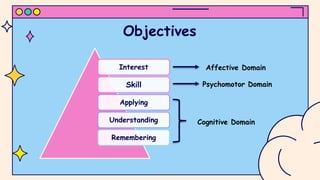
Objectives and specifications are used to define the desired learning outcomes for students. Objectives are specific, measurable behaviors that indicate the knowledge, skills, or attitudes to be gained by students. Objectives originate from broader aims and are tailored to individual subjects. Specifications provide a clear statement of what students are expected to be able to do, know, and value by the end of a lesson. Verbs are used in specifications to define observable behaviors within cognitive, psychomotor, and affective domains. Examples of specifications for different subjects are provided using domain-specific verbs.