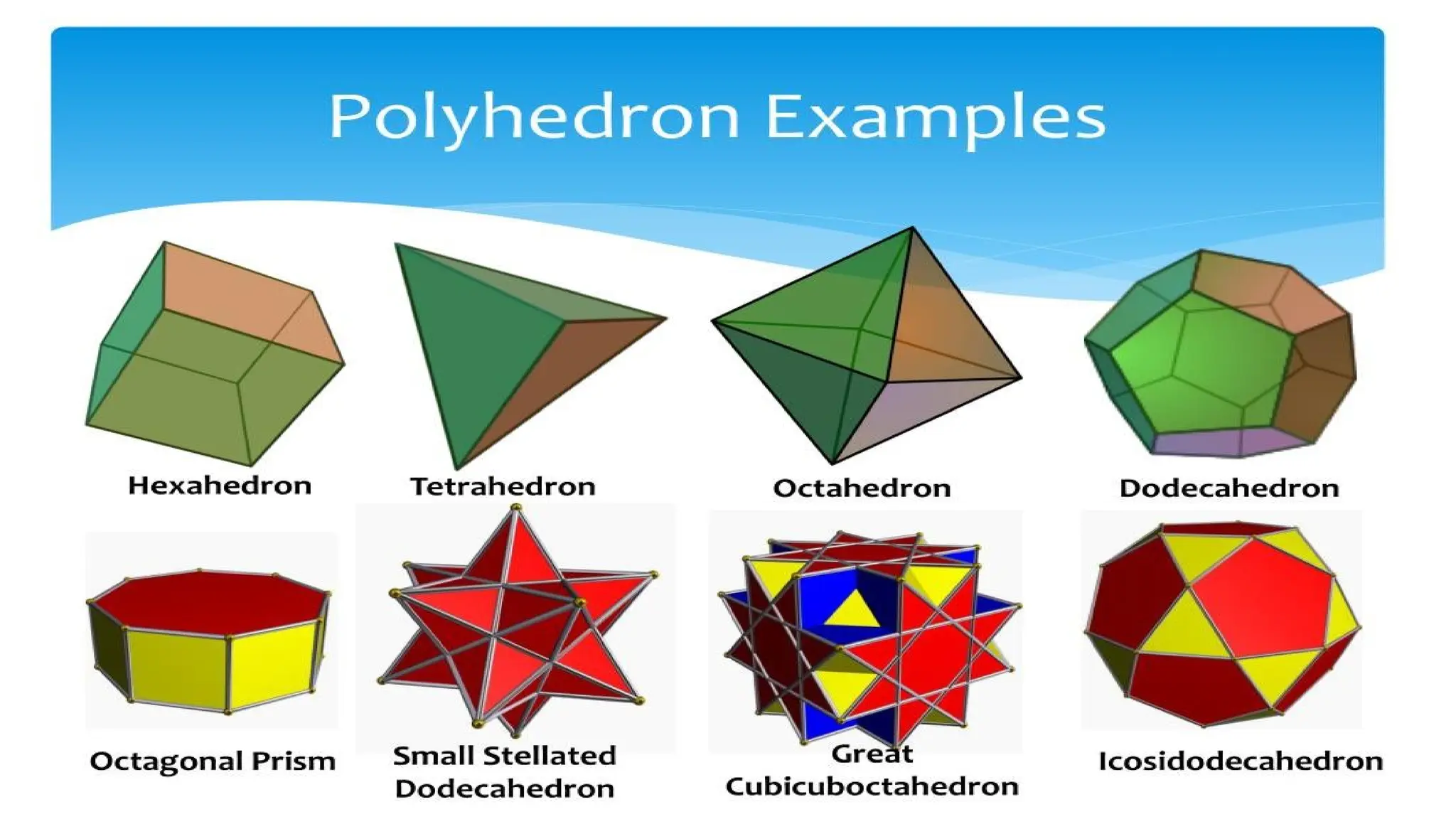
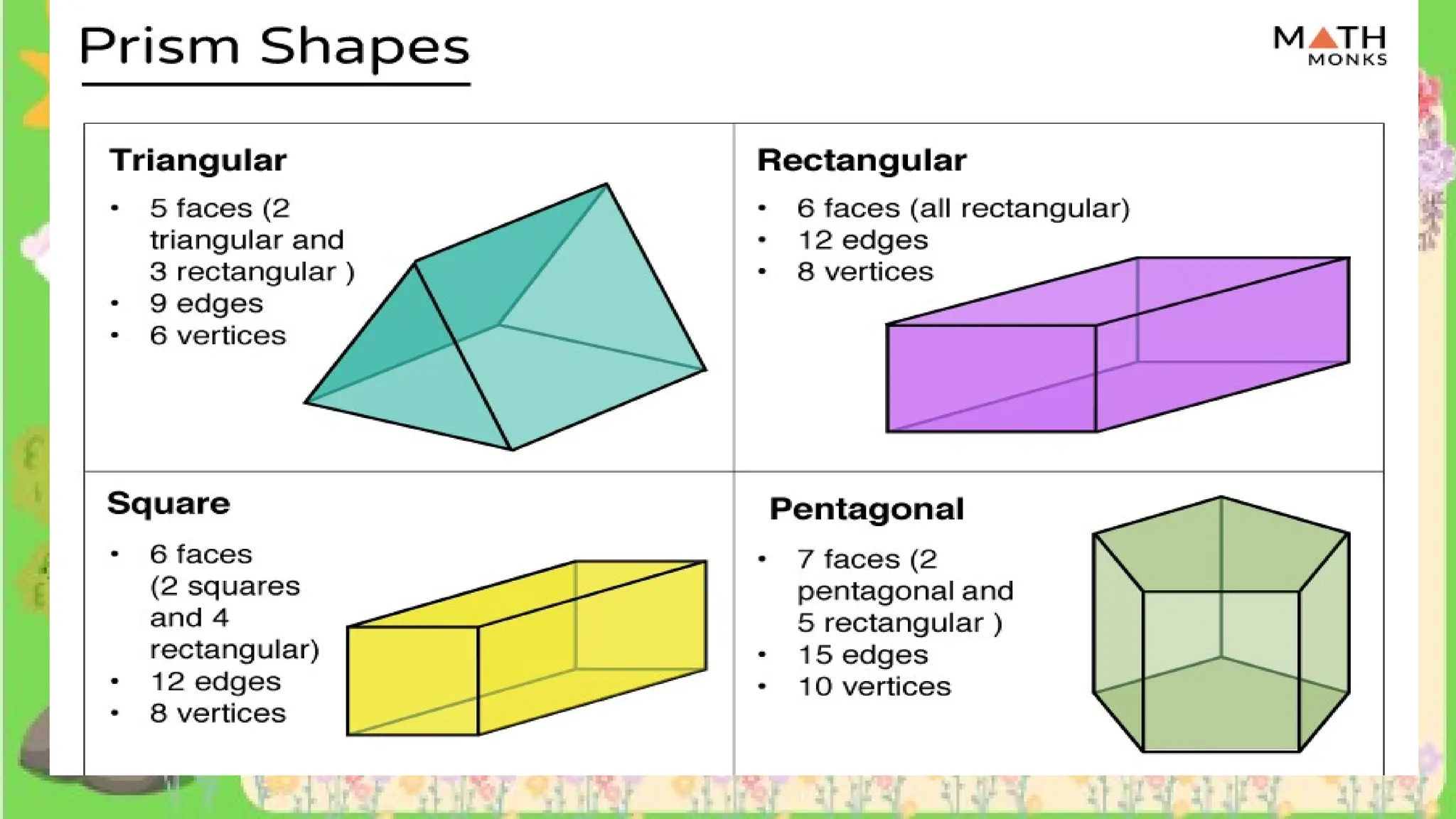
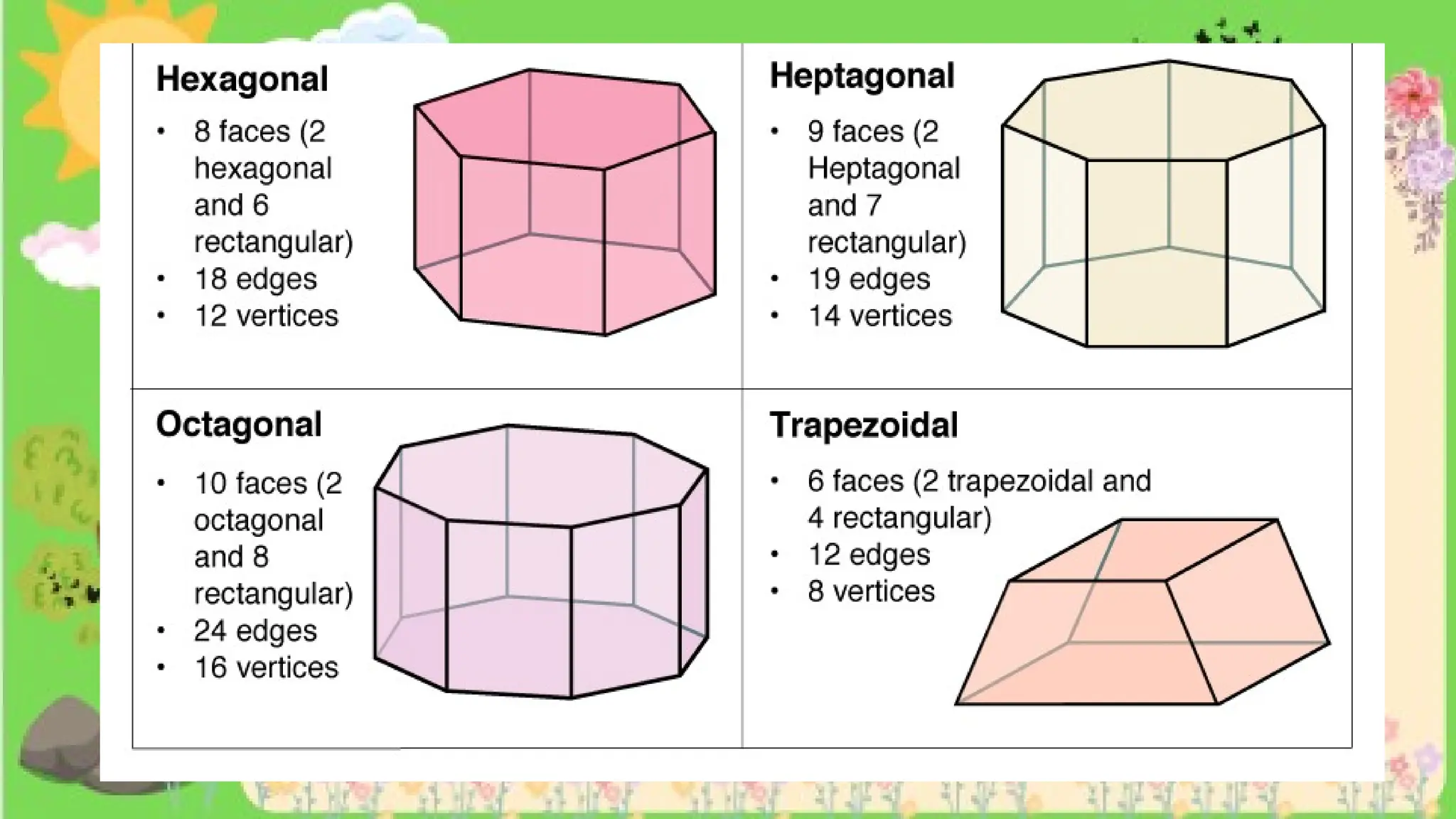
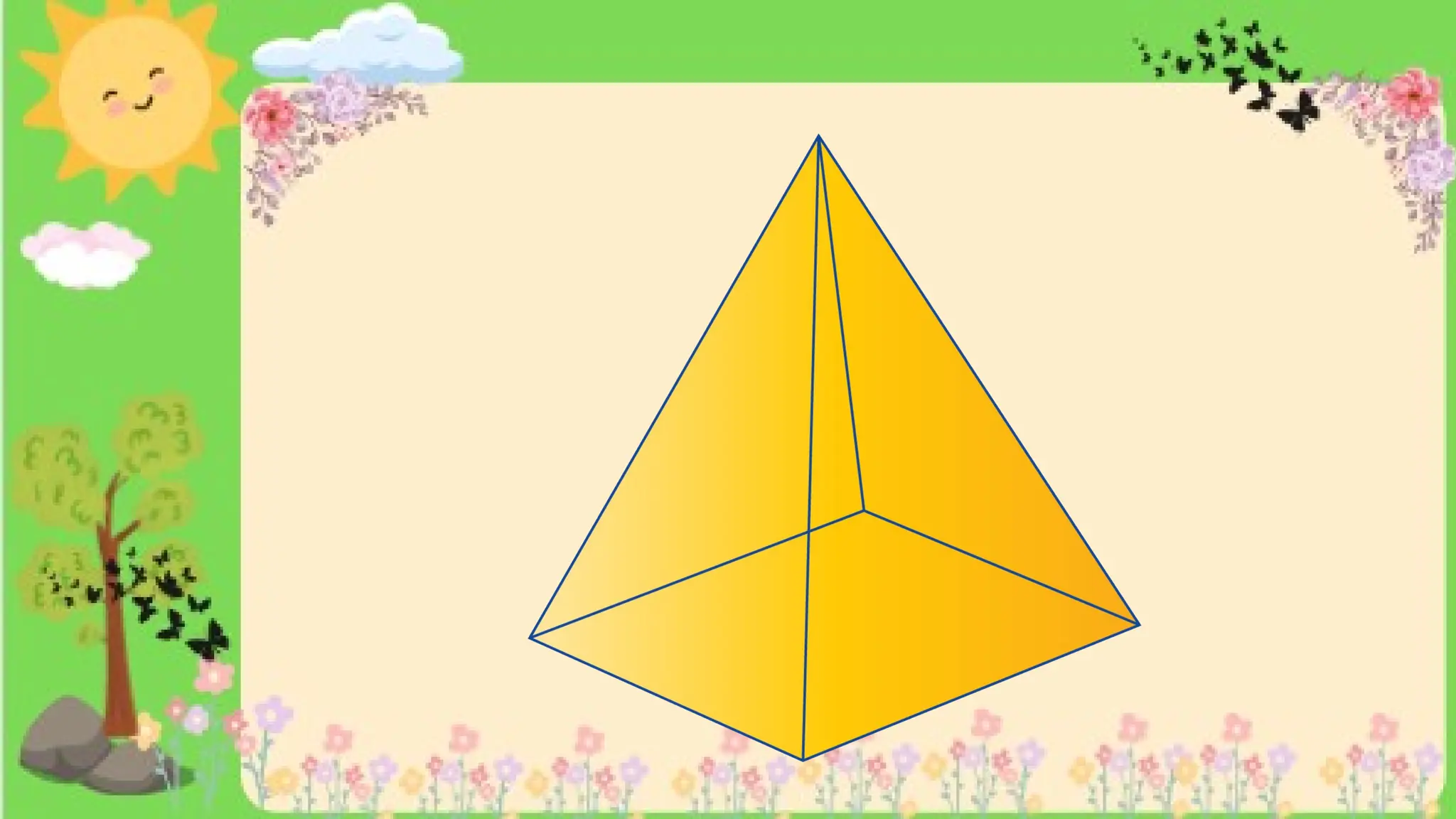
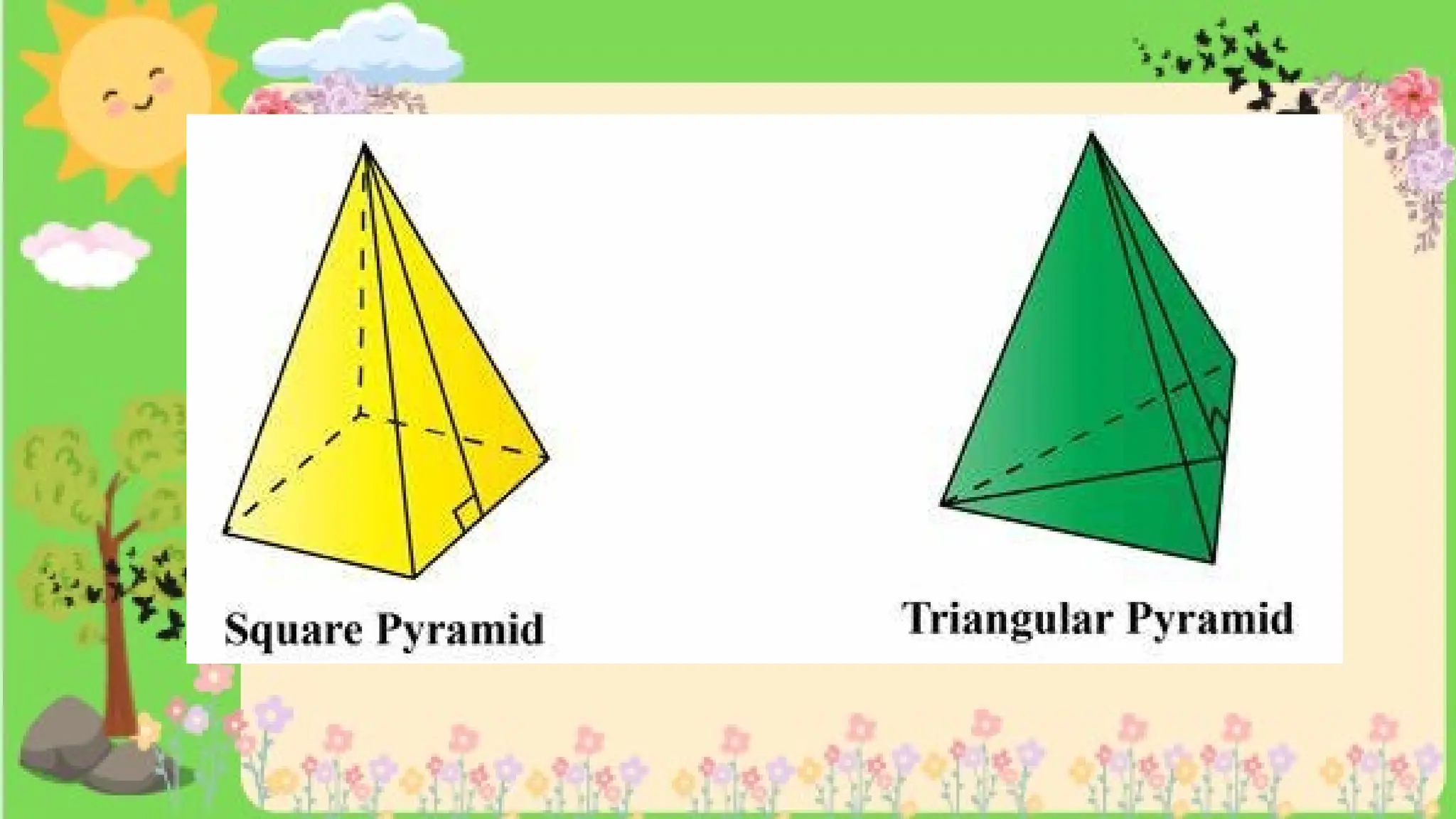
