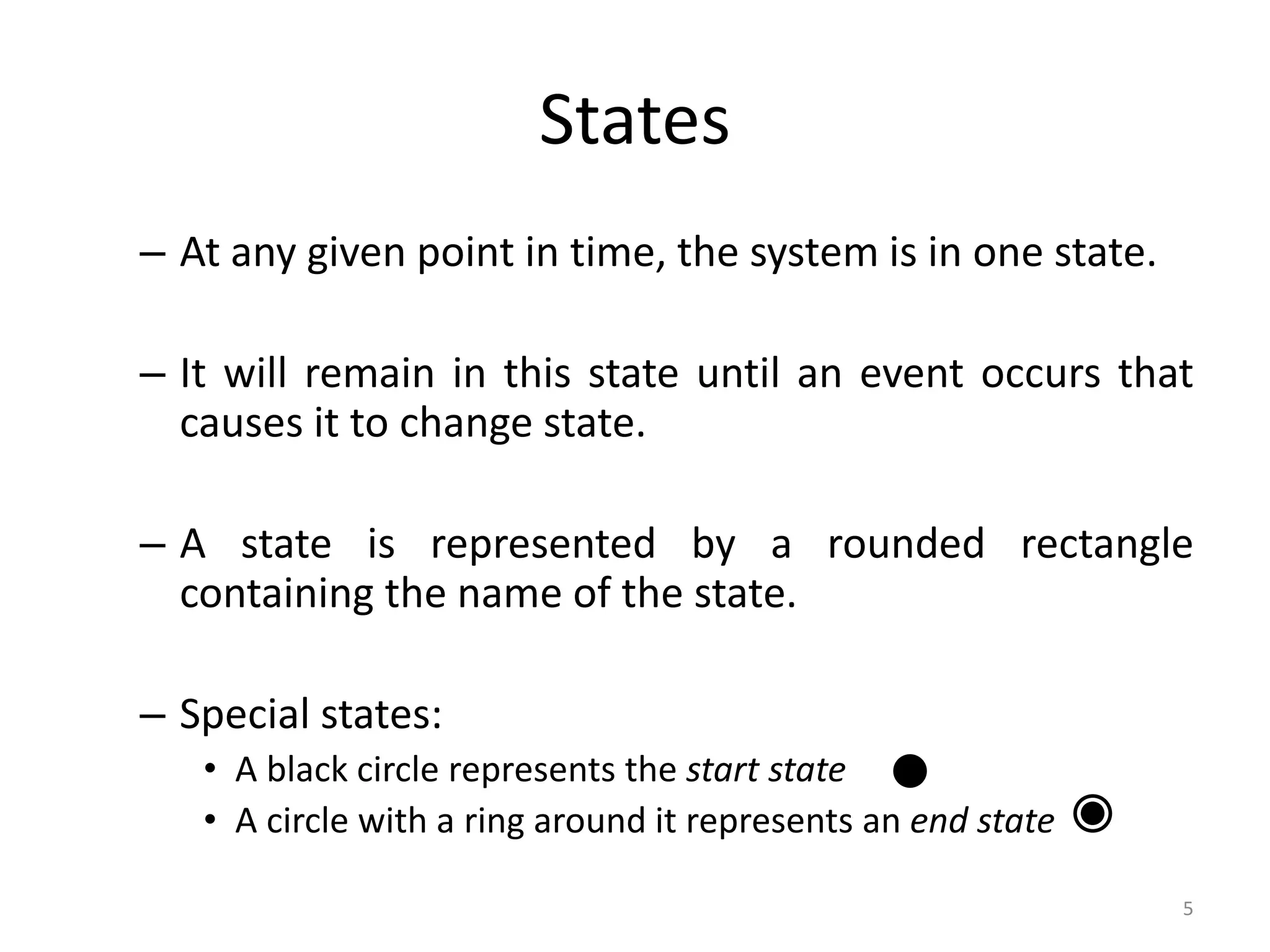
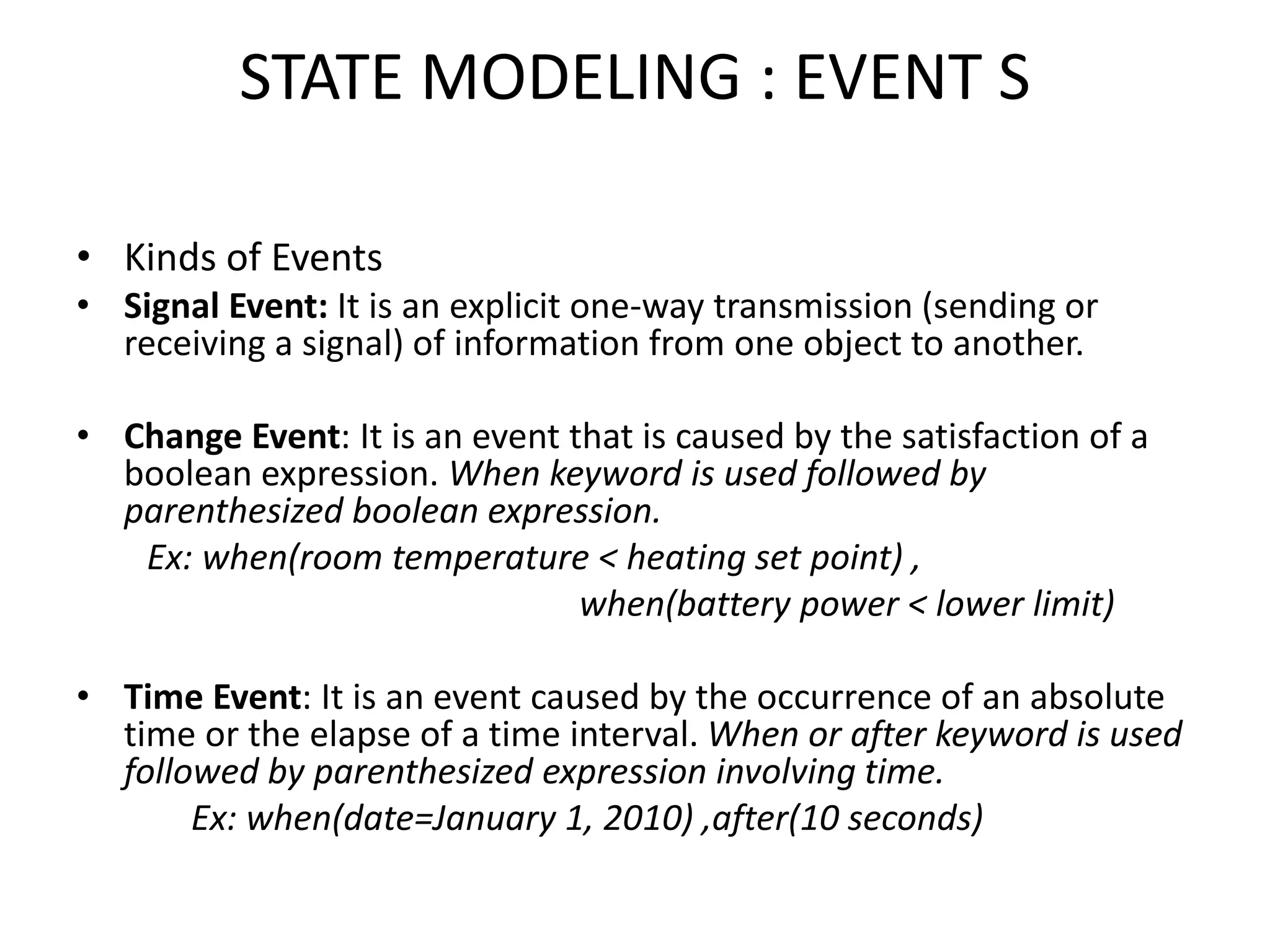
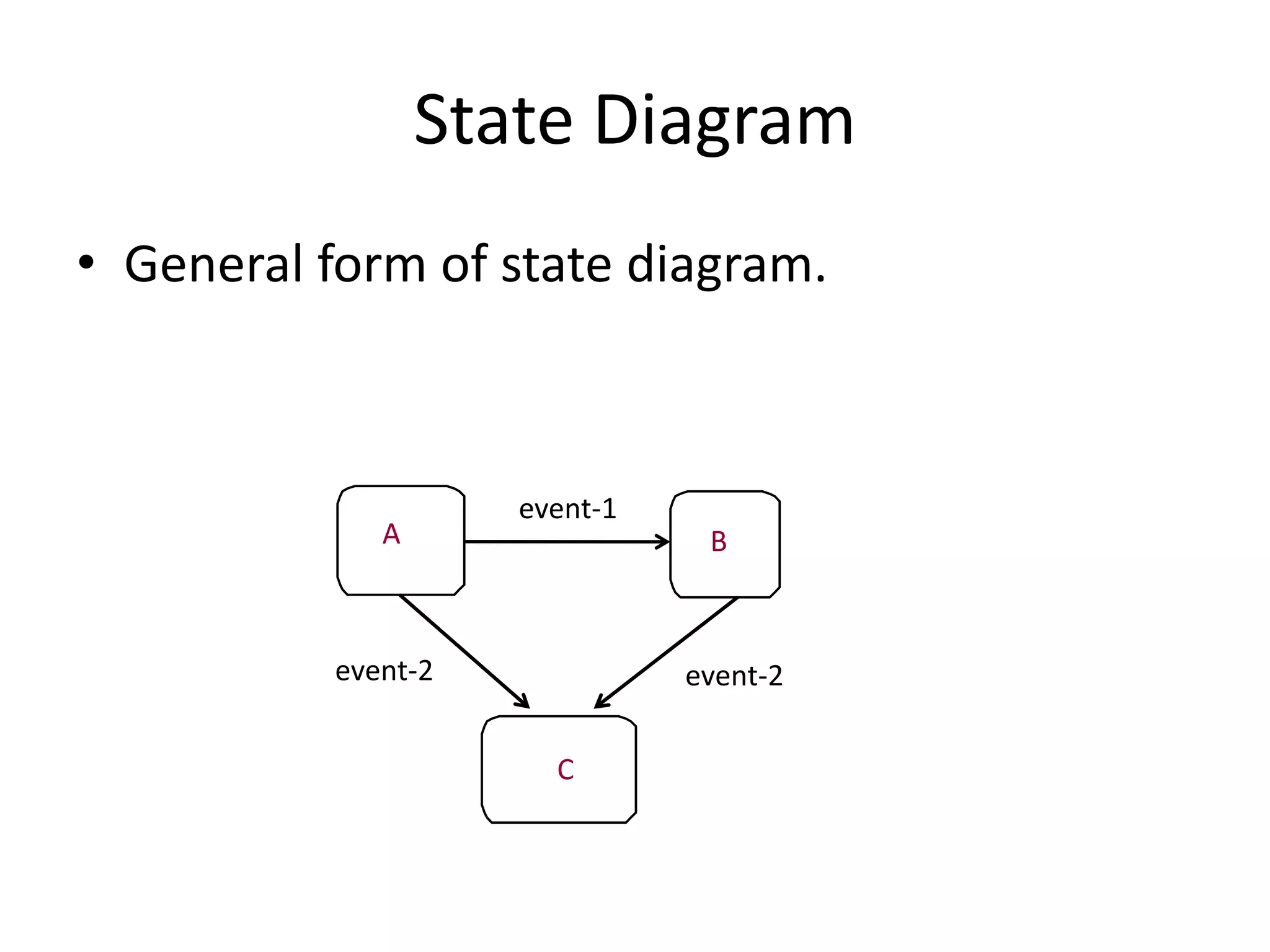
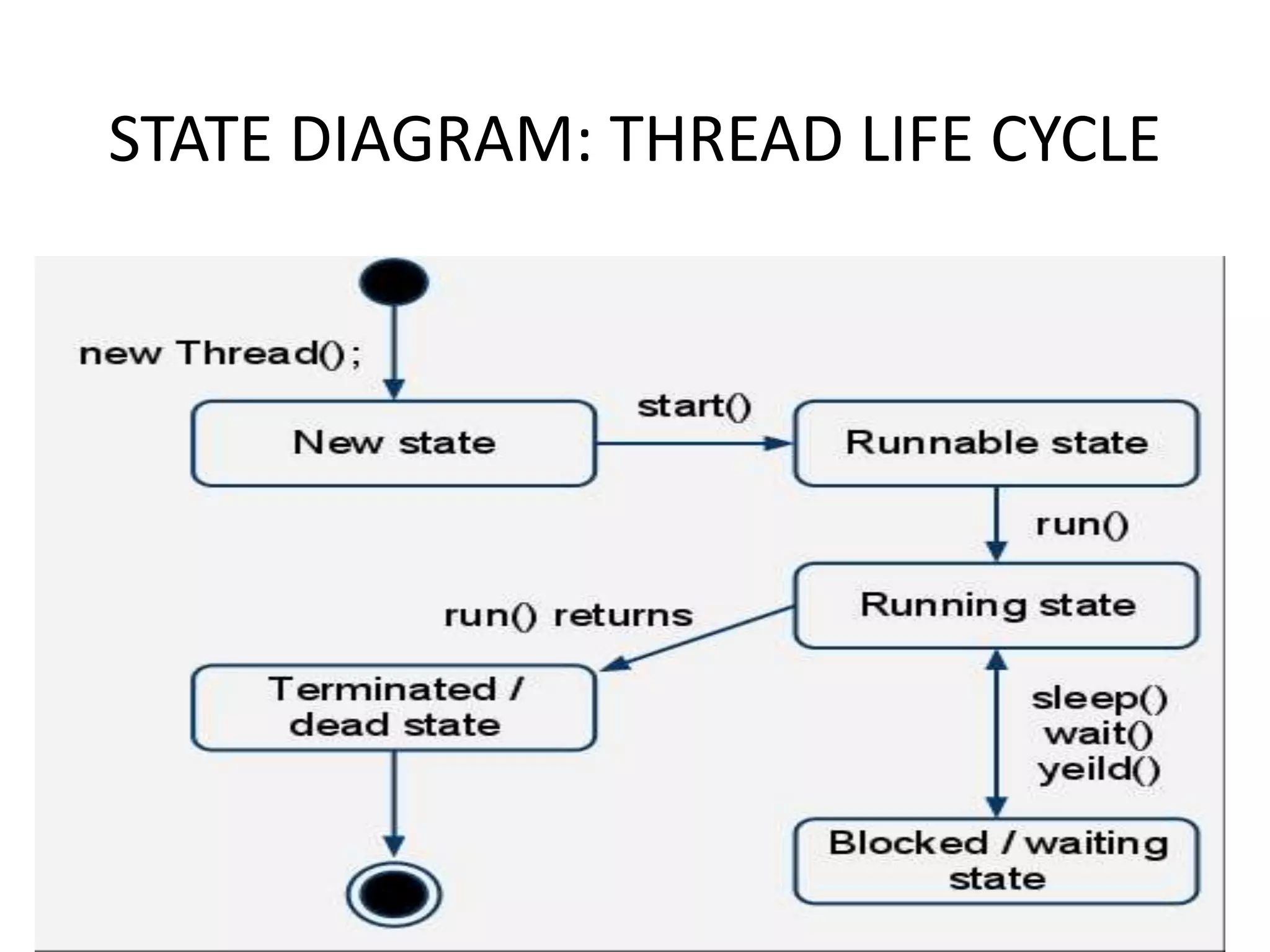
