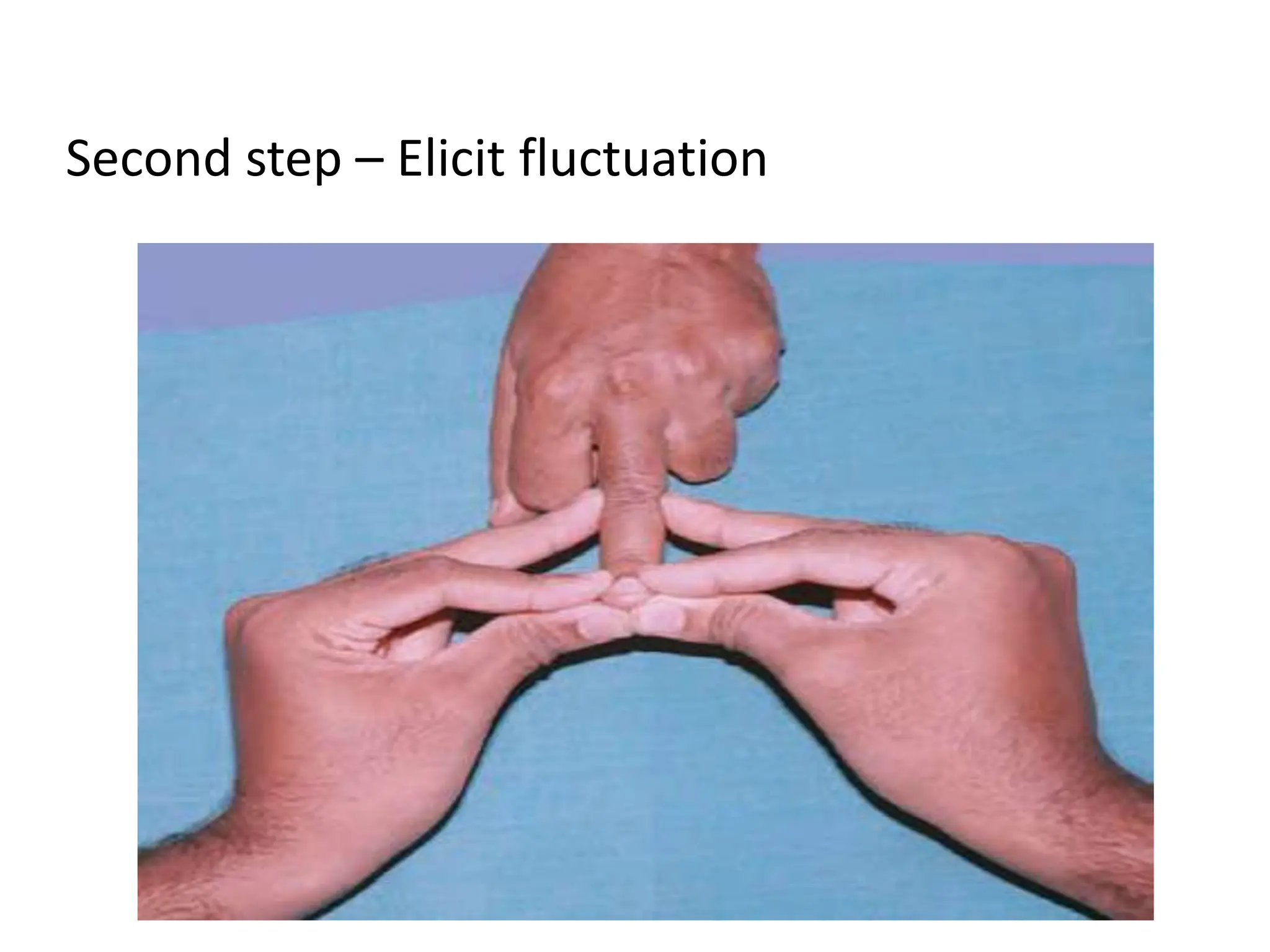
Clubbing refers to swelling of the fingers and toes with increased soft tissue mass and nail width. It is examined by assessing the angle between the nail and nail bed or using the shamroth window test. Causes include chronic lung and heart diseases resulting in hypoxia, as well as gastrointestinal diseases. Clubbing is graded based on changes to the nail bed and pulp tissue. It is a sign of underlying serious conditions and helps guide further medical evaluation.