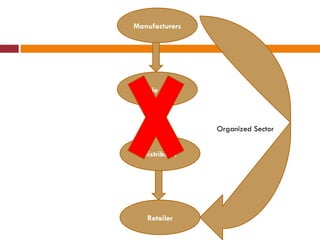
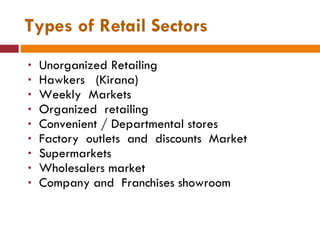
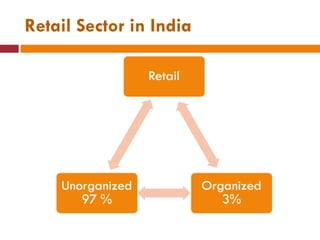
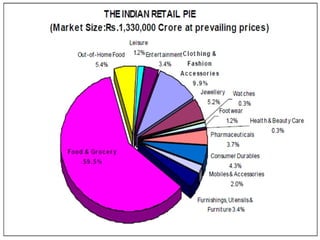
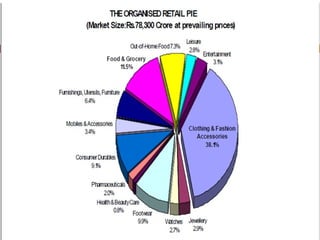
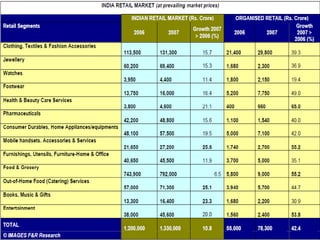
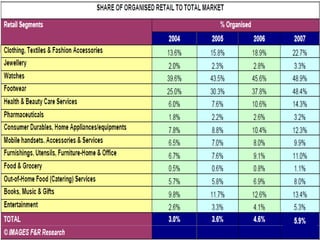
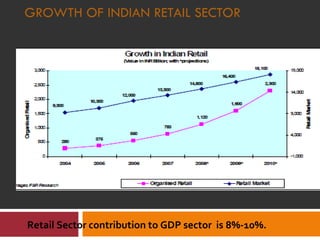
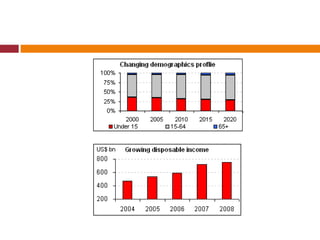
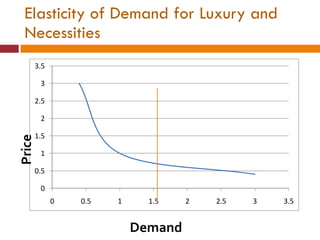
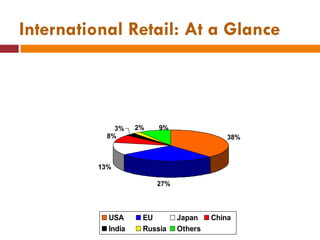
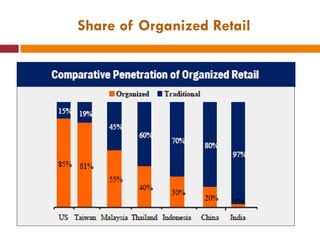
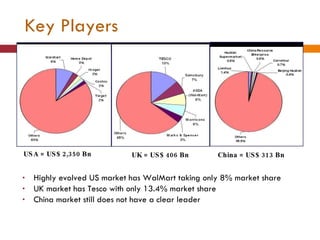
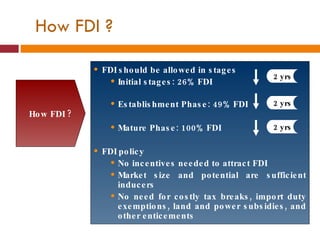
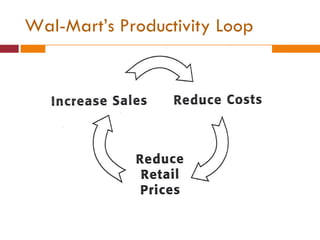
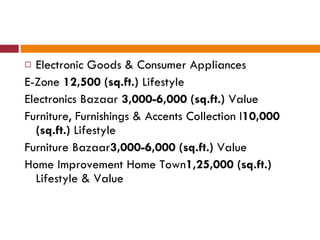
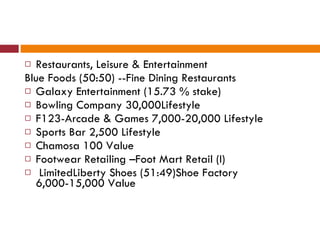
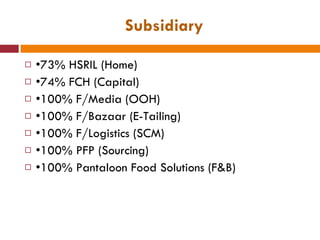
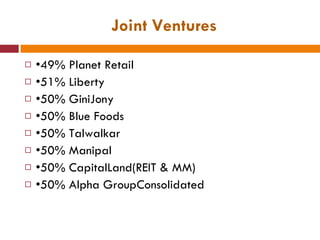
The document discusses the Indian retail sector. It outlines the evolution of retail in India from barter systems to modern organized retail chains and malls. It also discusses key players in the Indian retail space, factors driving growth in the sector, challenges faced, and strategies adopted by major retailers like Kishore Biyani to succeed in India.