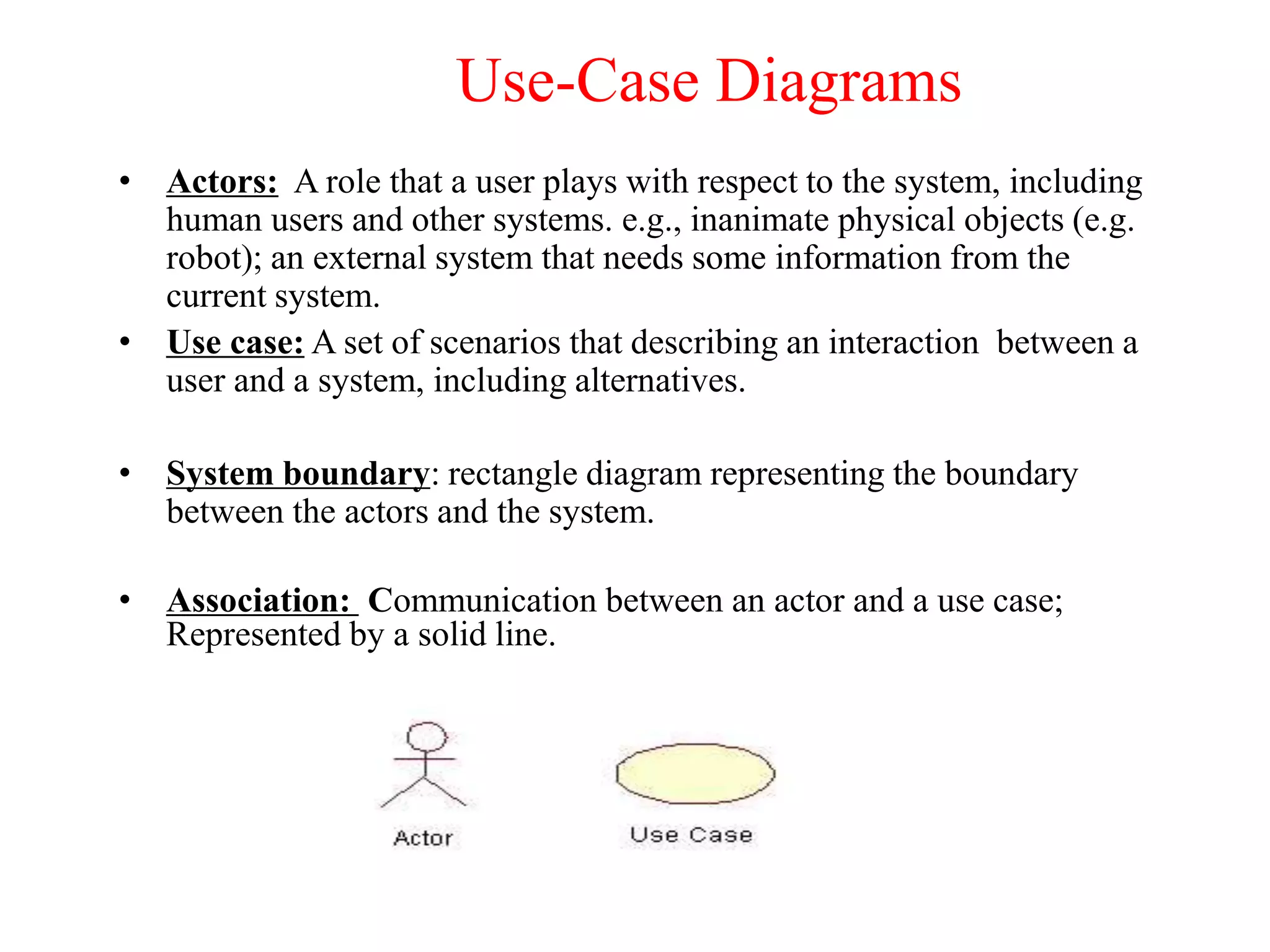
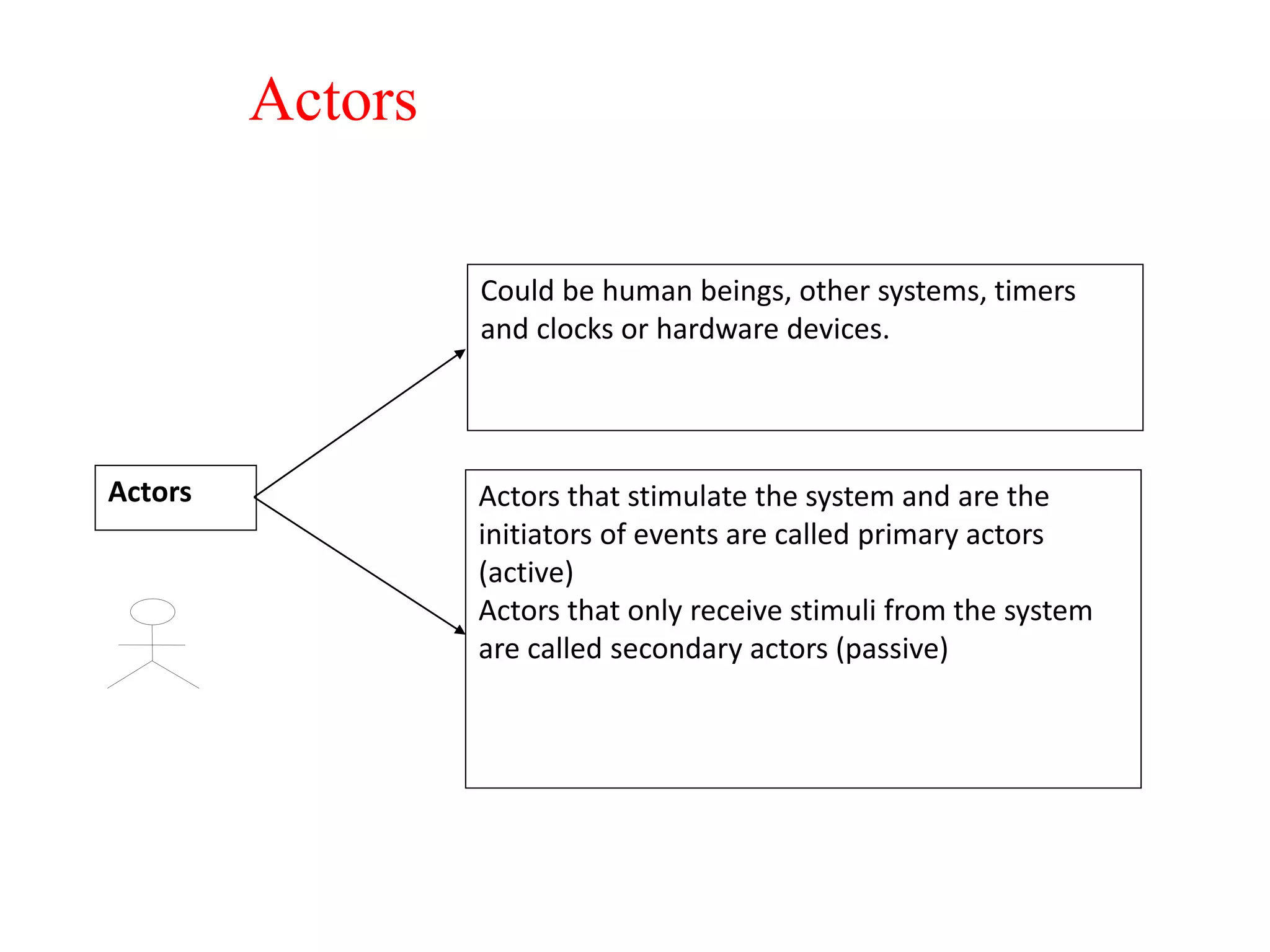
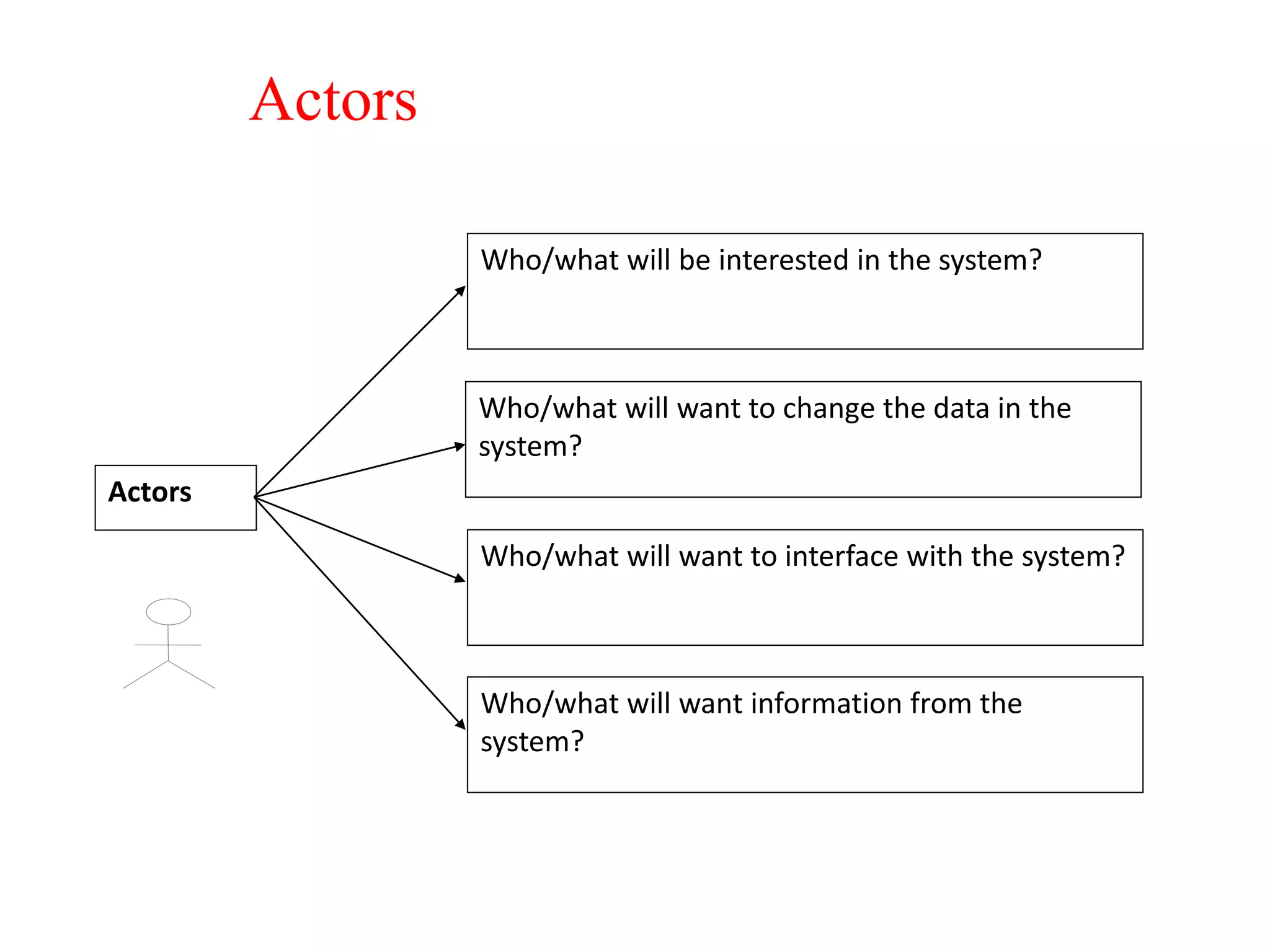
