This document defines key terms and concepts in solid geometry, including:
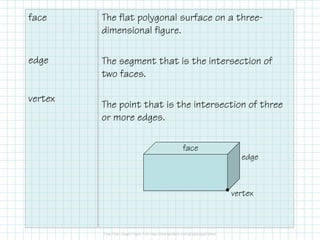
- Classifying three-dimensional figures according to their properties like faces, edges, and vertices.
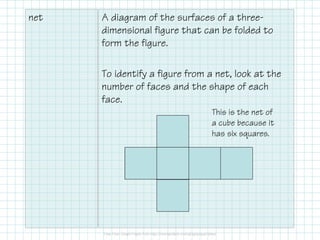
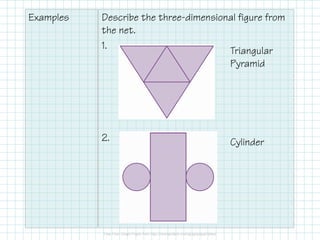
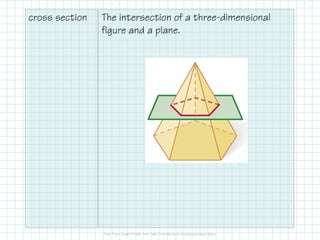
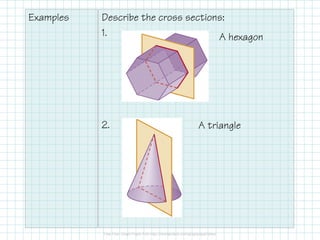
- Using nets and cross sections to analyze three-dimensional shapes.
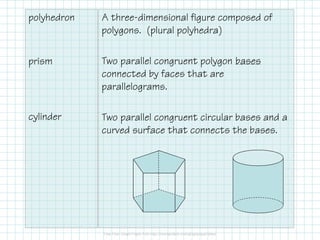
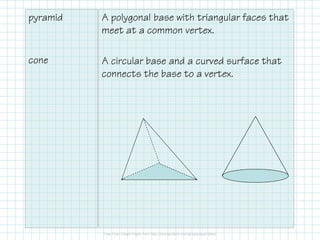
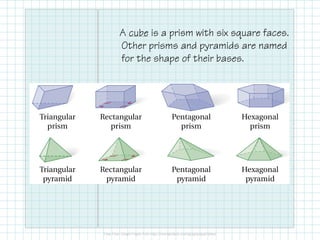
- Common solids like prisms, pyramids, cylinders, and their properties.
- Euler's formula relating the number of vertices, edges, and faces in a polyhedron.
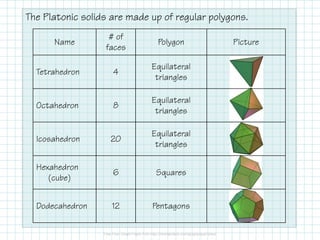
- The five Platonic solids - regular polyhedra with faces of identical regular polygons.