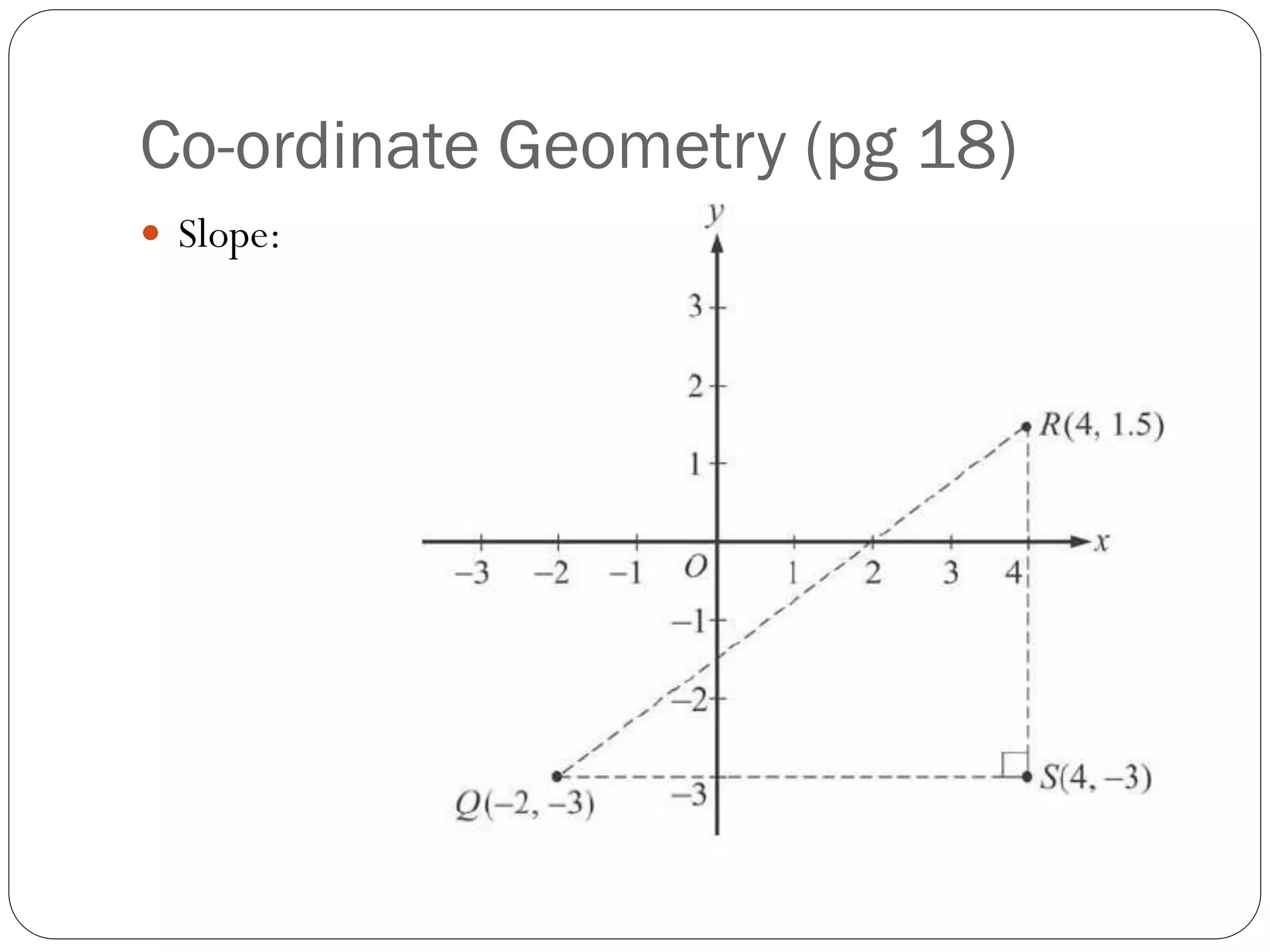