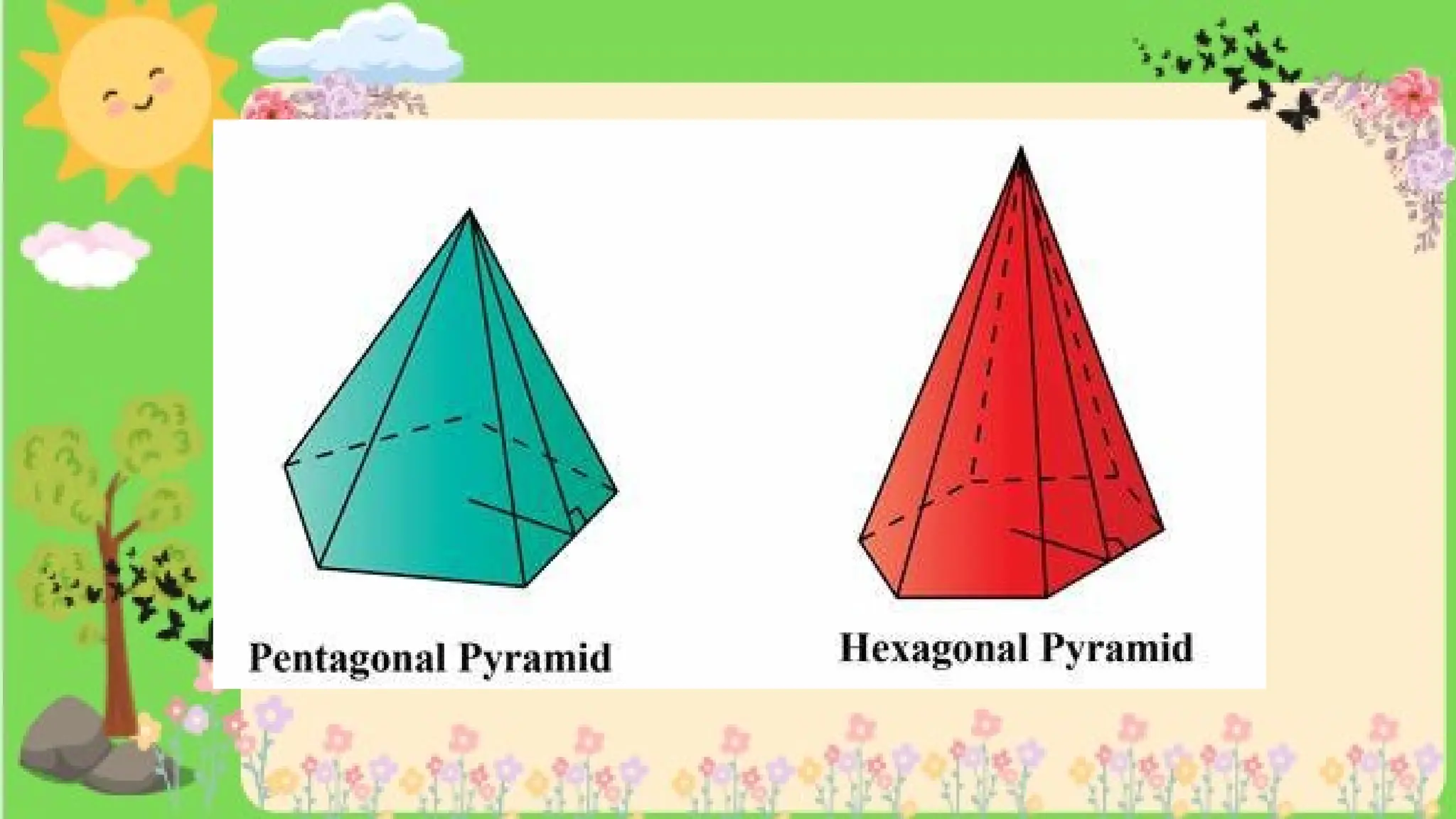
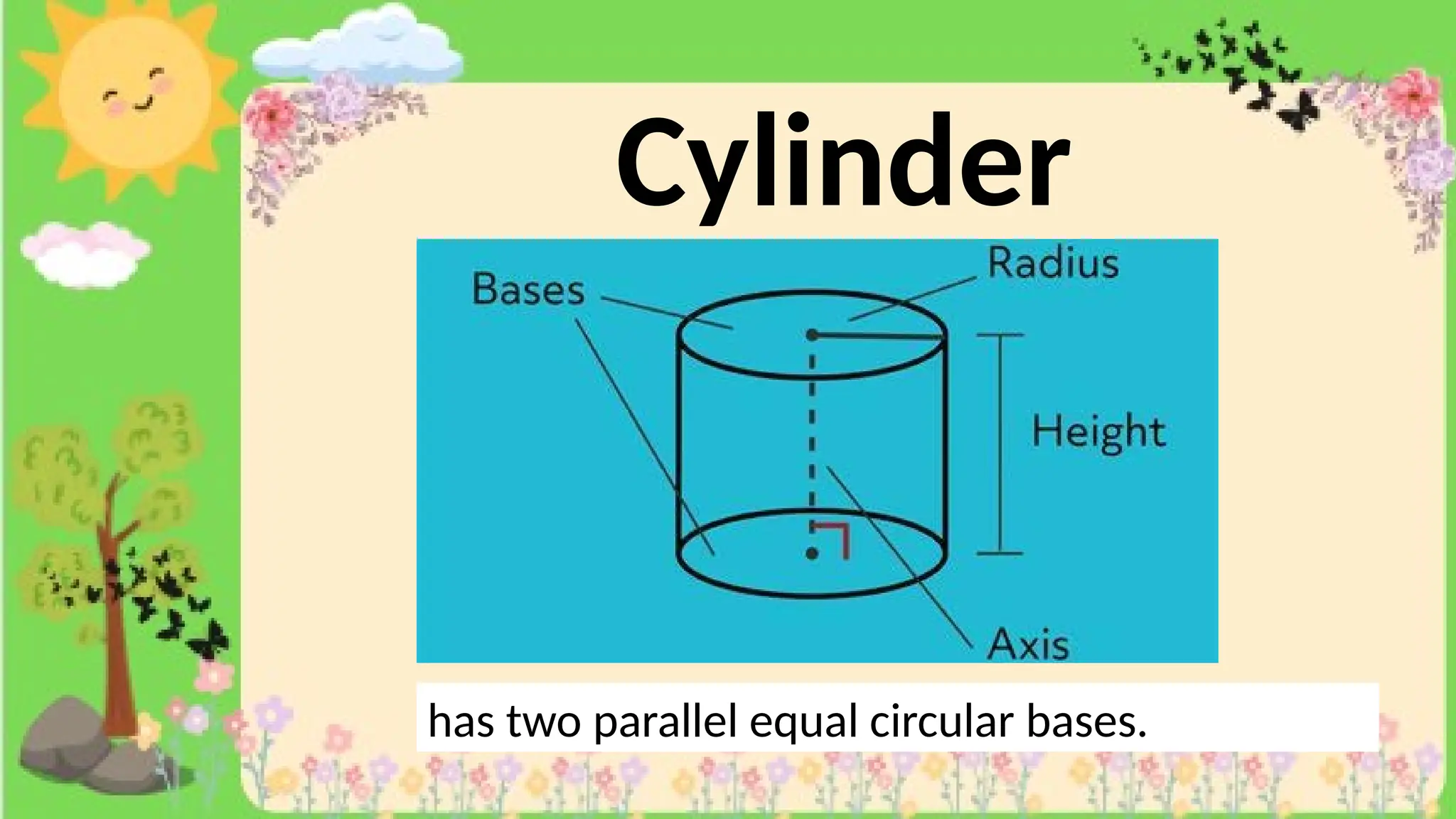
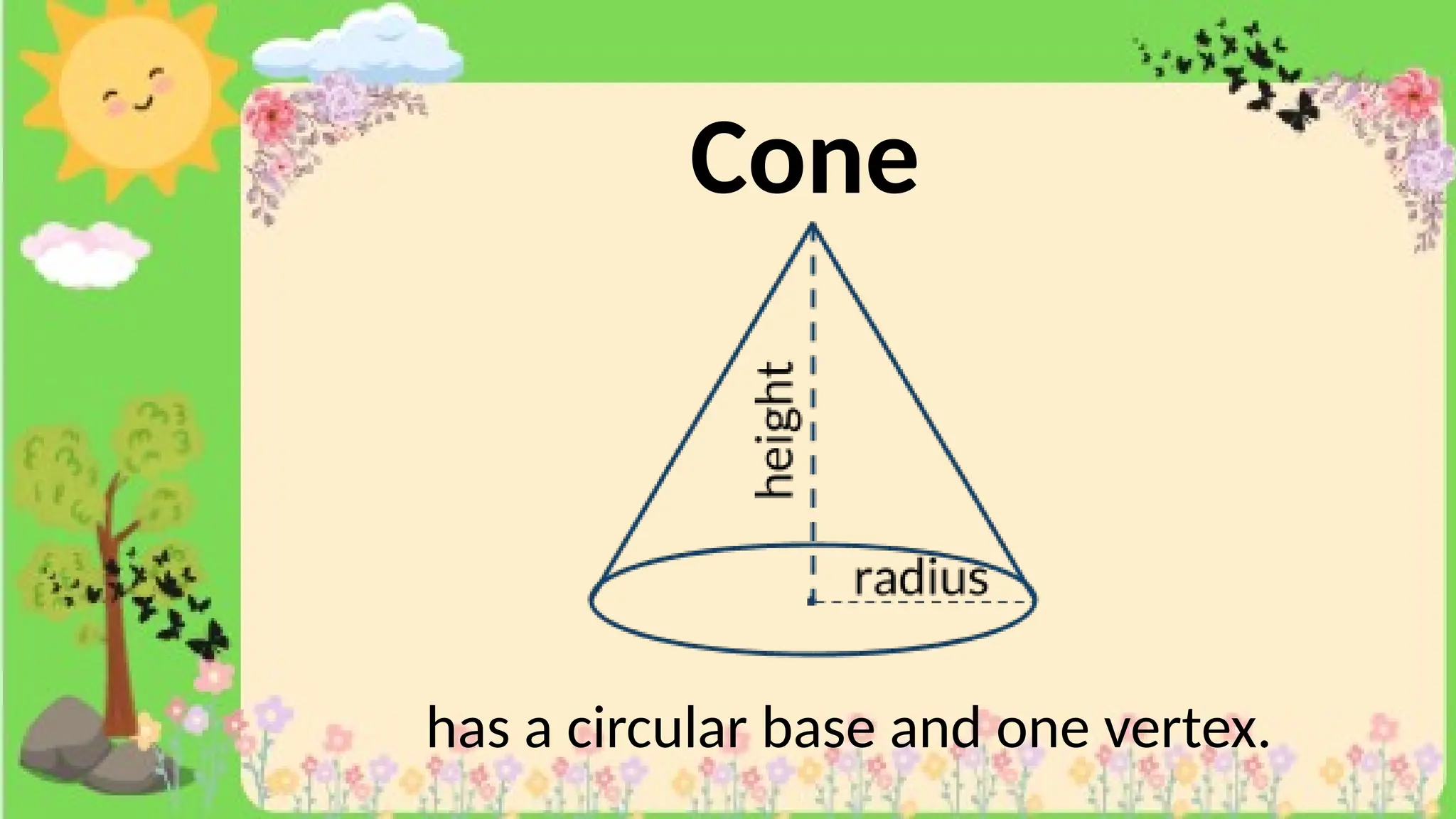
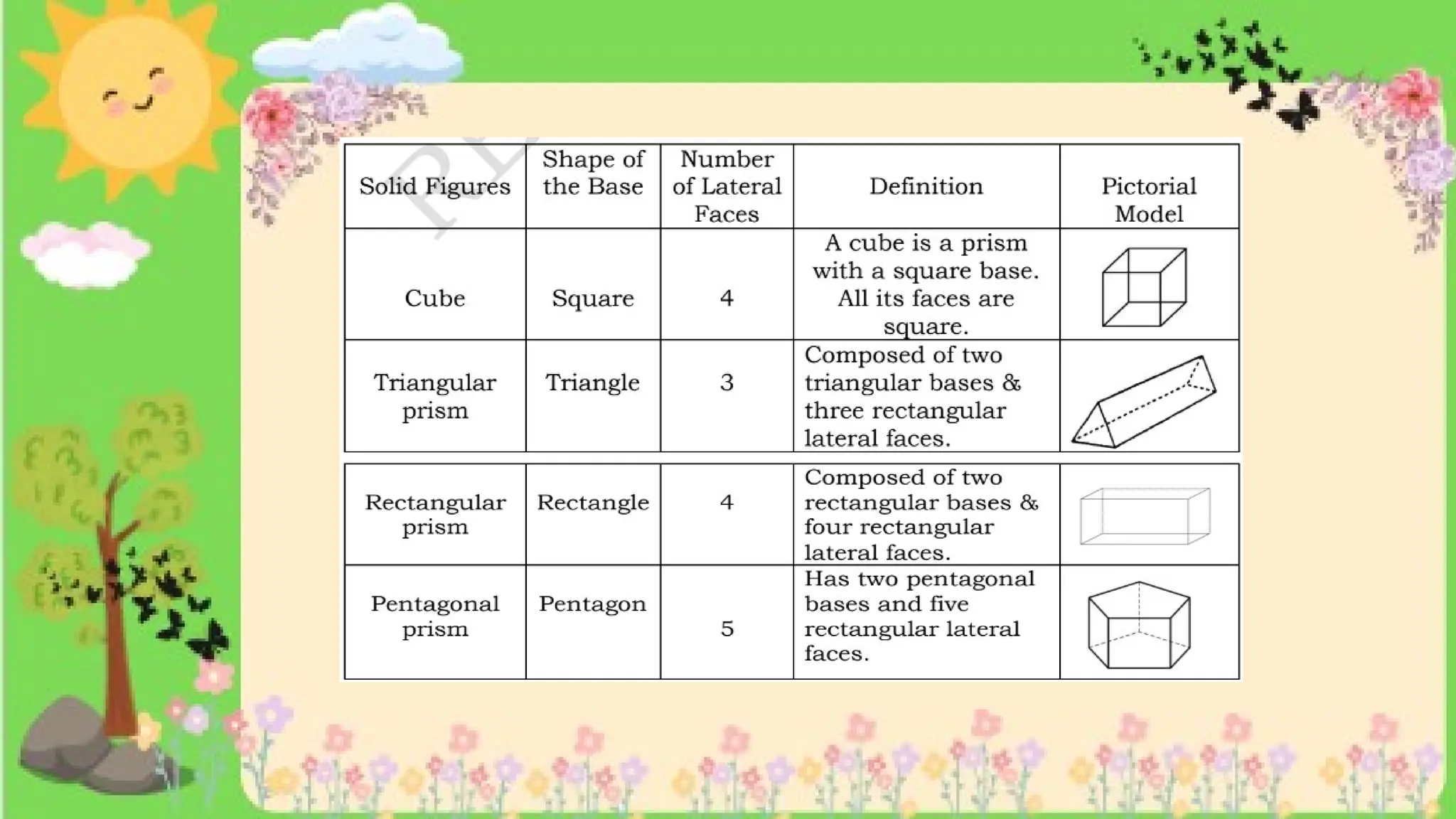
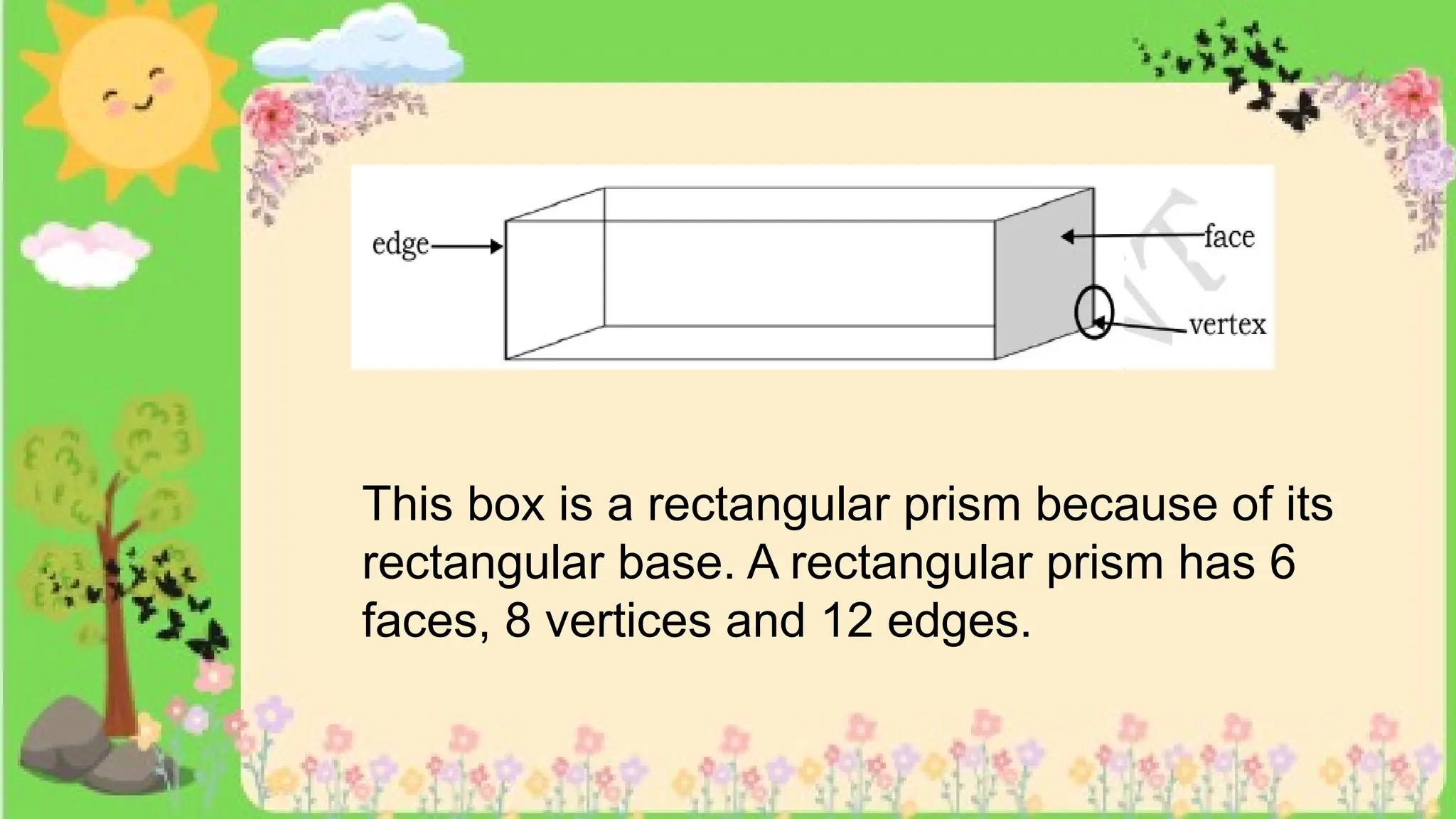
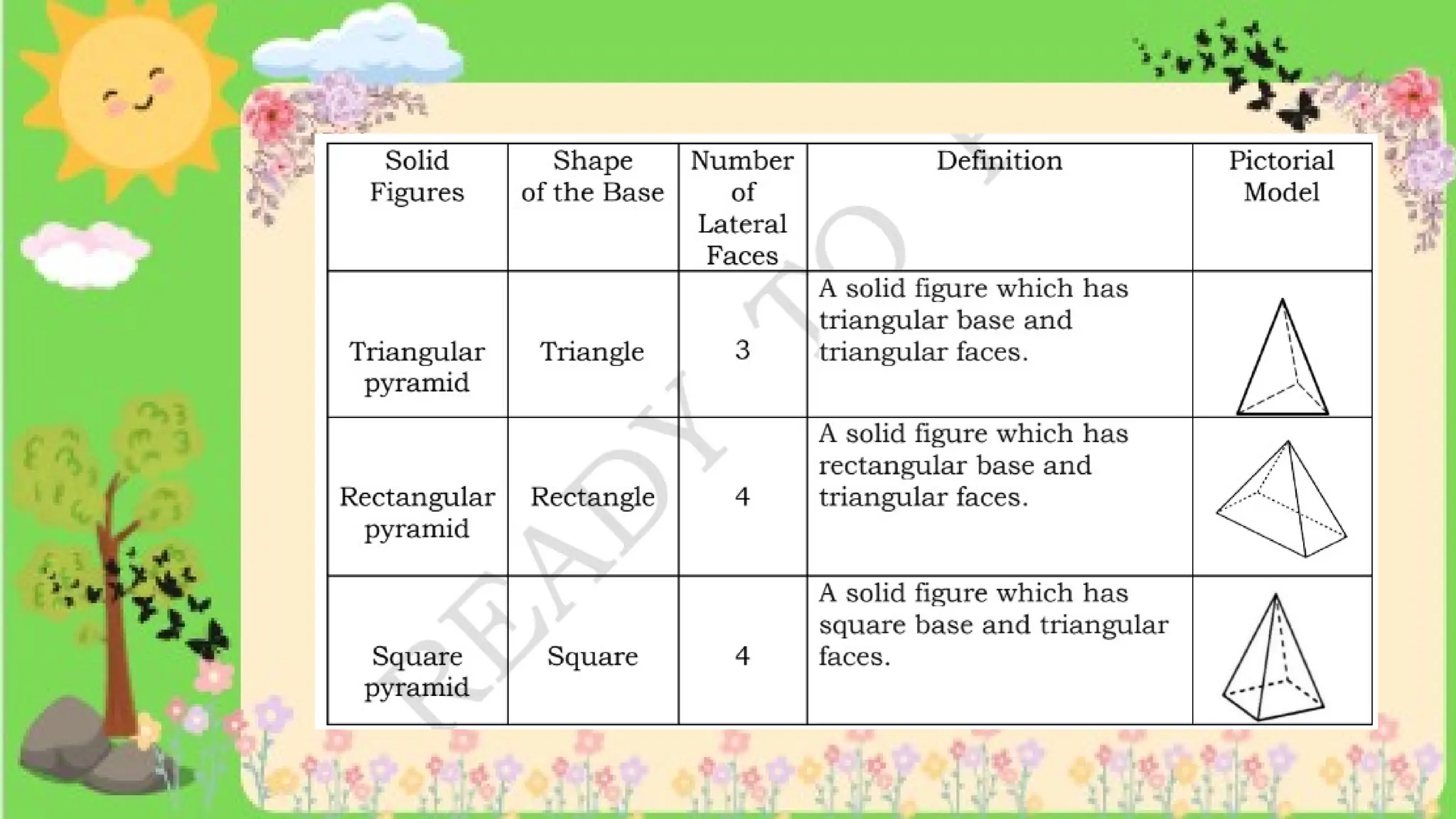
