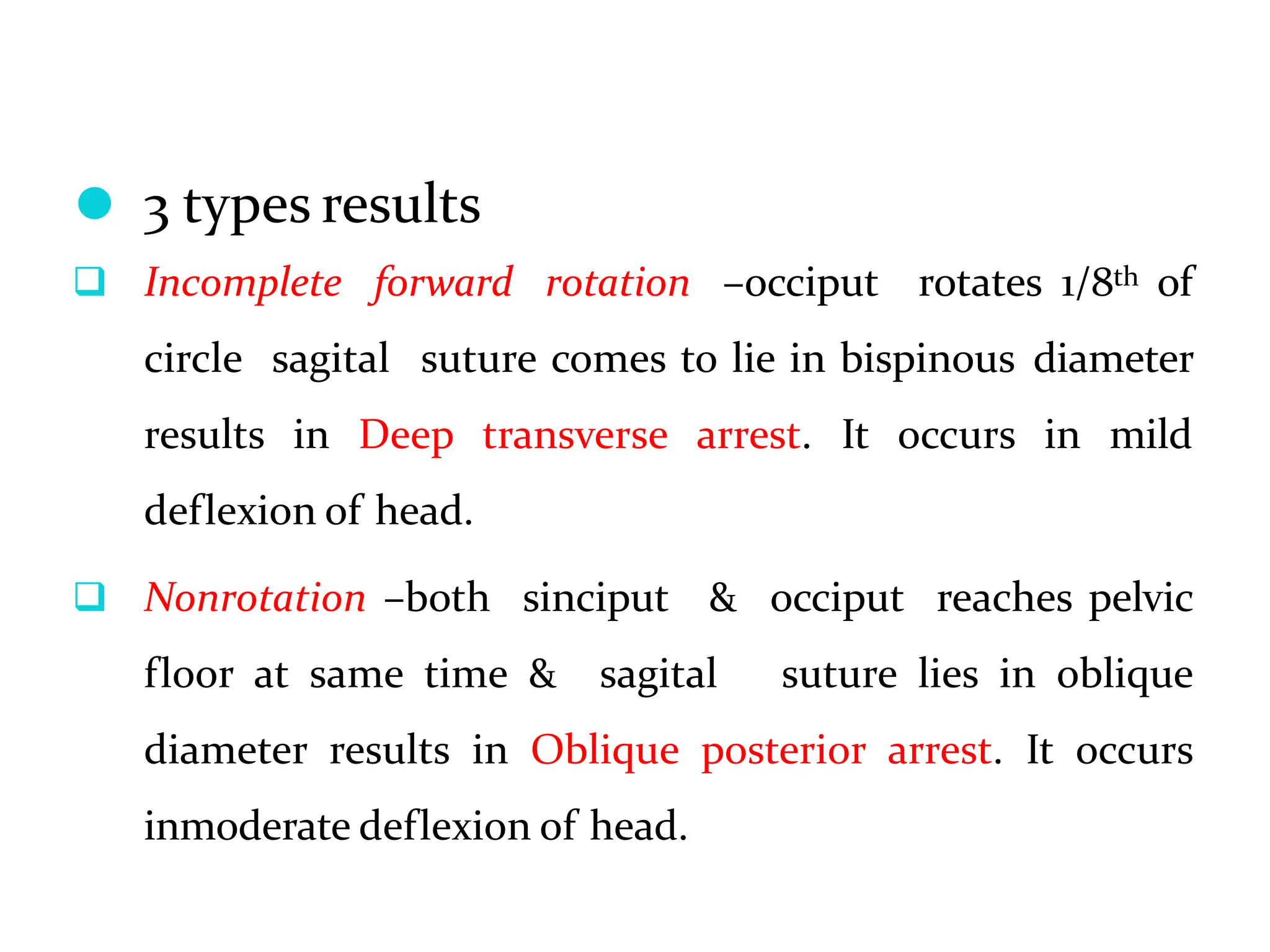
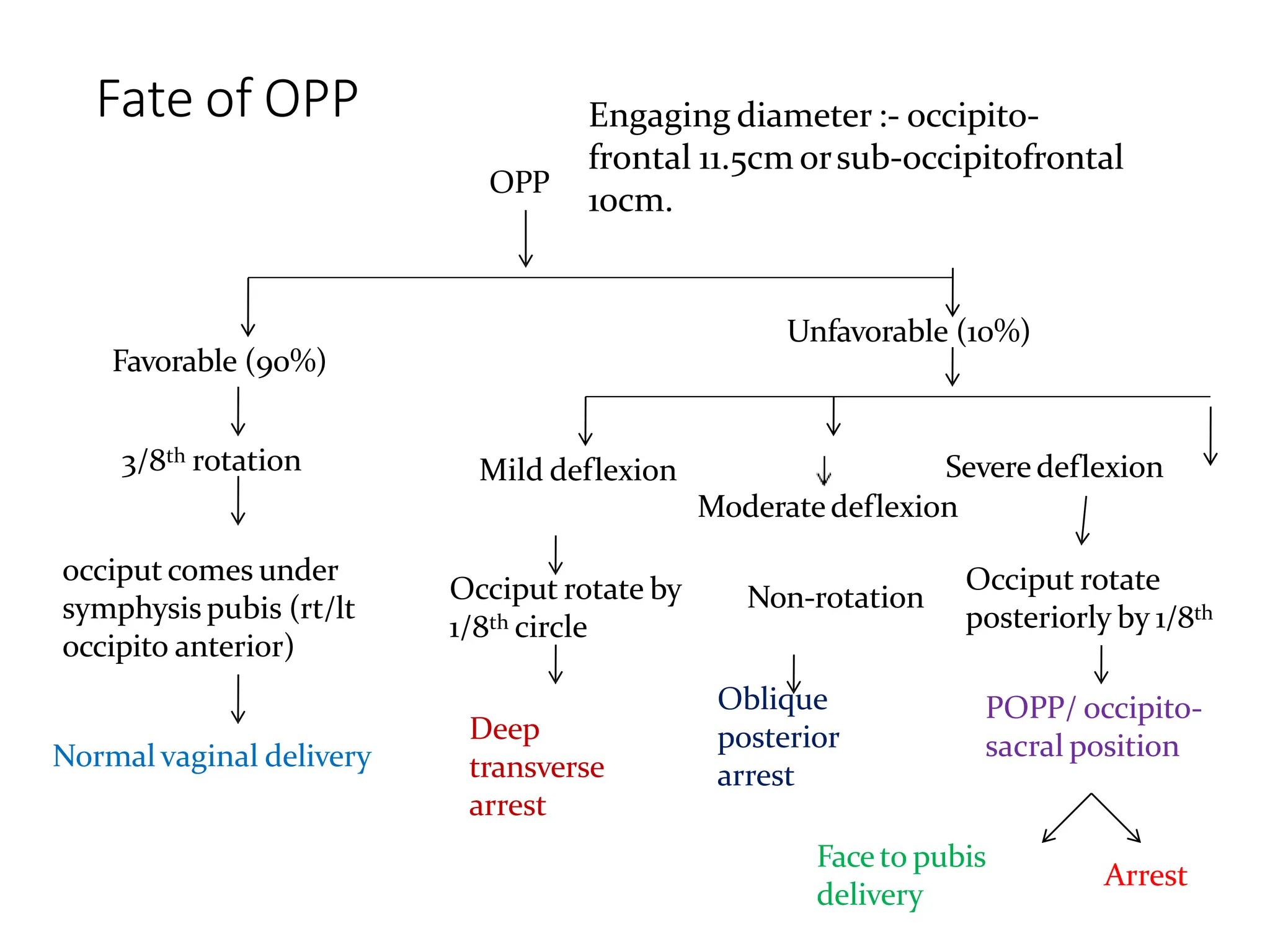
The document discusses the occipito-posterior position of the fetus, characterized by the occiput being positioned posteriorly over the sacrum, and outlines the incidence and causes of this position, as well as its impacts on labor. It describes the mechanism of labor, including how the head engages and potentially rotates during delivery, and outlines management strategies for both stages of labor, emphasizing the need for early diagnosis and potential interventions like cesarean sections if necessary. Additionally, it addresses complications and alternative methods of delivery in cases of labor obstruction.