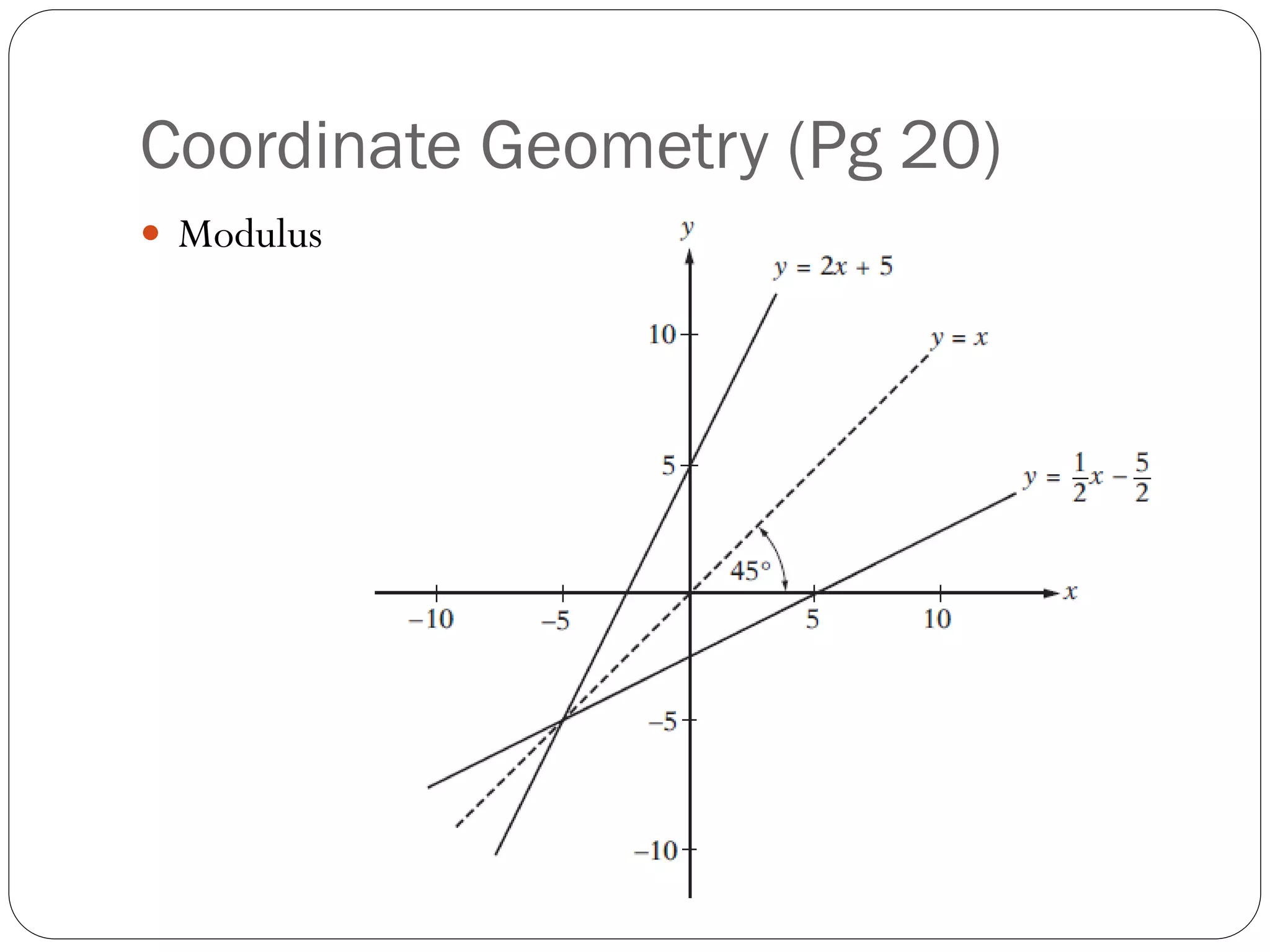