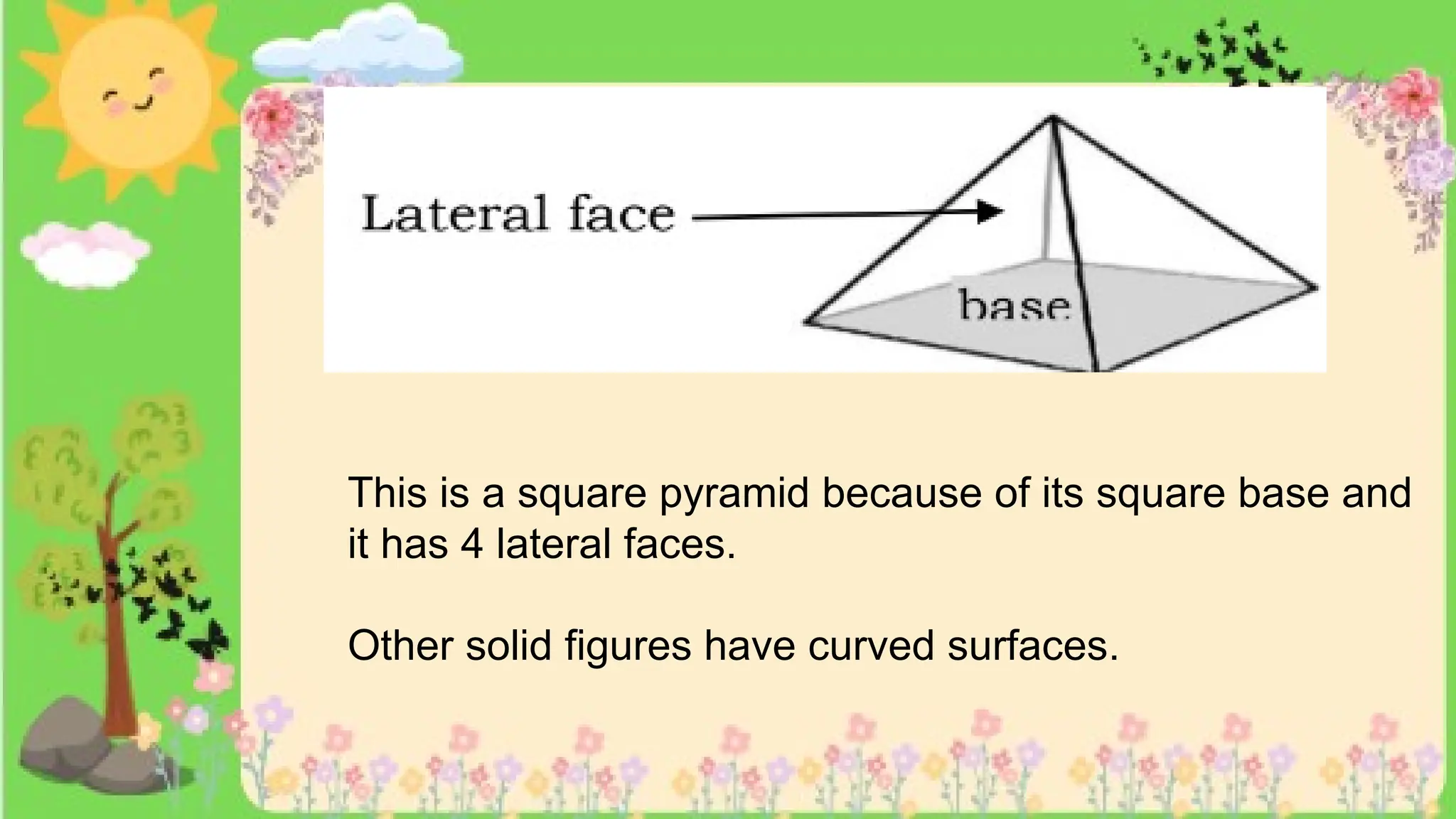
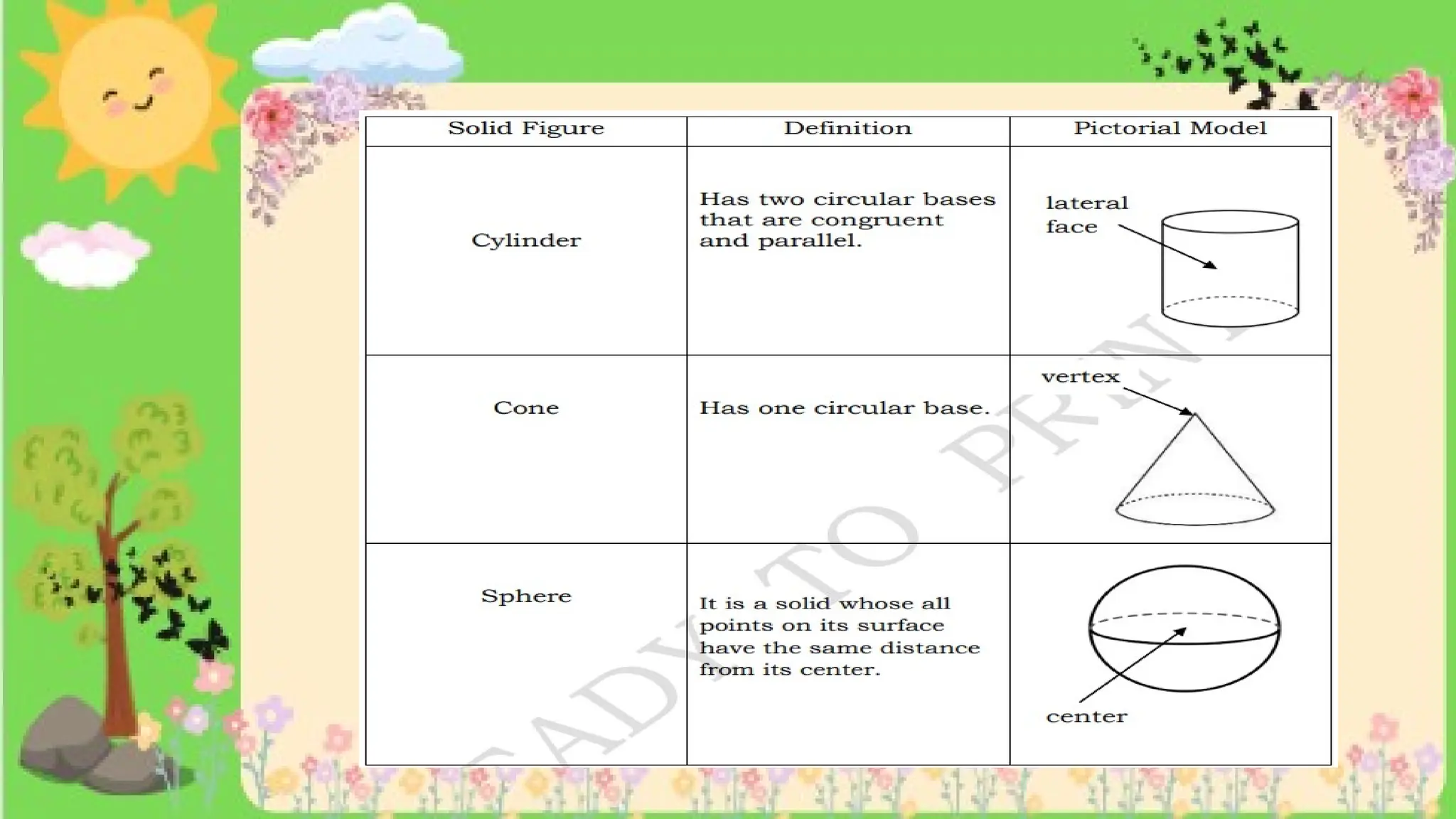
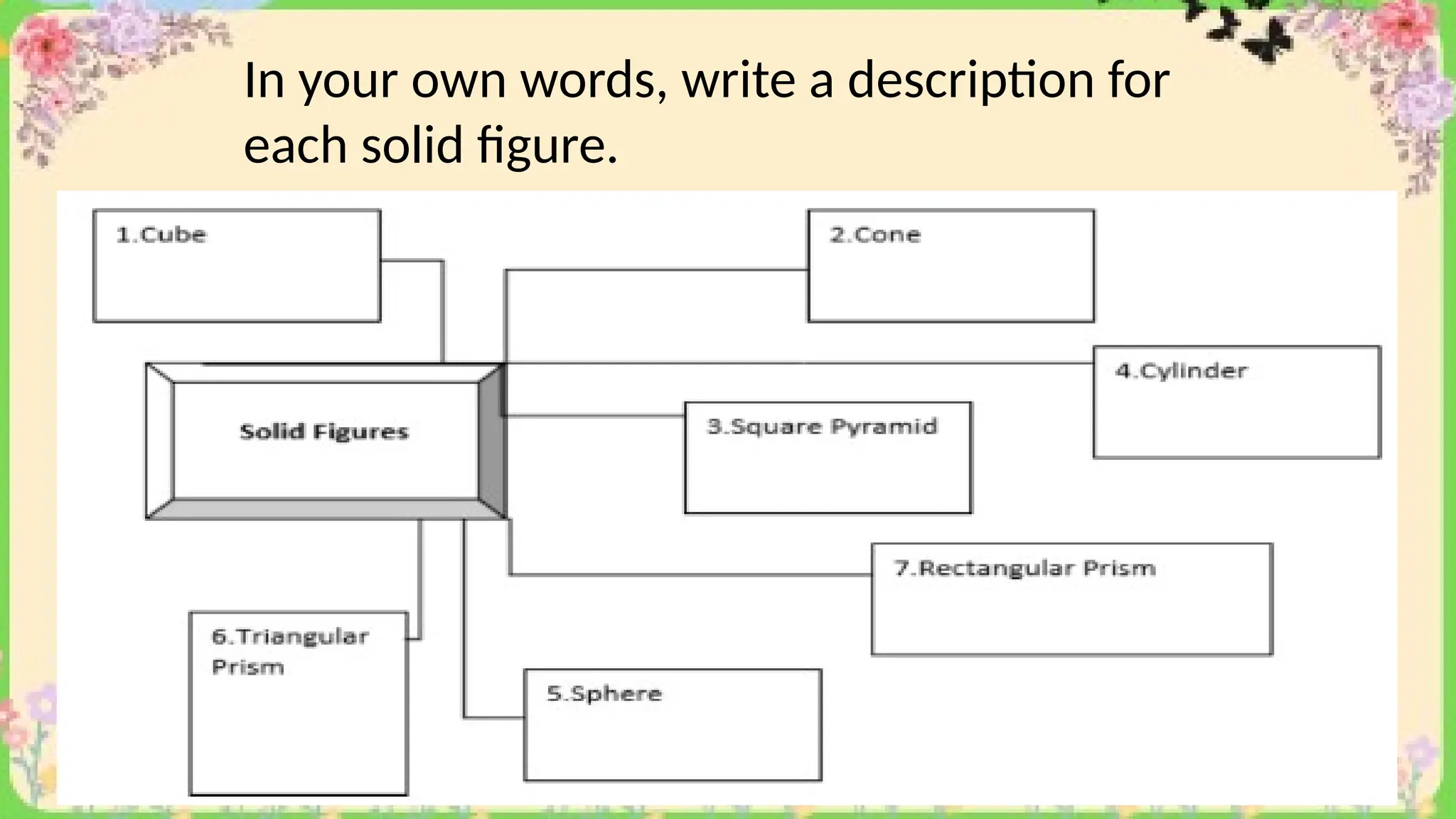
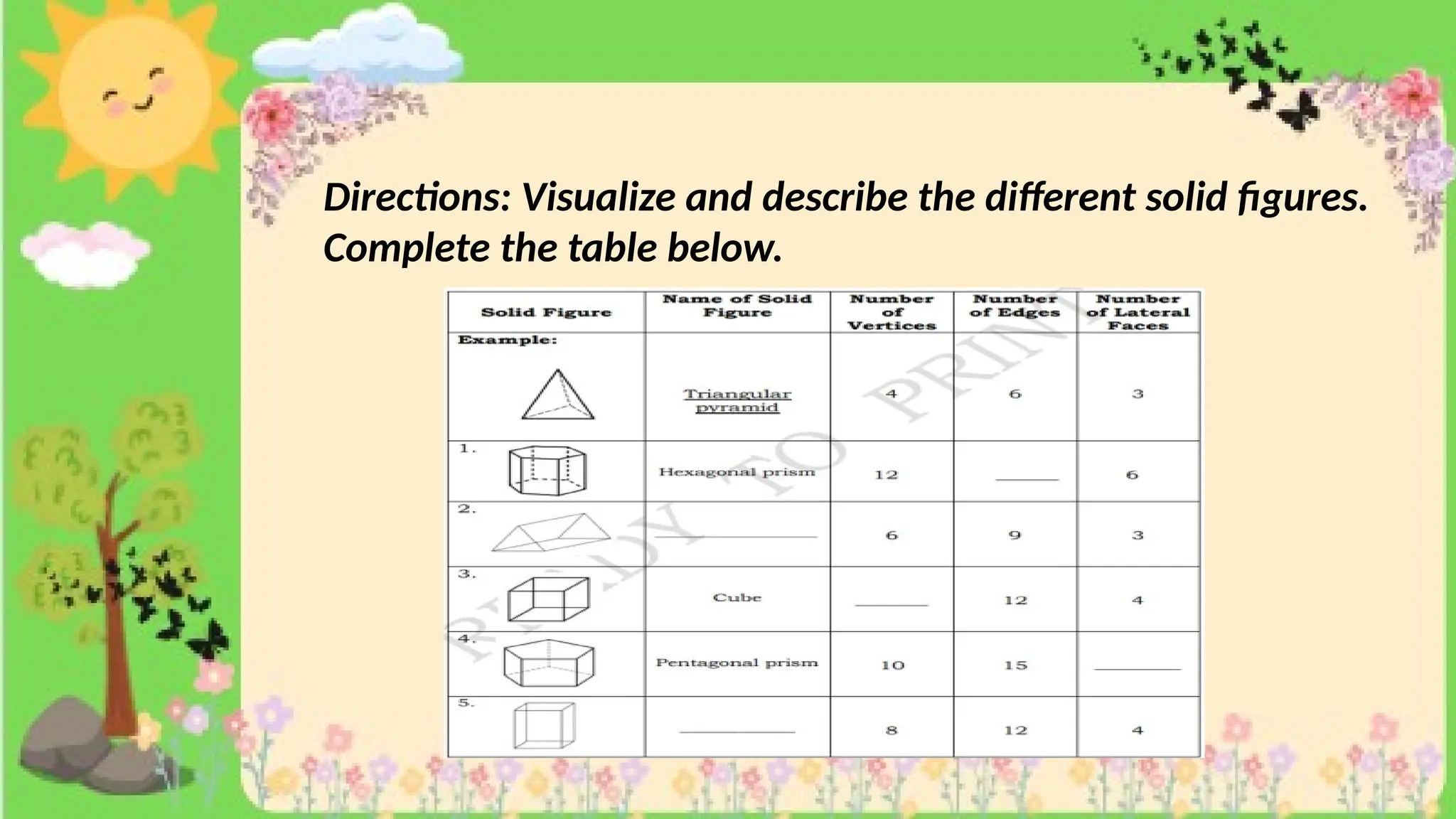
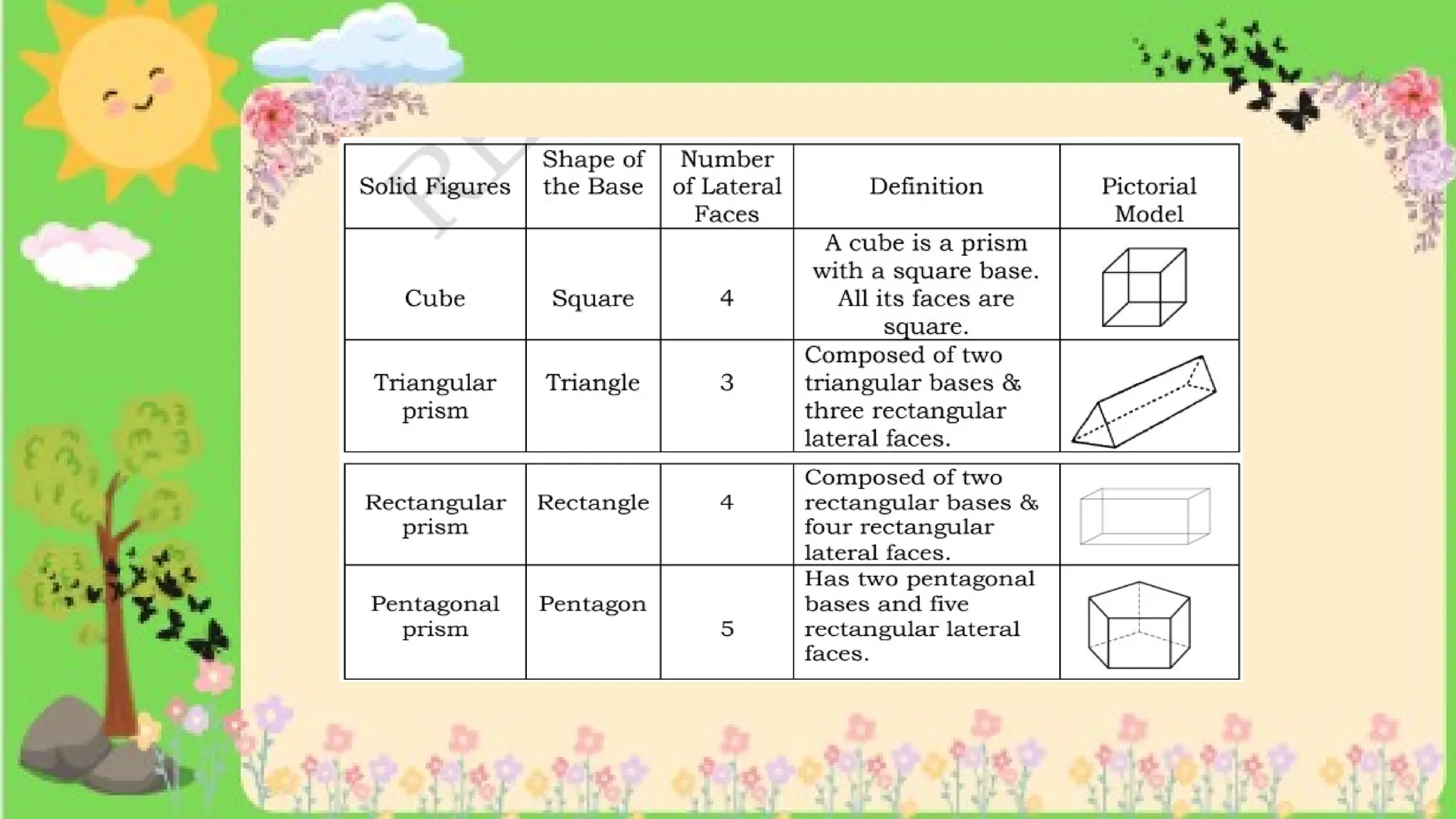
