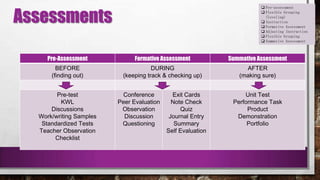
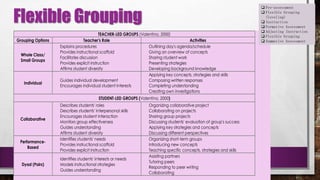
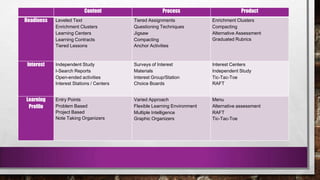
This document provides information about differentiated instruction. It begins by asking a series of multiple choice and short answer questions to assess knowledge of differentiation basics. These questions cover the three areas teachers can differentiate (content, process, product), how differentiation is developed according to students' readiness, interests, and learning profiles, and key terms like formative assessment and flexible grouping. The document then defines differentiation basics like pre-assessment, instruction, and summative assessment. It also explains flexible grouping strategies and how teachers can differentiate content, process, and product. Key terms explained include learning contracts, tiered activities, and tic-tac-toe boards.