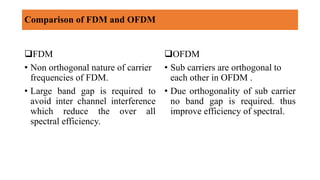
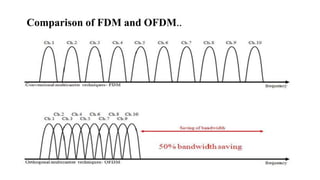
This document provides an introduction to orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) modulation technology. It discusses how OFDM works by splitting a high-rate data stream into several lower data streams that are transmitted in parallel using orthogonal subcarriers. This allows for high spectral efficiency and better bandwidth utilization compared to traditional frequency division multiplexing. The document also outlines some key advantages of OFDM like high data rates and its use in various wireless technologies. It provides mathematical expressions to describe the orthogonality principle and modulation/demodulation processes. Challenges related to high peak-to-average power ratio and synchronization are also summarized.
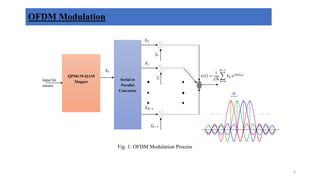

![Fig. 2: Block diagram Conventional OFDM System
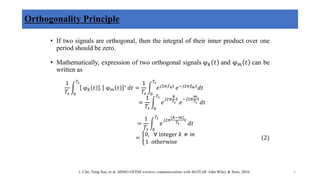
𝑌𝑘[𝑁 − 1]
𝑌𝑘[0]
𝑥 𝑛 =
1
𝑁 𝑘=0
𝑁−1
𝑋𝑘 . 𝑒𝑗
2𝜋𝑘𝑛
𝑁 , 0 ≤ 𝑛 ≤ 𝑁 − 1
QPSK/QAM
De-mapper
𝑋𝑘[0]
𝑋𝑘[𝑁 − 1]
𝑦𝑛[0]
𝑦𝑛[𝑁 − 1]
Transmitted
signal
Received
signal
S/P
S/P
FFT
P/S
Cyclic Prefix
Removal
Cyclic Prefix
Addition
P/S
IFFT
Channel
QPSK/QAM
Mapper
Input
Output
IFFT/FFT based Implementation
Frequency Domain Time Domain
𝑋𝑘
8
1. Cho, Yong Soo, et al. MIMO-OFDM wireless communications with MATLAB. John Wiley & Sons, 2010.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/u-4l-123ofdm-230405190540-04d372c4/85/U-4-L-1-2-3_OFDM-pptx-8-320.jpg)

![Challenges in OFDM System
• In spite of several advantageous features, the OFDM systems have two
major concerns i.e.
1. High PAPR of transmitted signal
2. Synchronization at the receiver.
• The effects of all these issues are appearing in the form of degradation of
BER performance and inter-symbol interference(ISI) [1].
1. Cho, Yong Soo, et al. MIMO-OFDM wireless communications with MATLAB. John Wiley & Sons, 2010.
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/u-4l-123ofdm-230405190540-04d372c4/85/U-4-L-1-2-3_OFDM-pptx-10-320.jpg)