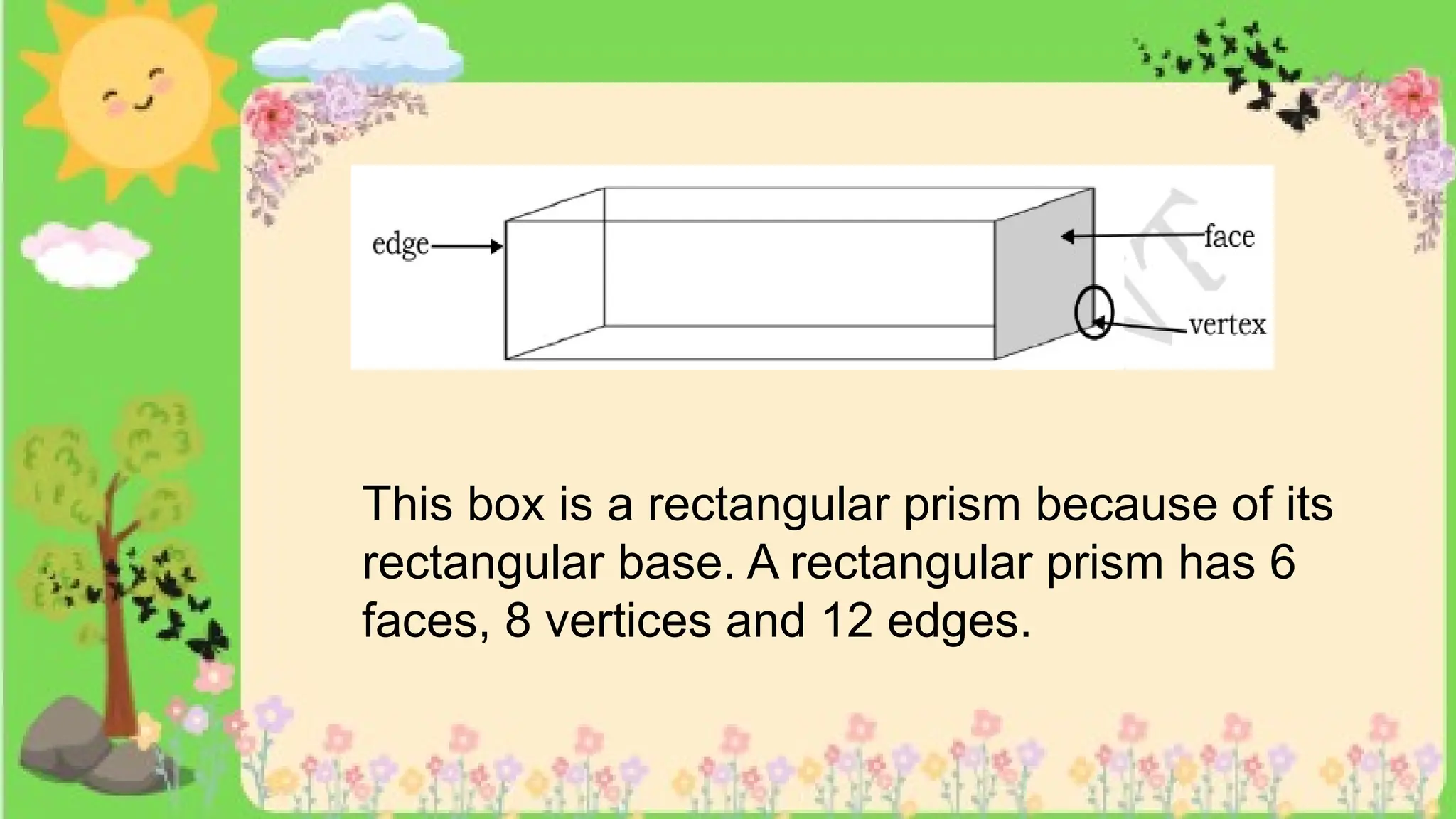
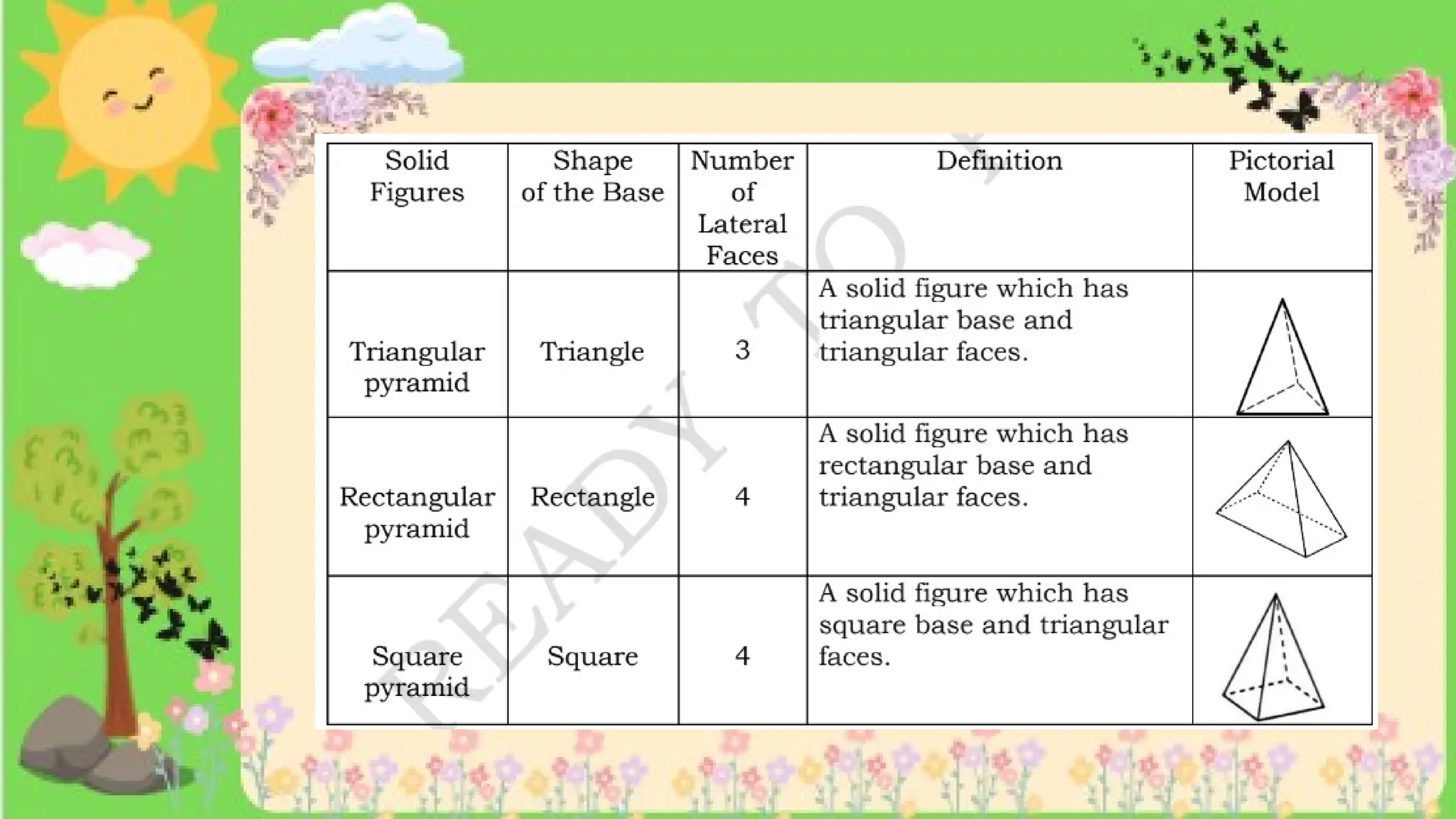
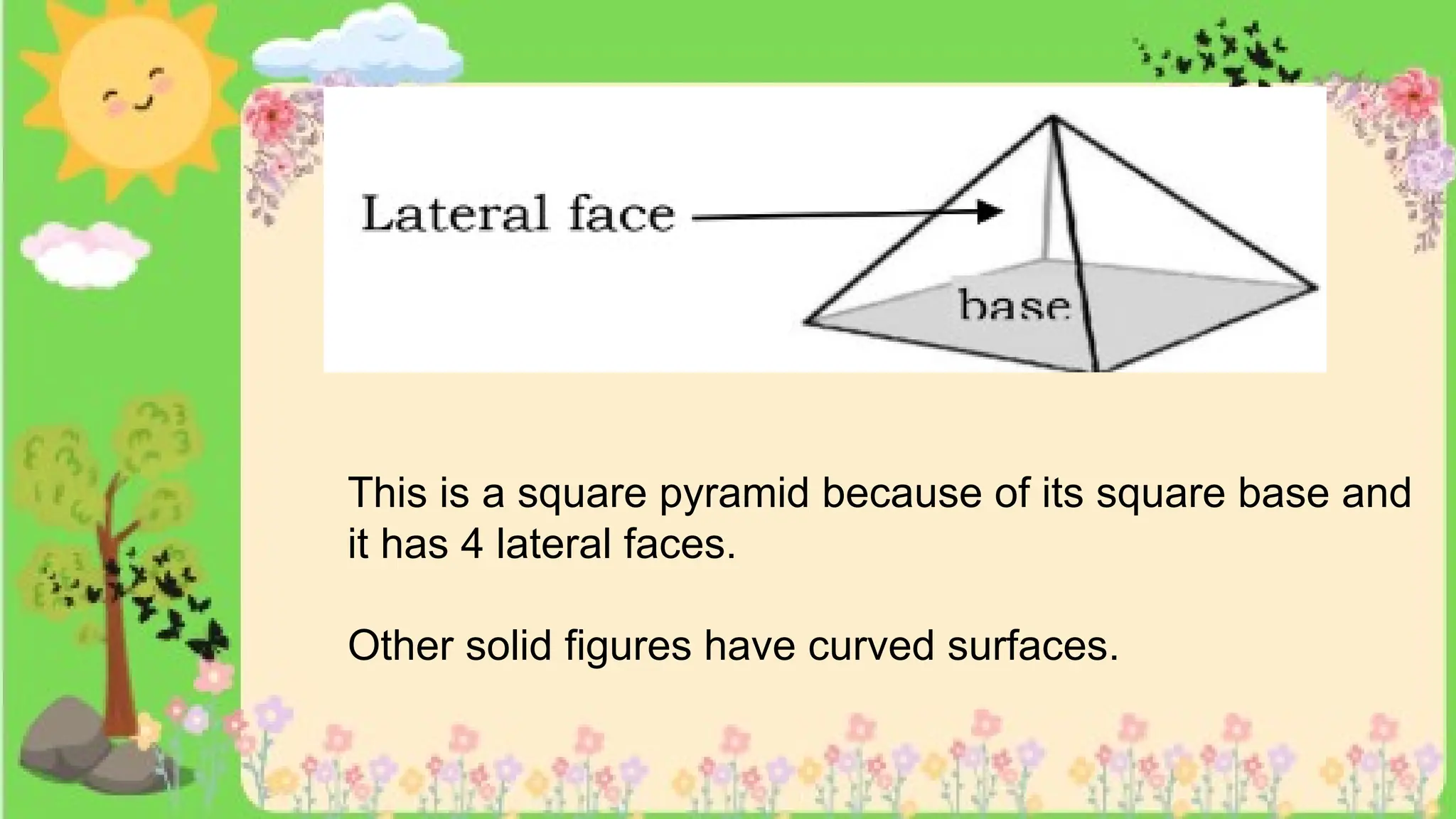
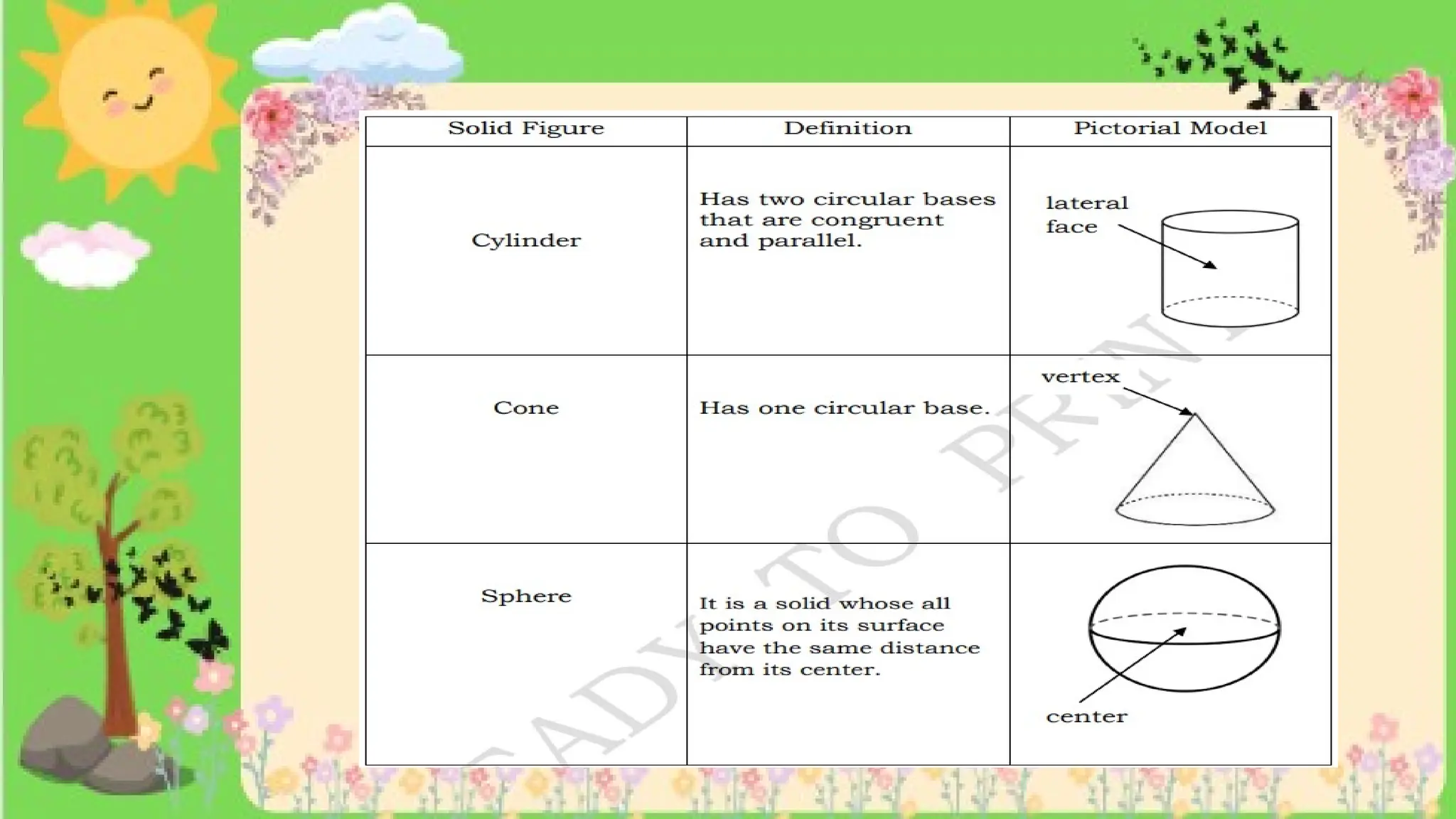
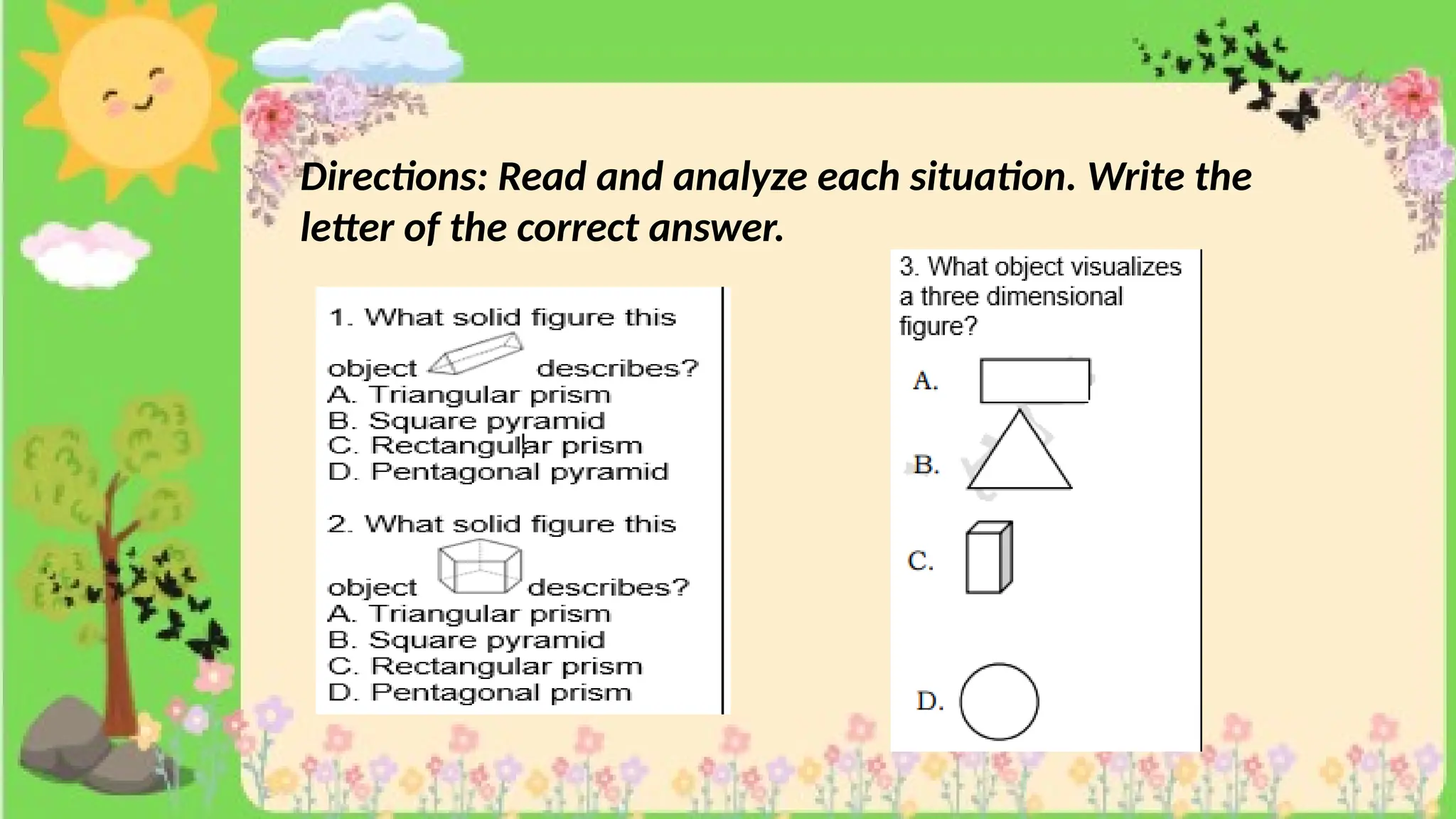
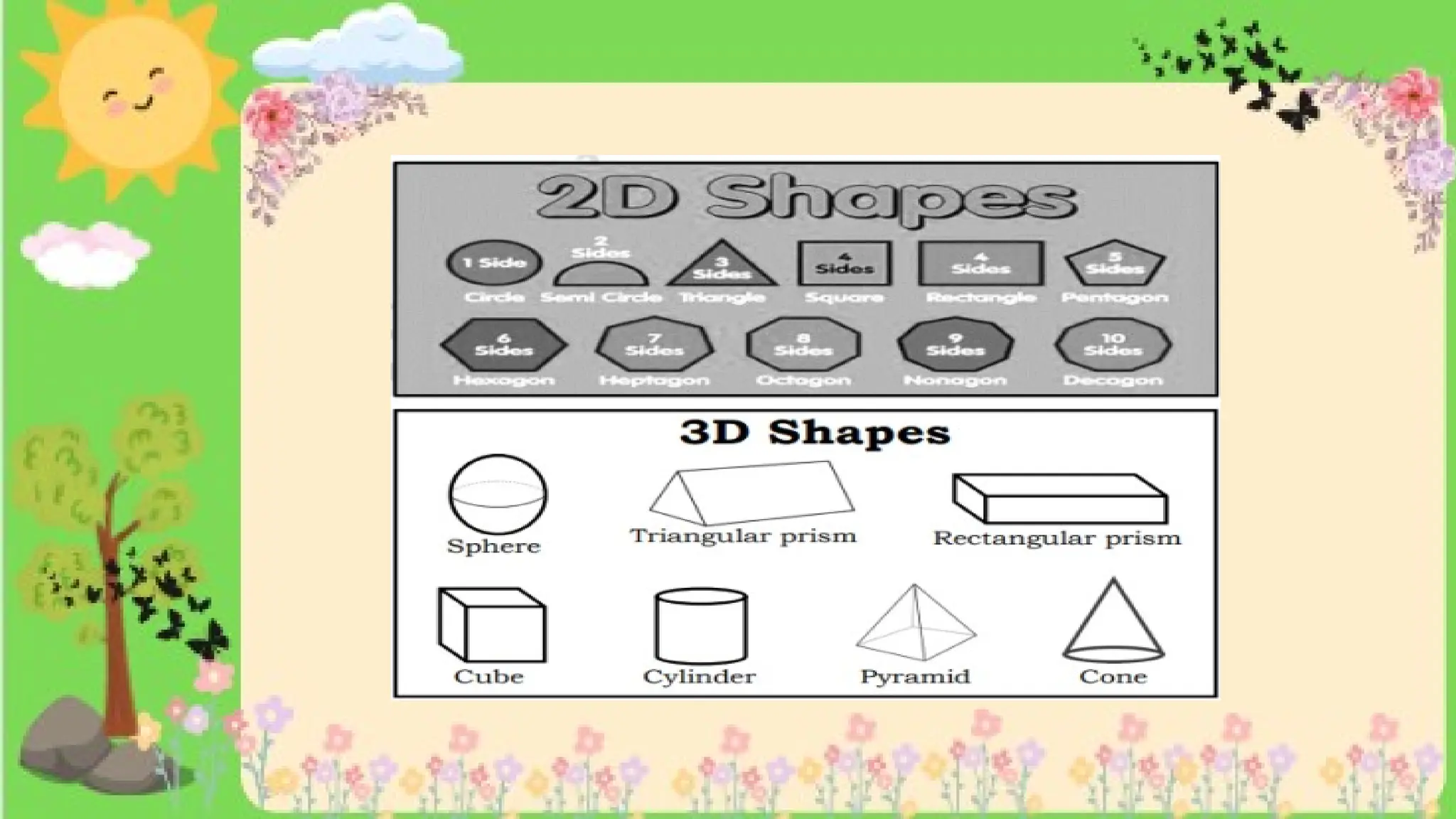
