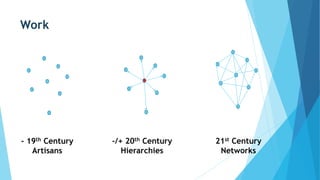
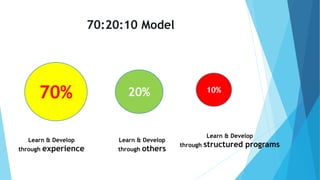
This document summarizes a seminar on social learning. The seminar discussed how work and learning have changed from individual and hierarchical models to collaborative networks. Social learning through knowledge sharing, teamwork, and informal learning was said to be valuable. The importance of social learning for connecting with others, asking questions, and gaining adaptive skills was also discussed. Different types of organizational learning were presented, including learning from experience, groups, individuals, accidents, and formal training. Implementing social learning requires focused conversations and sharing knowledge through collaboration. The 70:20:10 model for learning through experience, others, and structured programs was presented as a framework for development.