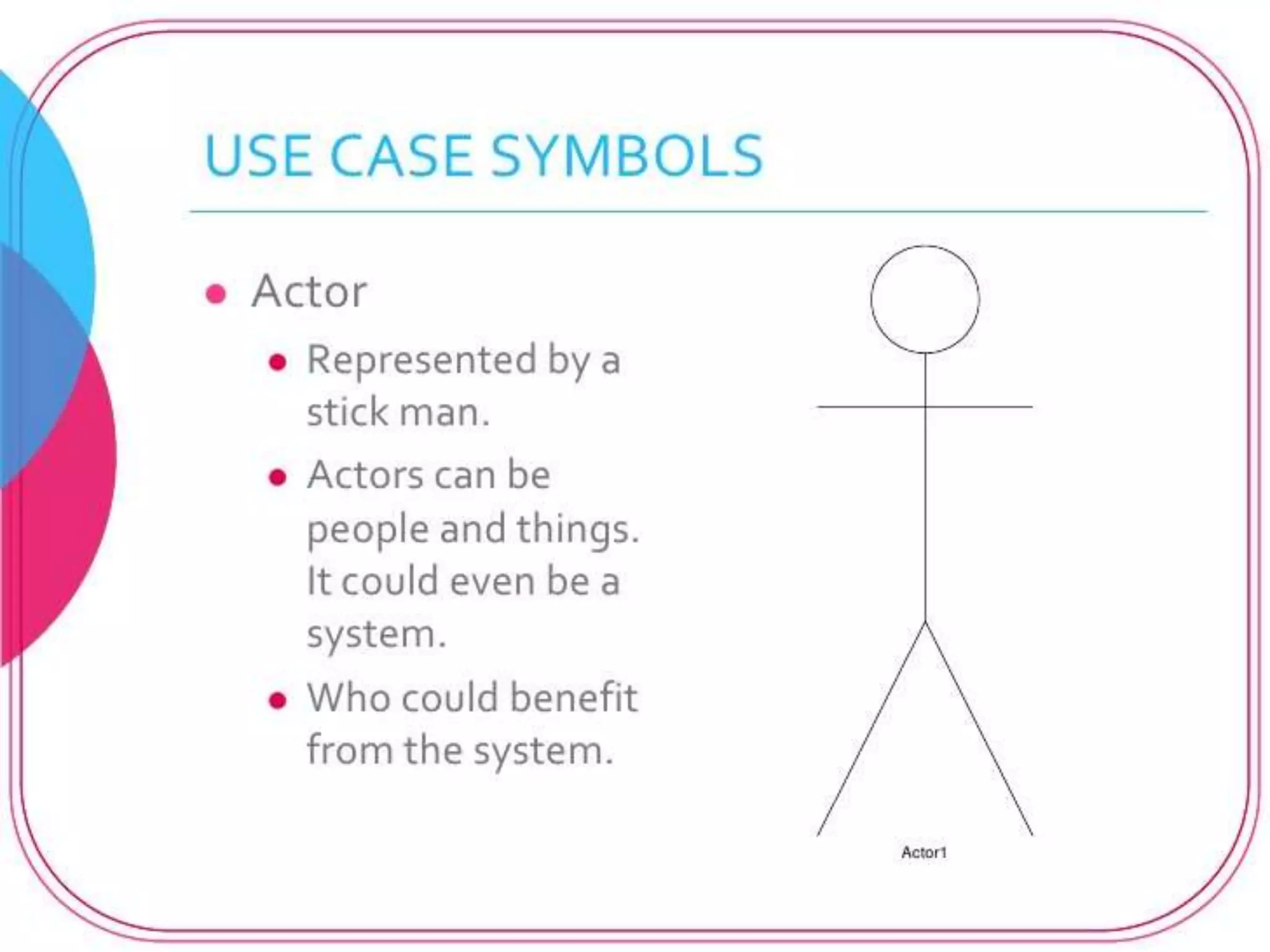
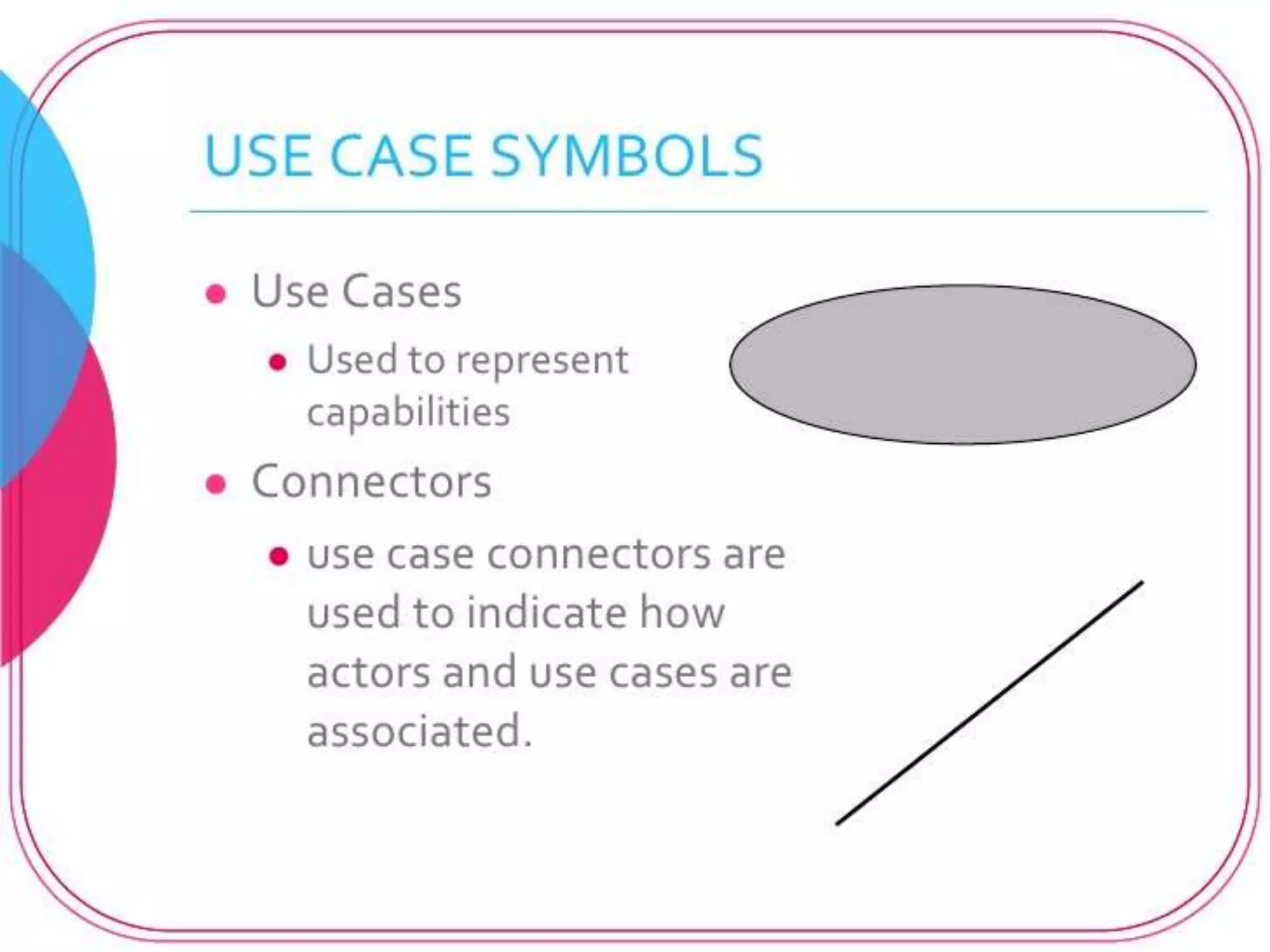
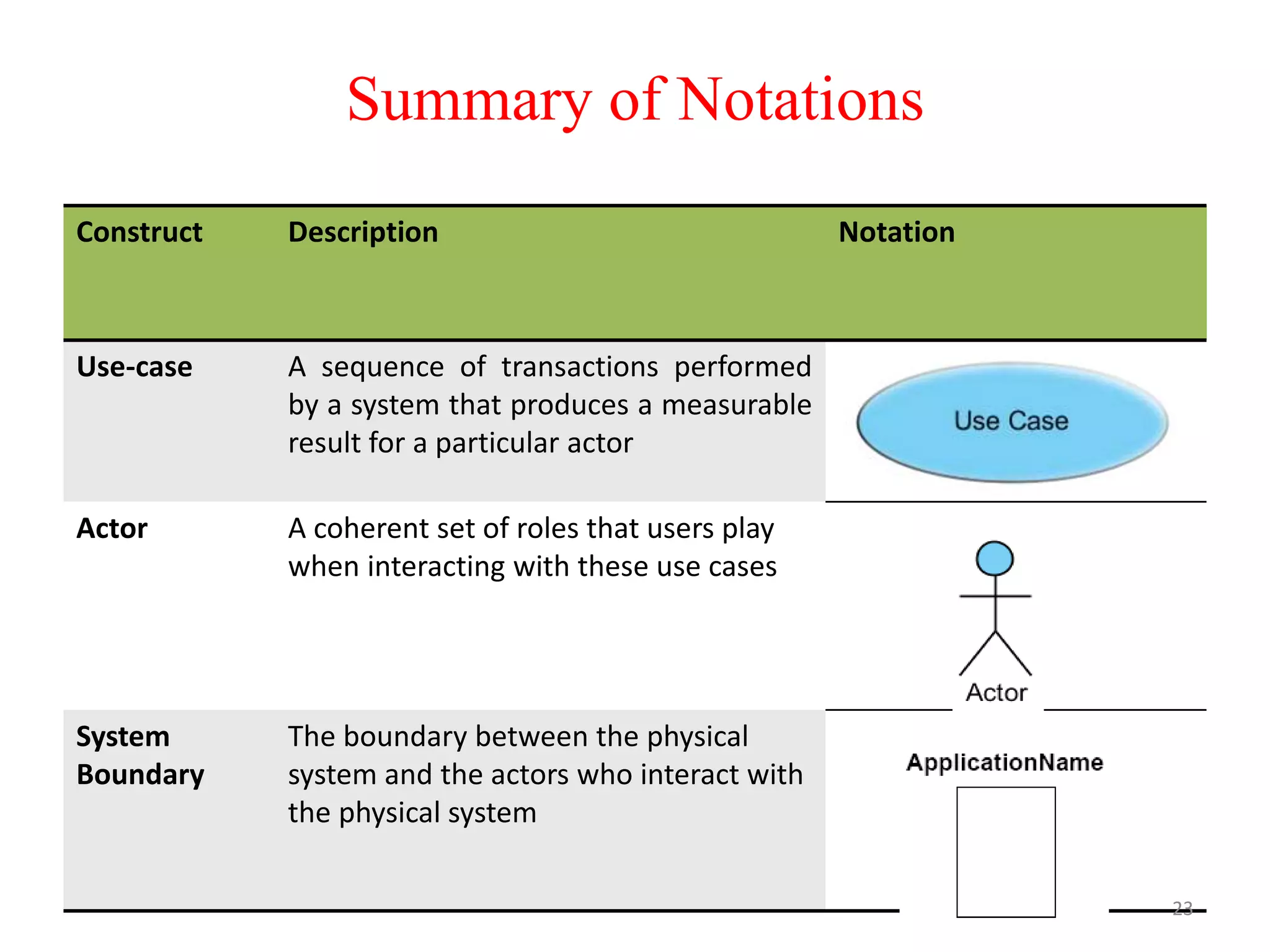
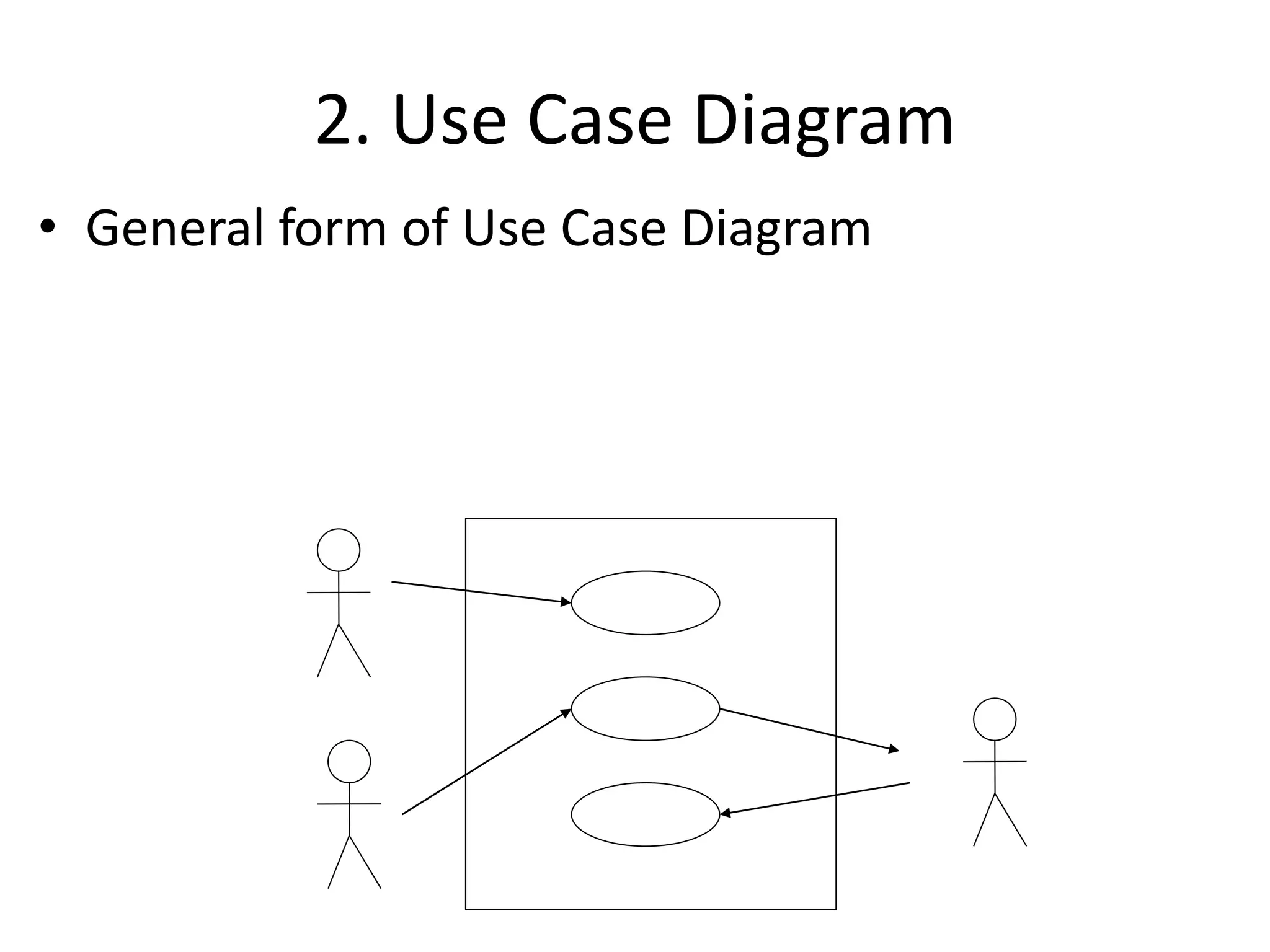