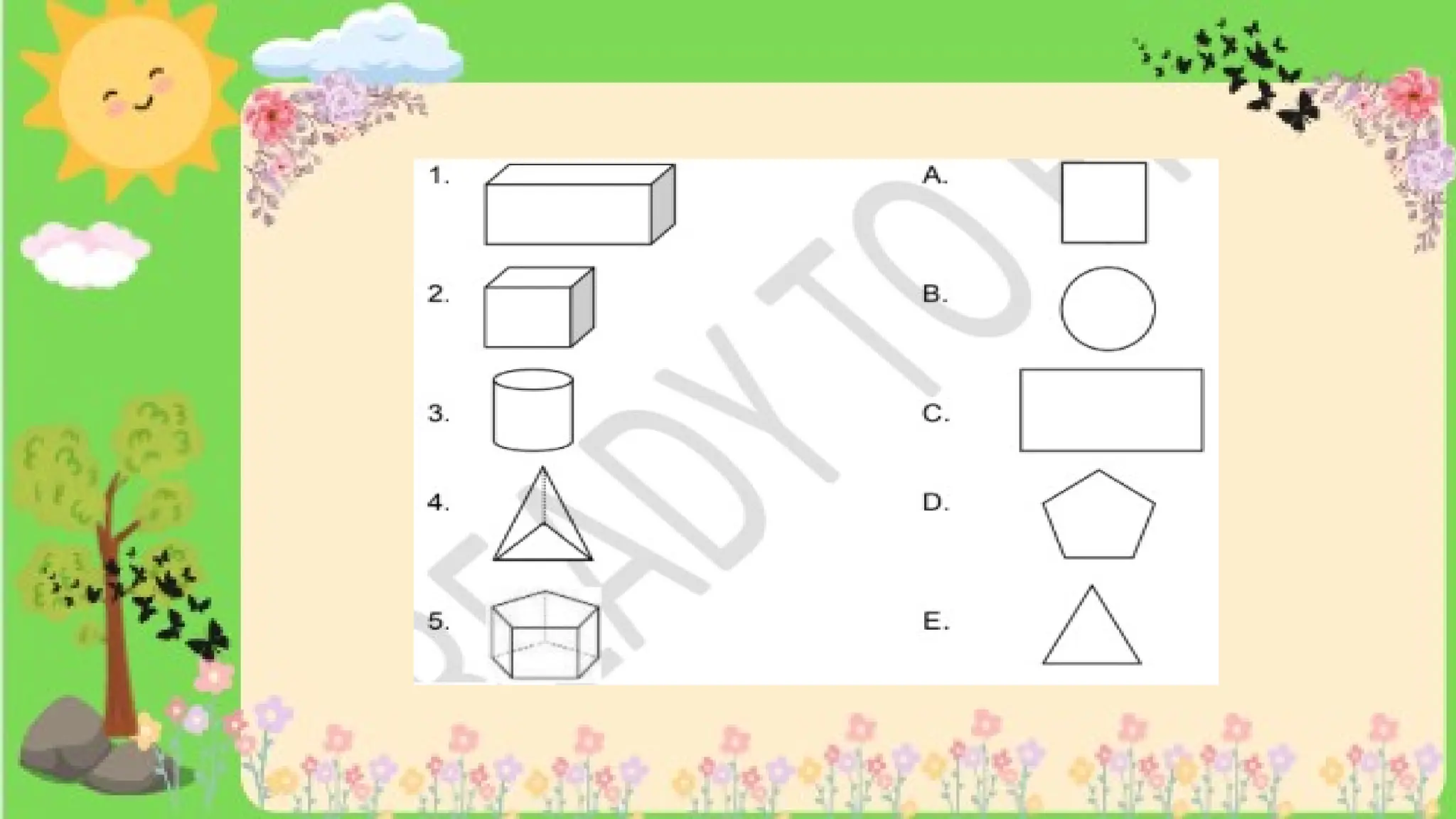
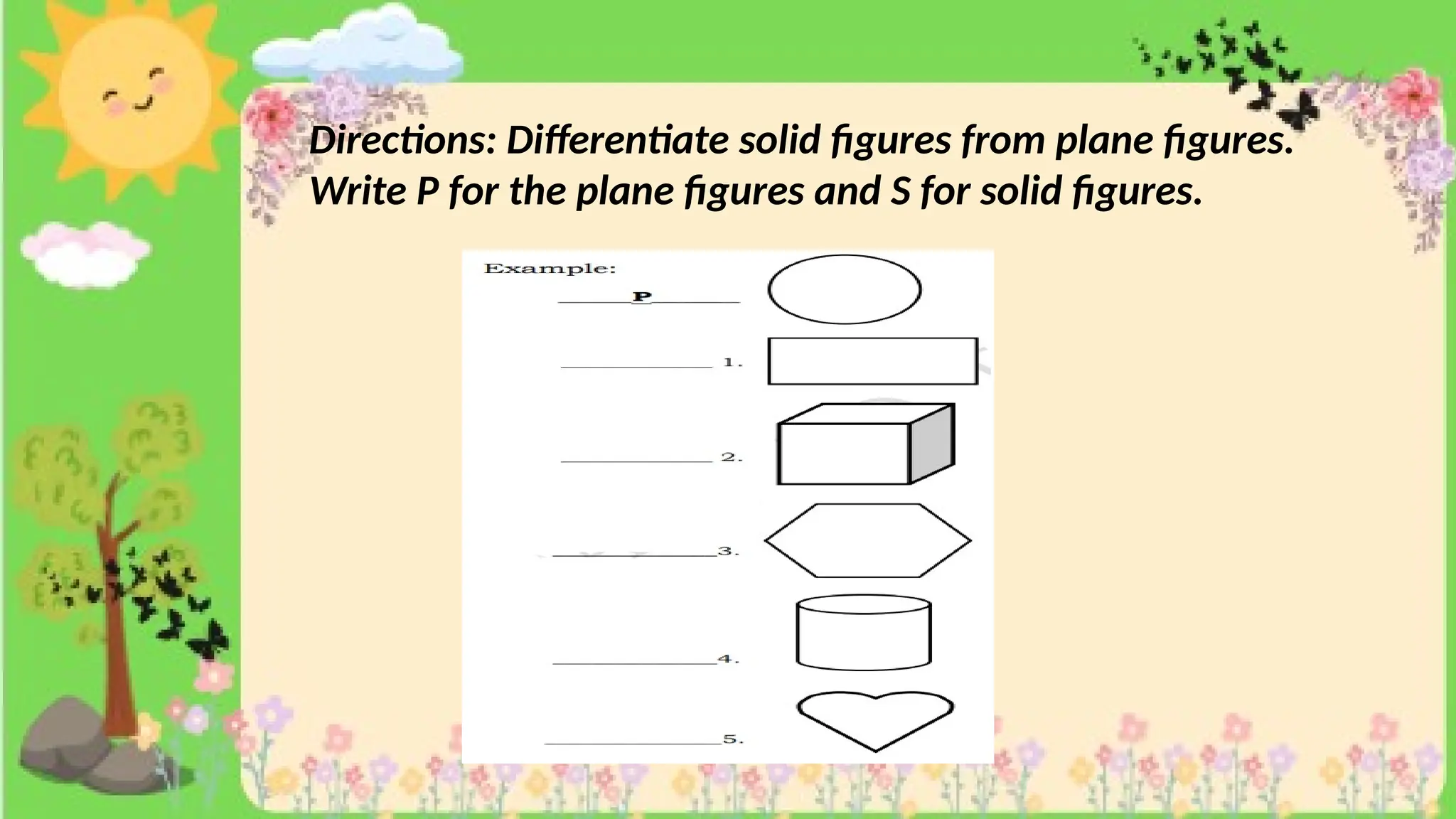
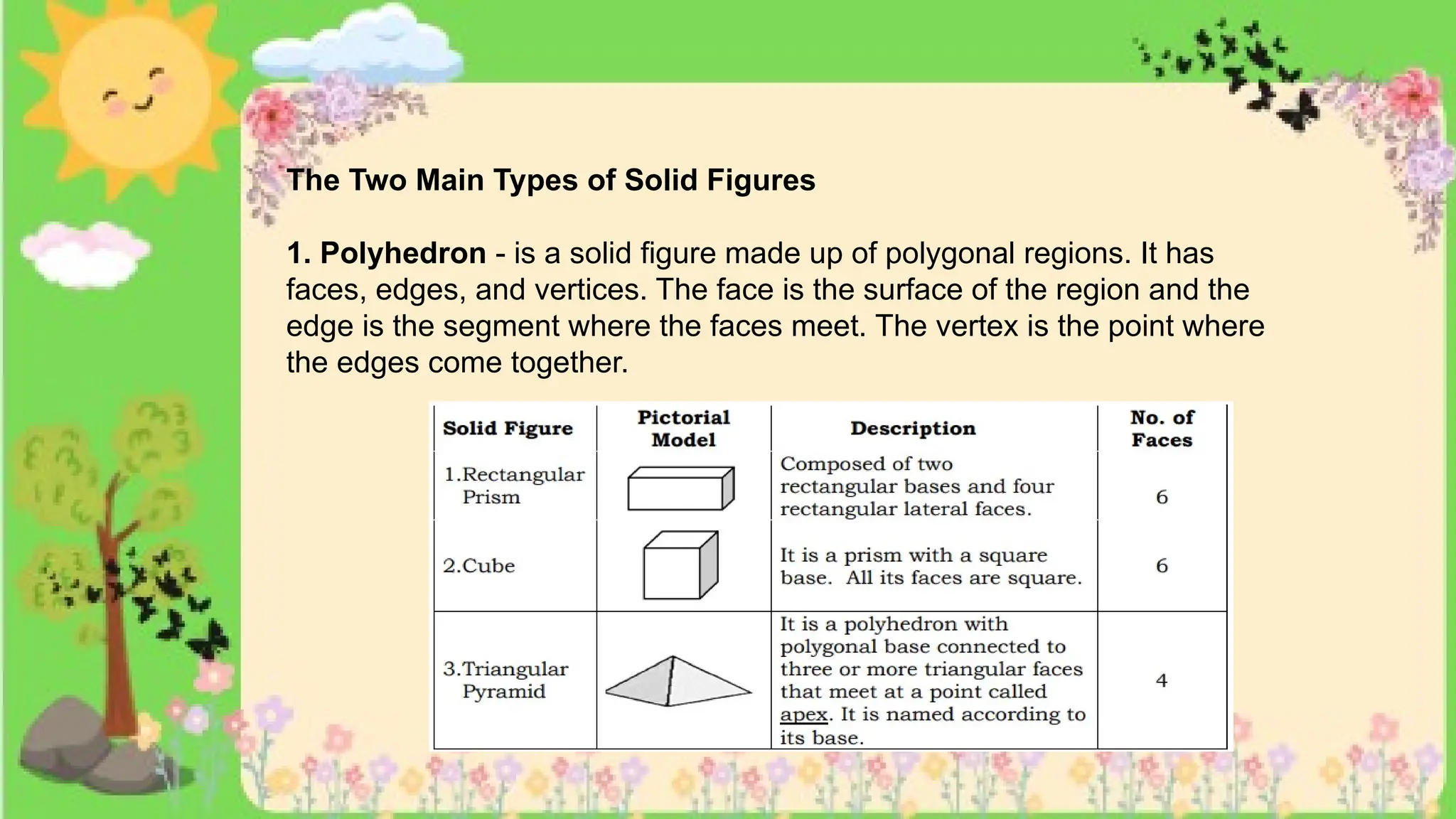
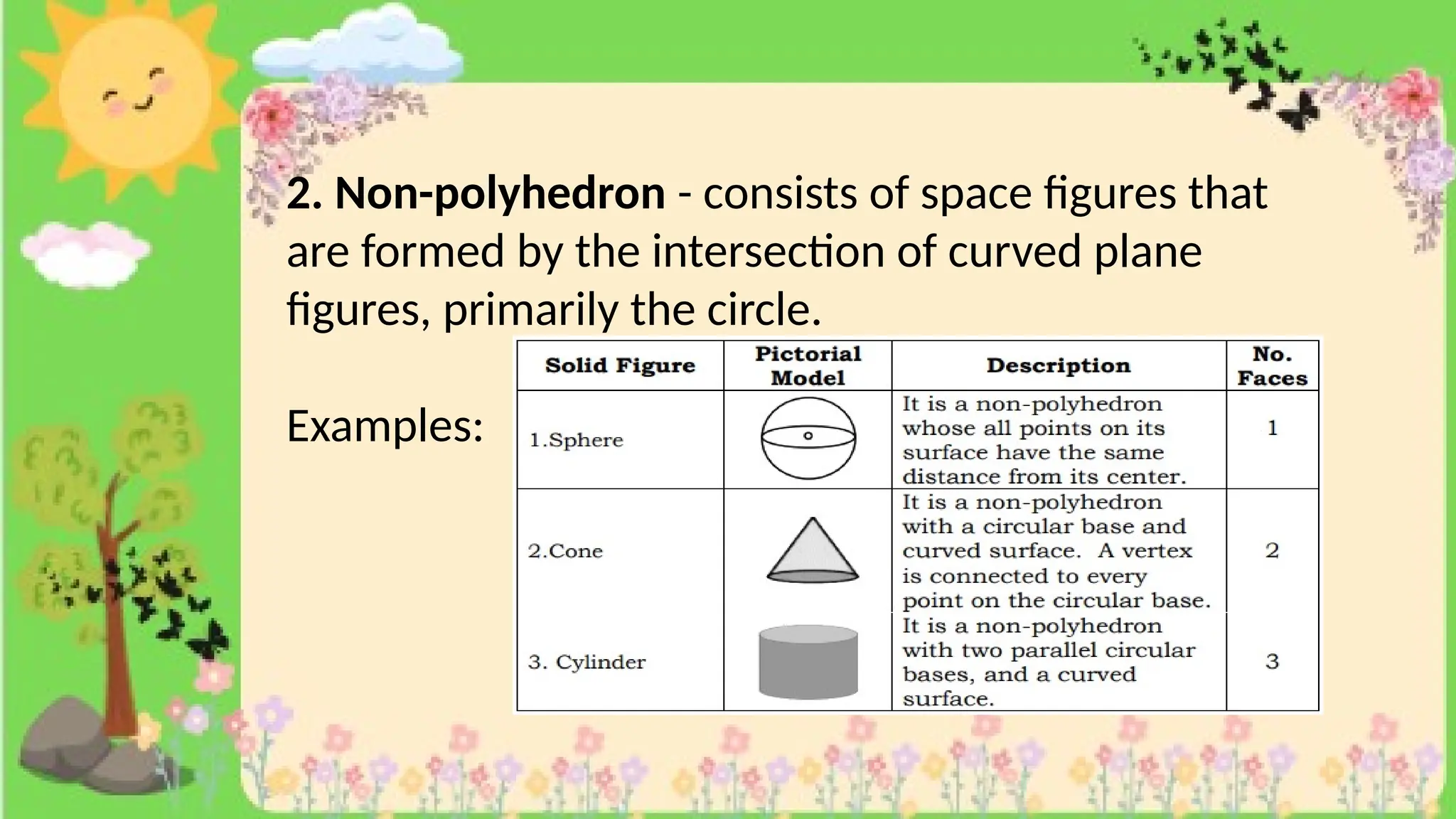
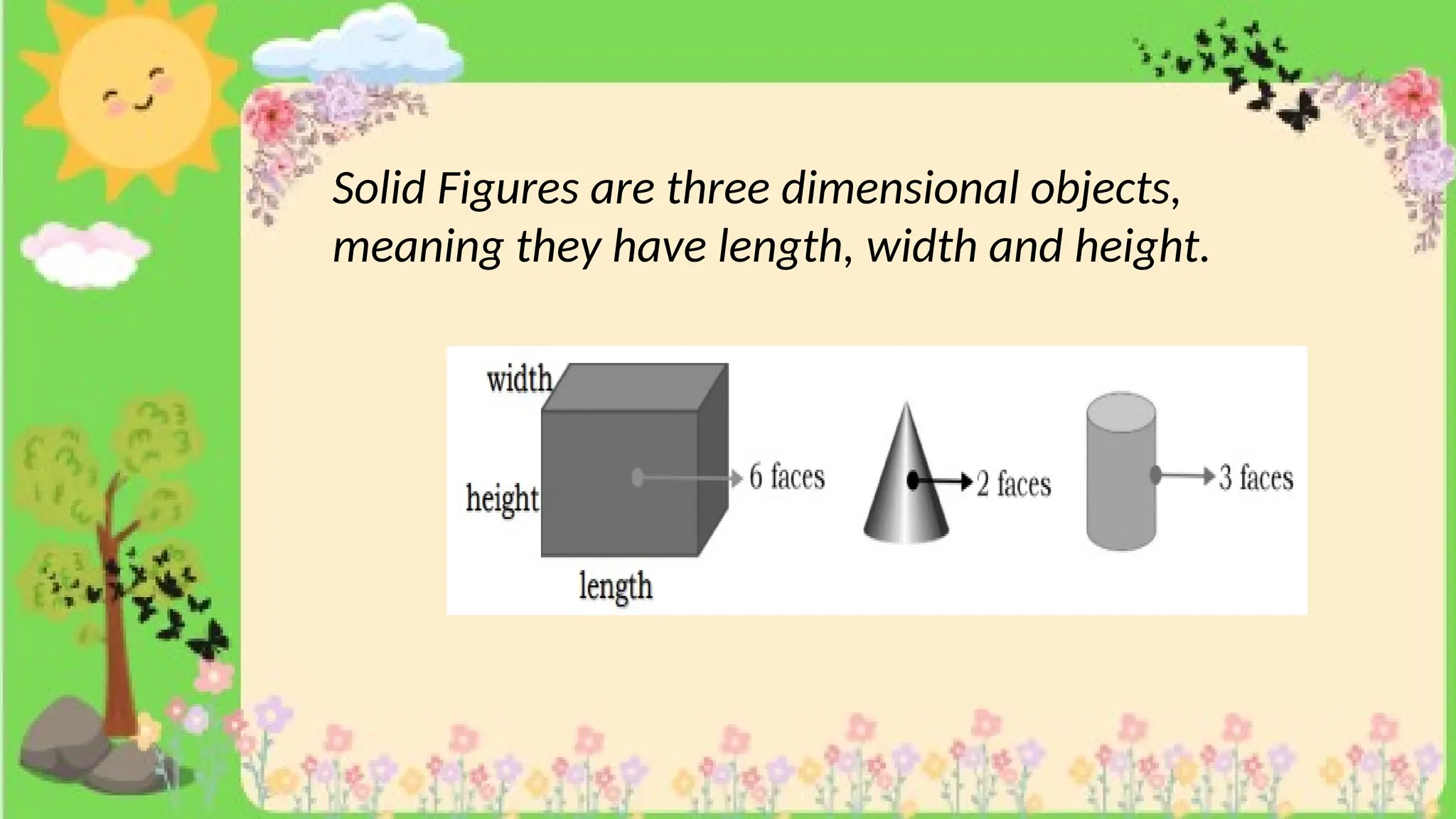
