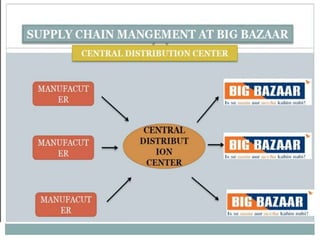
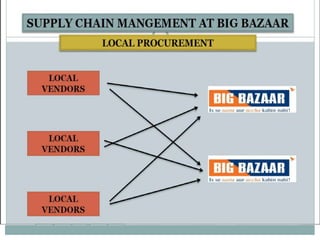
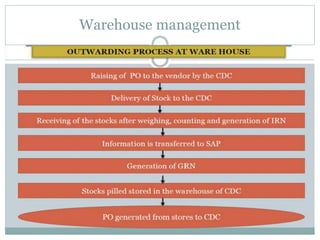
This document summarizes a presentation by a group on operations at Big Bazaar, an Indian retail chain. It outlines the objectives of studying Big Bazaar's supply chain management and warehouse operations. It then describes how procurement occurs from centralized distribution centers and local vendors. Inventory is managed through an automated replenishment system. The document also details warehouse inbound processing, damage/defective stock management, inventory management practices, stock management on the store floor, and advantages and disadvantages of inventory management. Key findings emphasize the importance of visual merchandising, product promotions, staff training, and using IT systems.