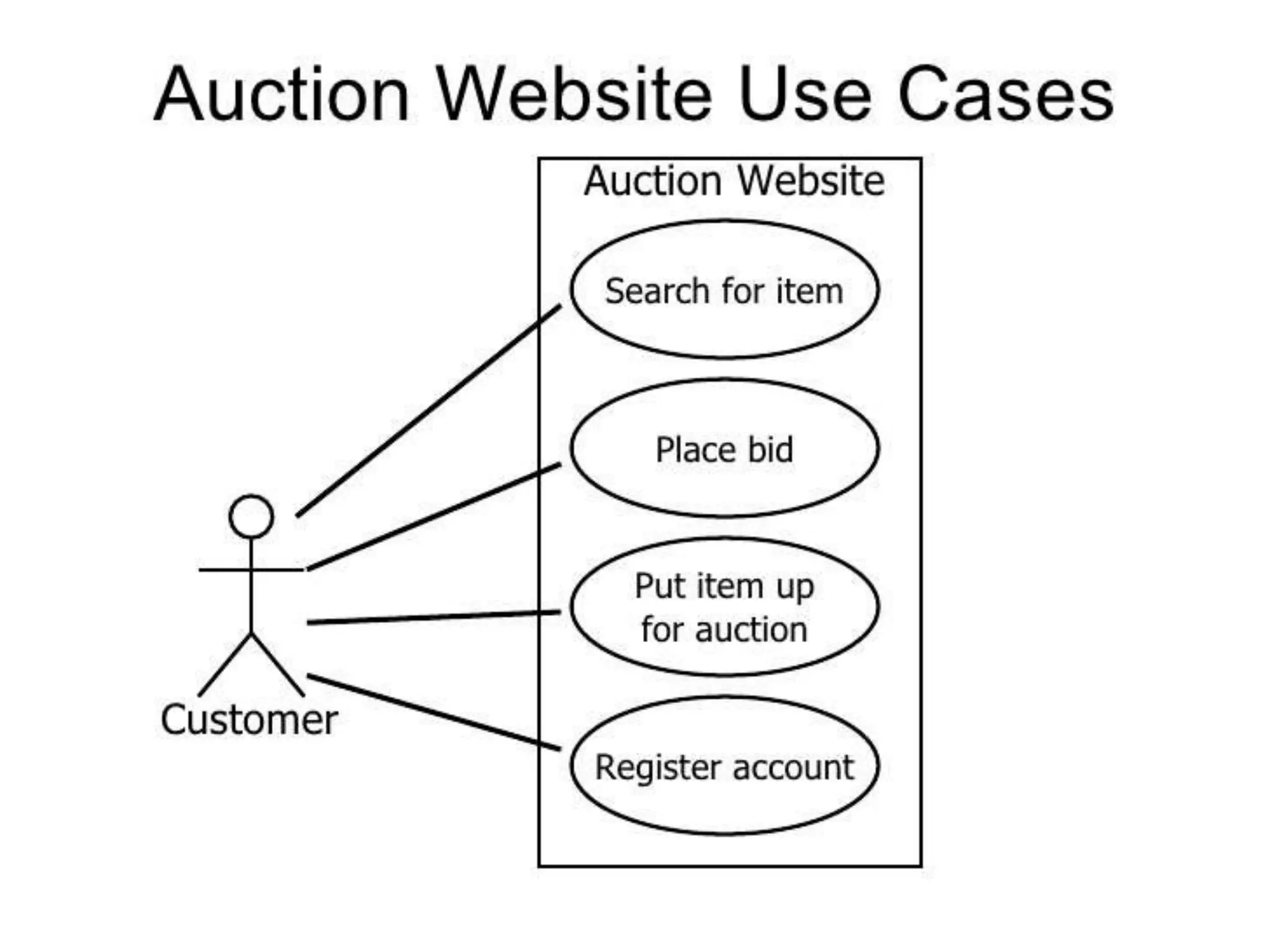
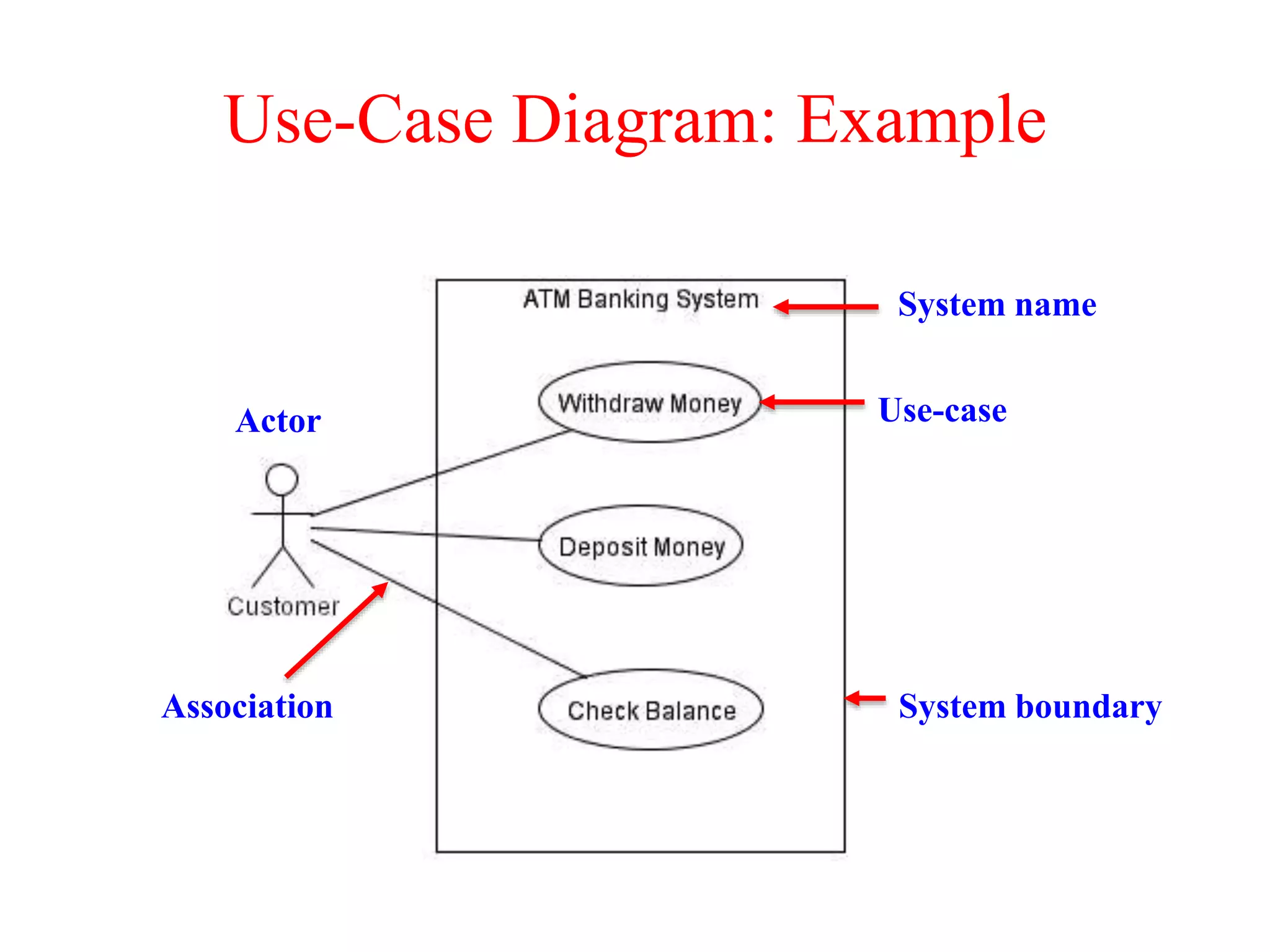
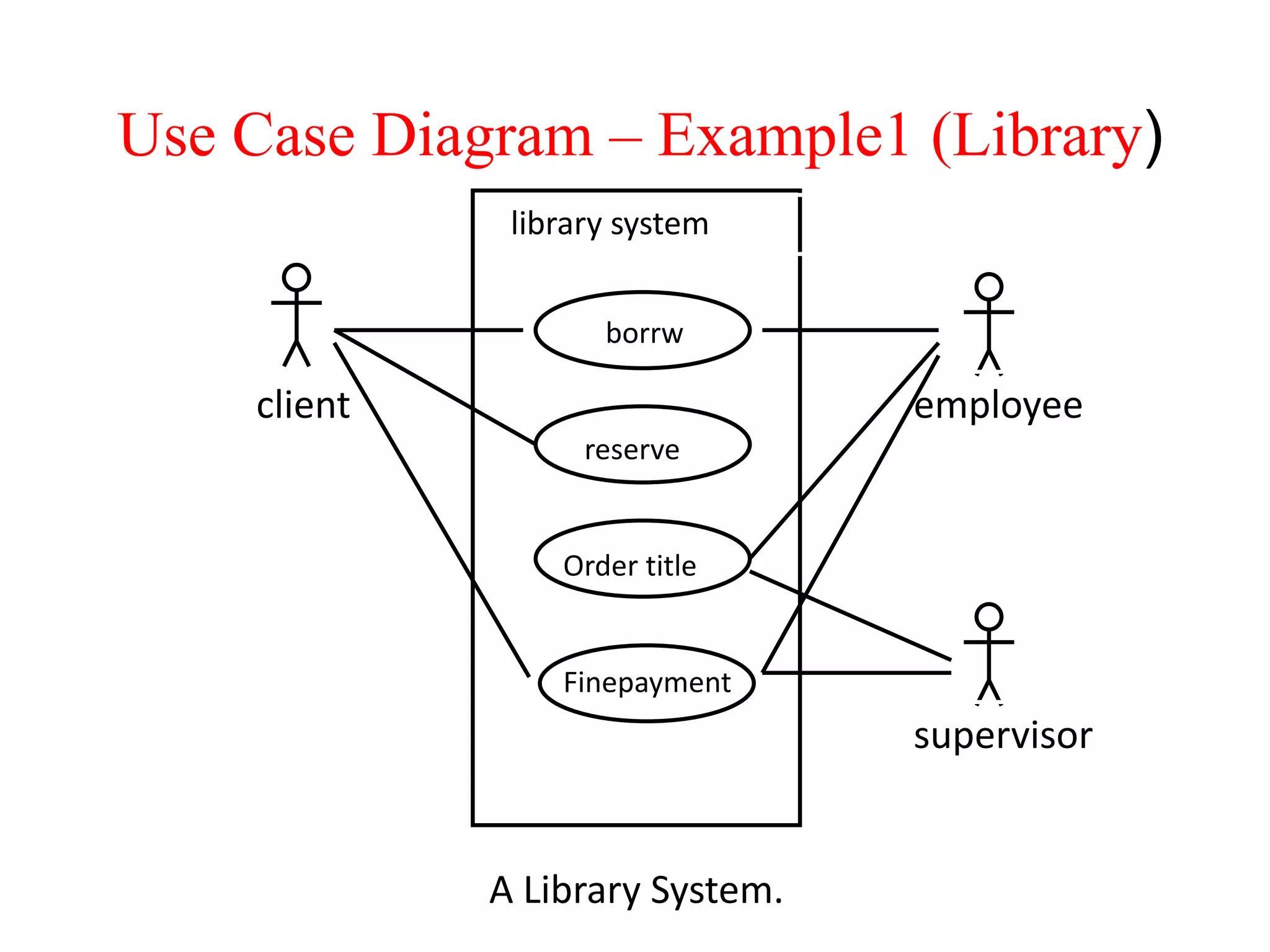