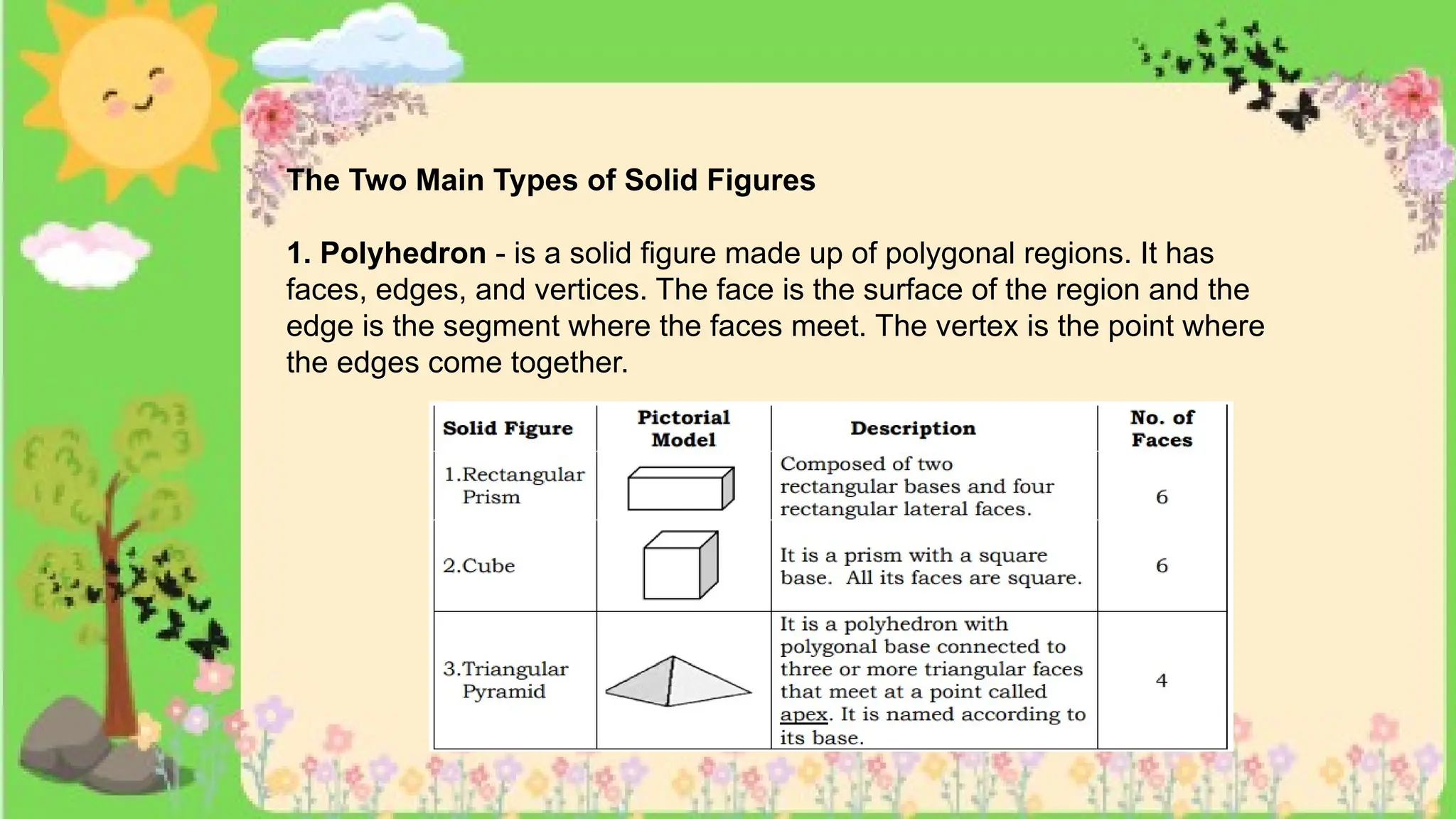
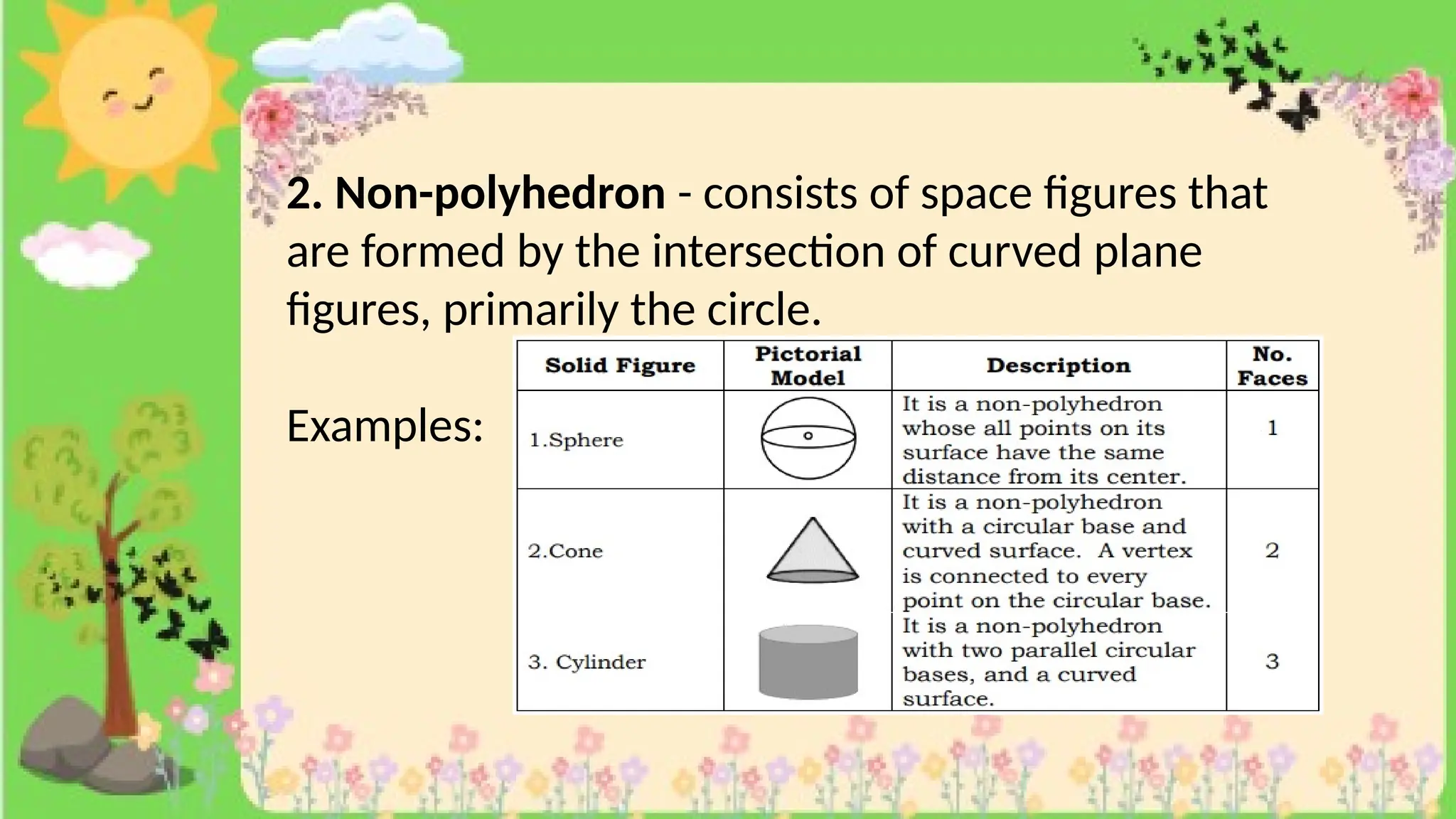
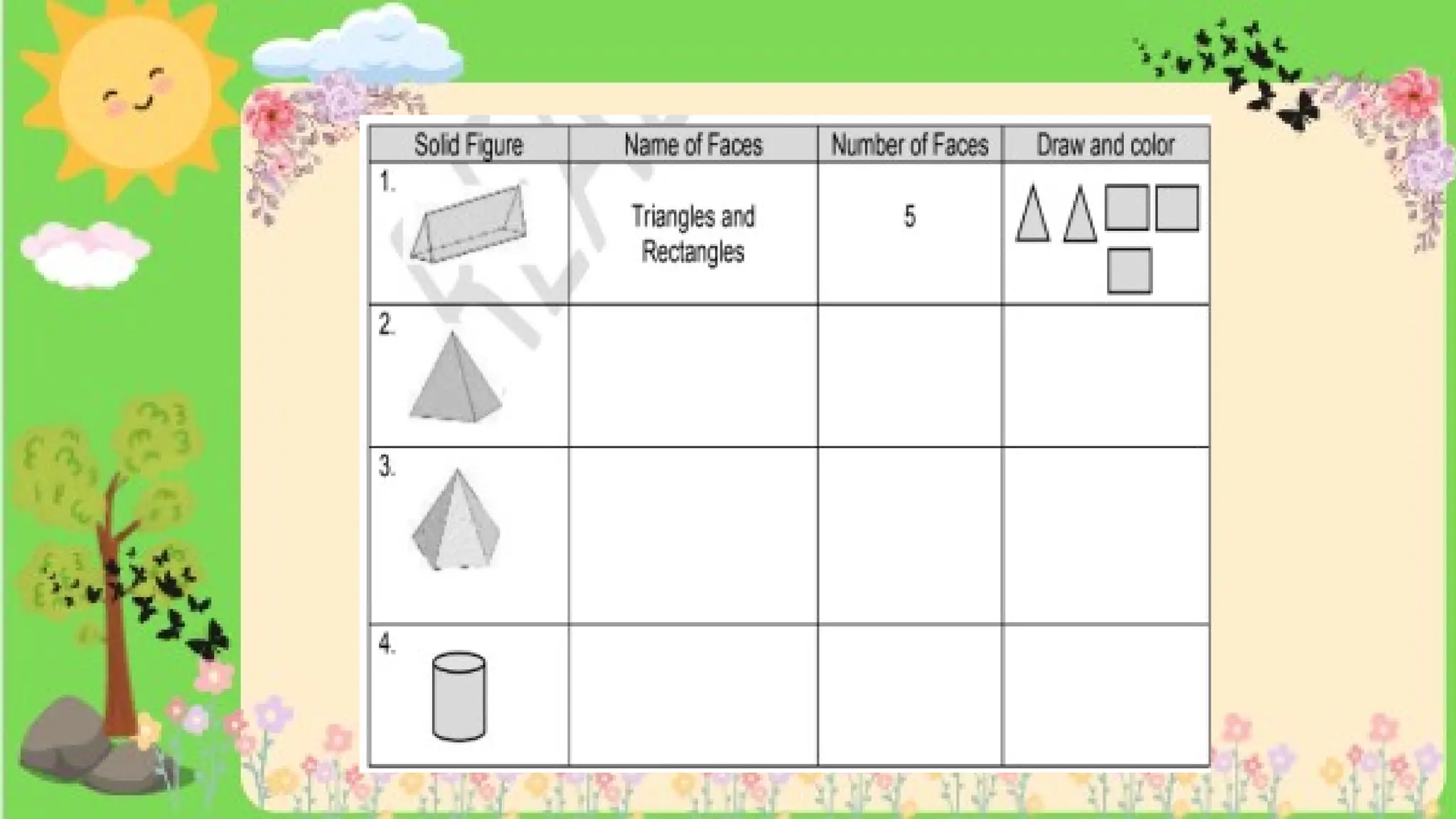
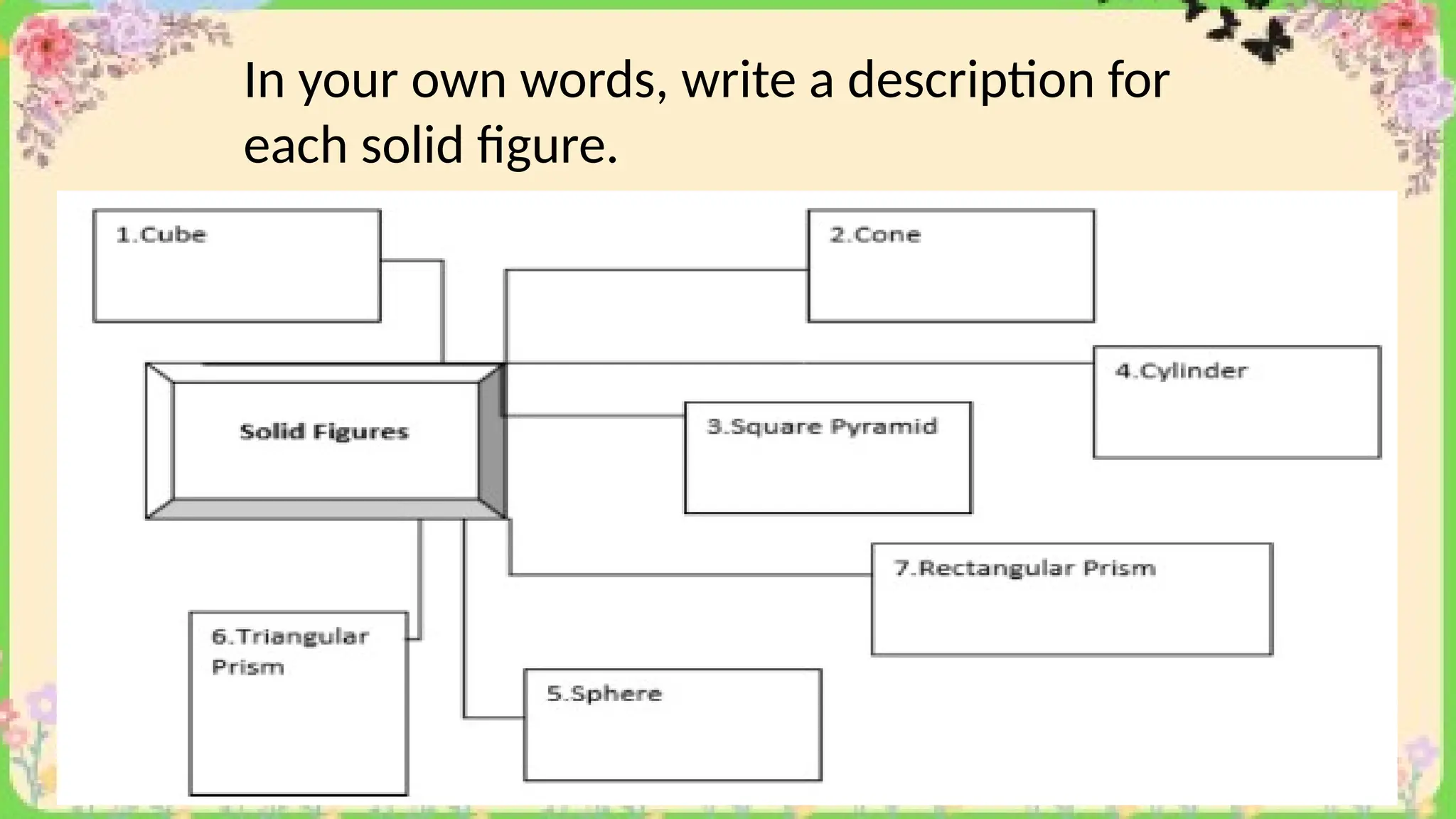
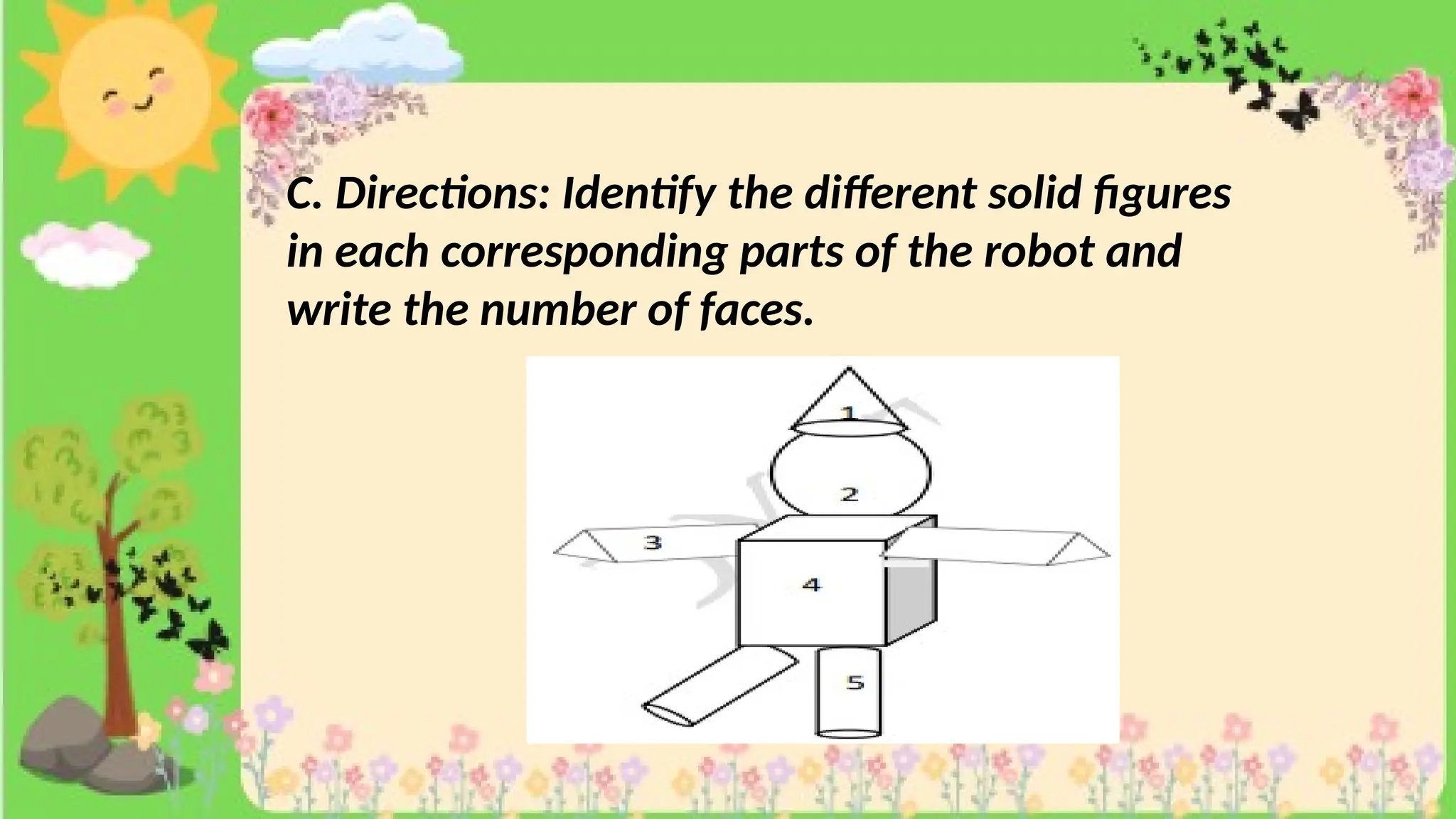
The document provides definitions and descriptions of various solid figures, including polyhedrons (such as cubes, prisms, and pyramids) and non-polyhedrons (like cylinders, cones, and spheres). It outlines characteristics such as faces, edges, and vertices, and distinguishes between two-dimensional (plane) and three-dimensional (solid) figures. Activities throughout the document encourage visualization, identification, and analysis of these geometric shapes.