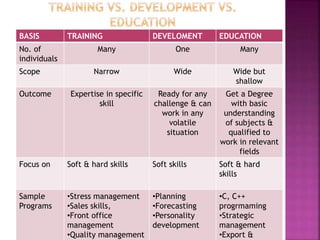
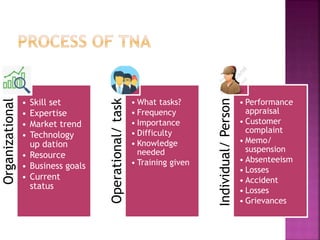
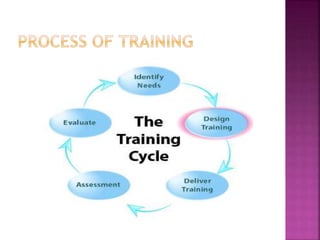
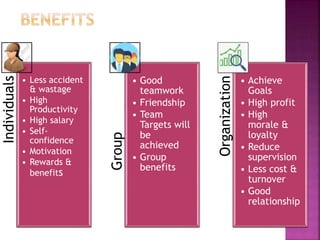
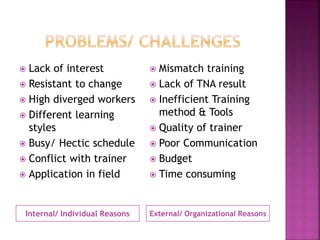
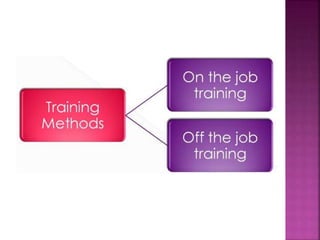
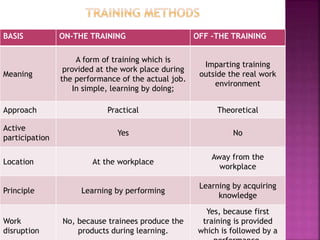
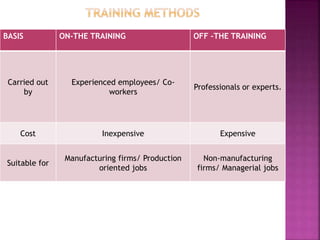
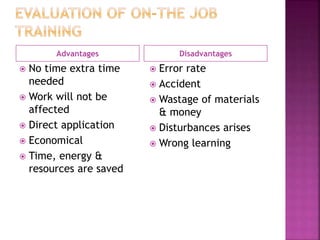
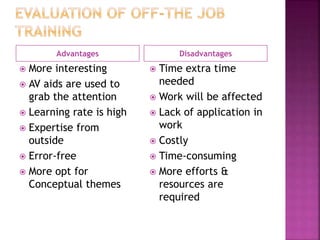
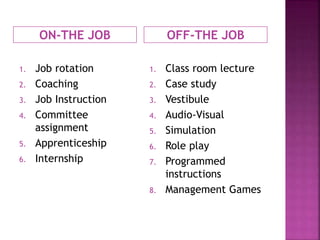
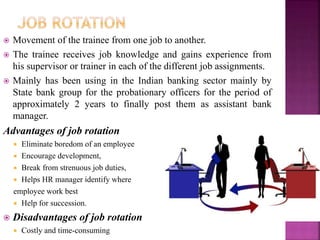
The document discusses various training methods used to enhance employee skills. It compares on-the-job training, which occurs at the workplace, to off-the-job training conducted outside of work. Some common on-the-job methods include job rotation, coaching, and apprenticeships, while classroom lectures, simulations, and role plays are examples of off-the-job training. Both approaches have advantages and disadvantages depending on the type of skills and industry.