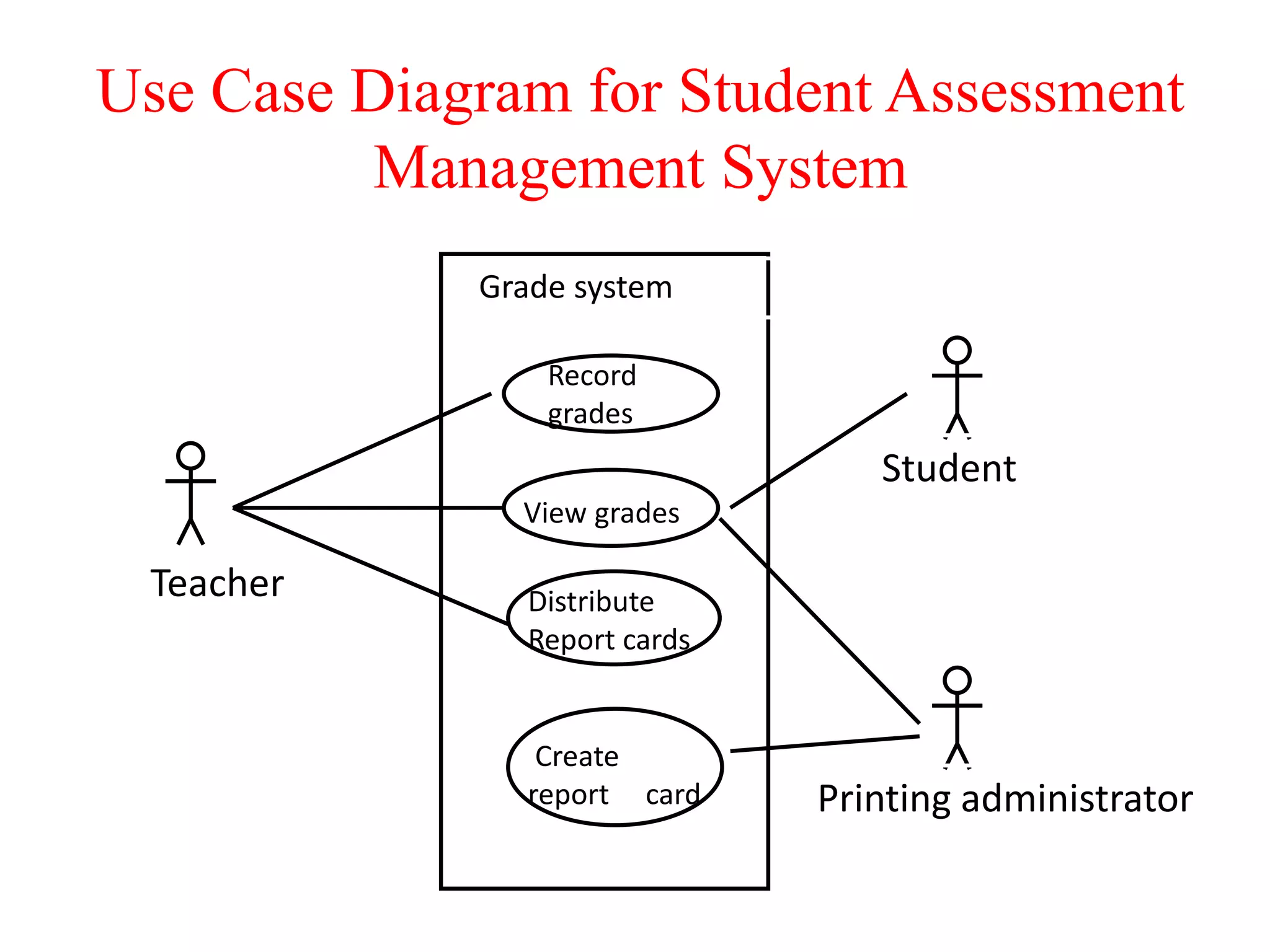
The document provides an overview of state modeling and interaction modeling techniques. It defines key concepts like events, conditions, states, and transitions that are used in state diagrams. It also discusses use case diagrams, which model user interactions with a system through actors and use cases. The document explains that state diagrams describe the behavior and life cycles of objects in response to events, while use case and interaction diagrams elaborate the functional requirements and interactions between users and a system.