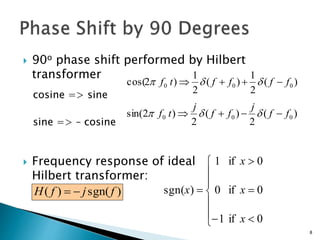
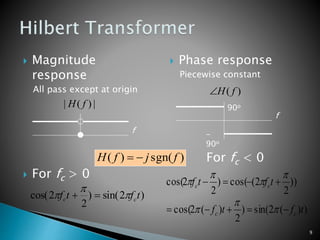
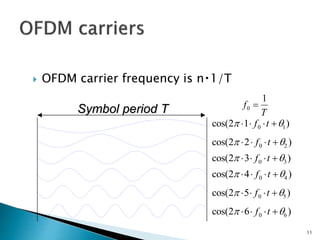
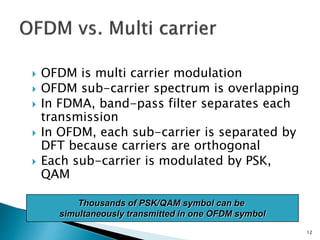
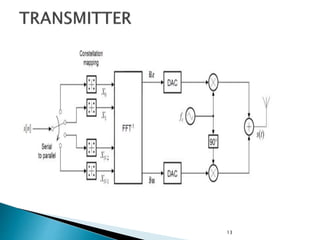
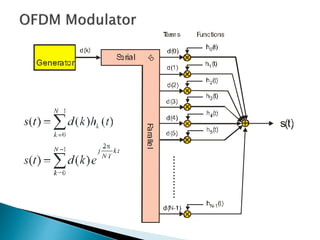
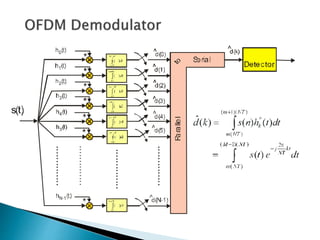
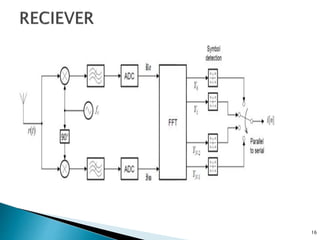
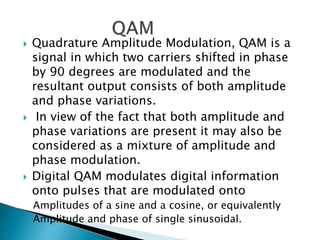
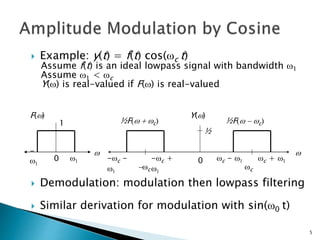
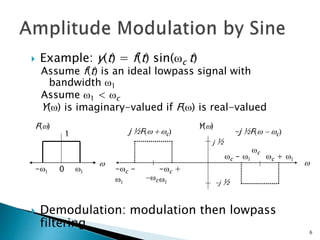
This document discusses quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) and orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM). It provides background on digital modulation techniques before explaining the theories and mechanisms of QAM and OFDM. QAM uses two carriers shifted by 90 degrees that are modulated based on both amplitude and phase. OFDM is a multi-carrier modulation scheme where each carrier's amplitude is modulated and the subcarriers are separated by their orthogonal frequencies. The document outlines advantages such as high data rates and robustness to multipath fading, as well as disadvantages like sensitivity to frequency offsets. It concludes that OFDM performs better than single carriers for multipath channels when guard intervals are implemented properly.



![7
Serial/Parallel
Map to 2-D
constellation
Impulse modulator
Impulse modulator
Pulse shaping gT(t)
Local
Oscillator
+
90o
Pulse shaping gT(t)
d[n]
an
bn
a*(t)
b*(t)
s(t)
1 J
Matched
Delay
Matched delay matches delay through 90o phase shifter
bit
stream](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ofdmqam-160122105201/85/Ofdm-amp-qam-7-320.jpg)