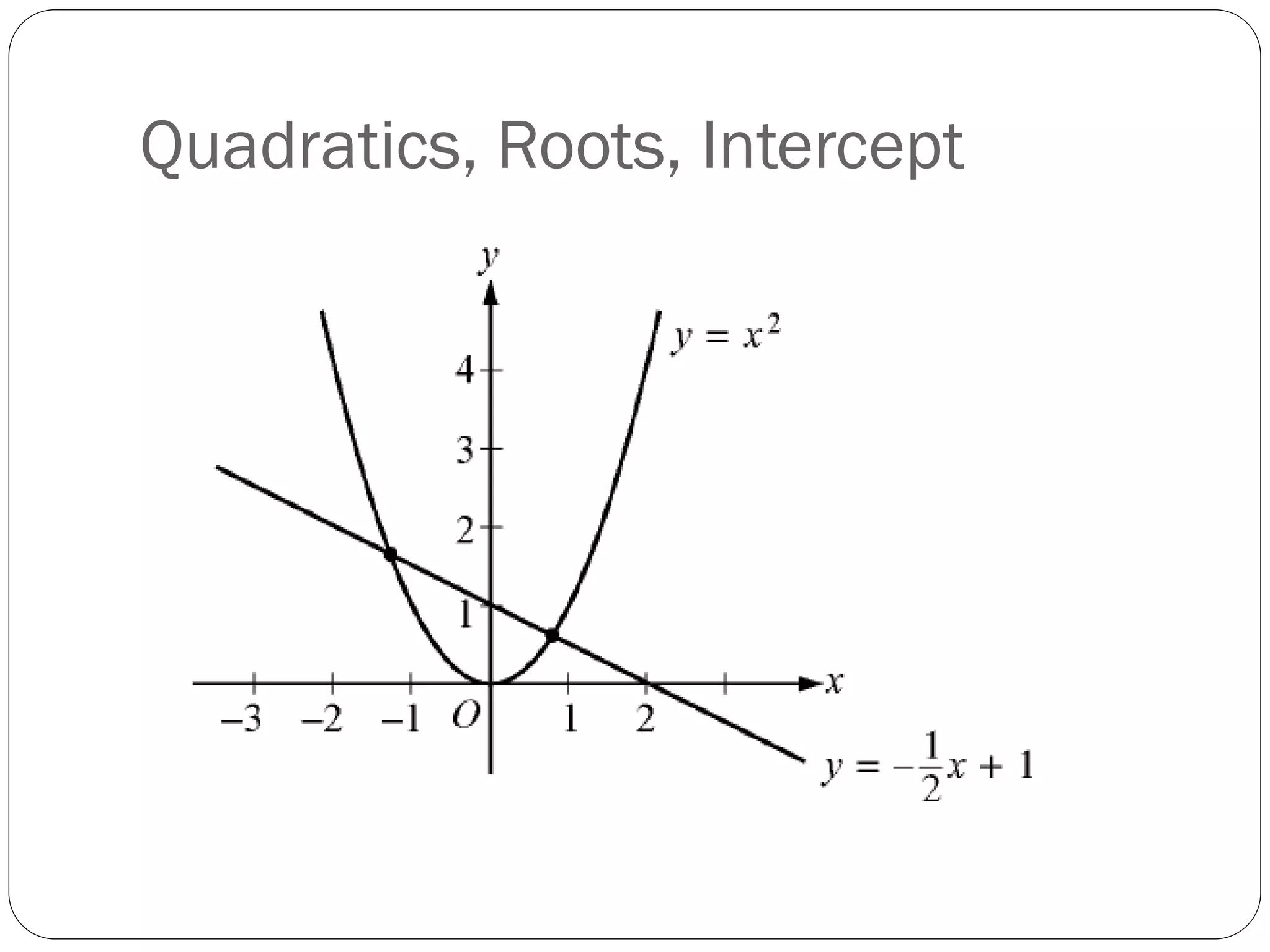
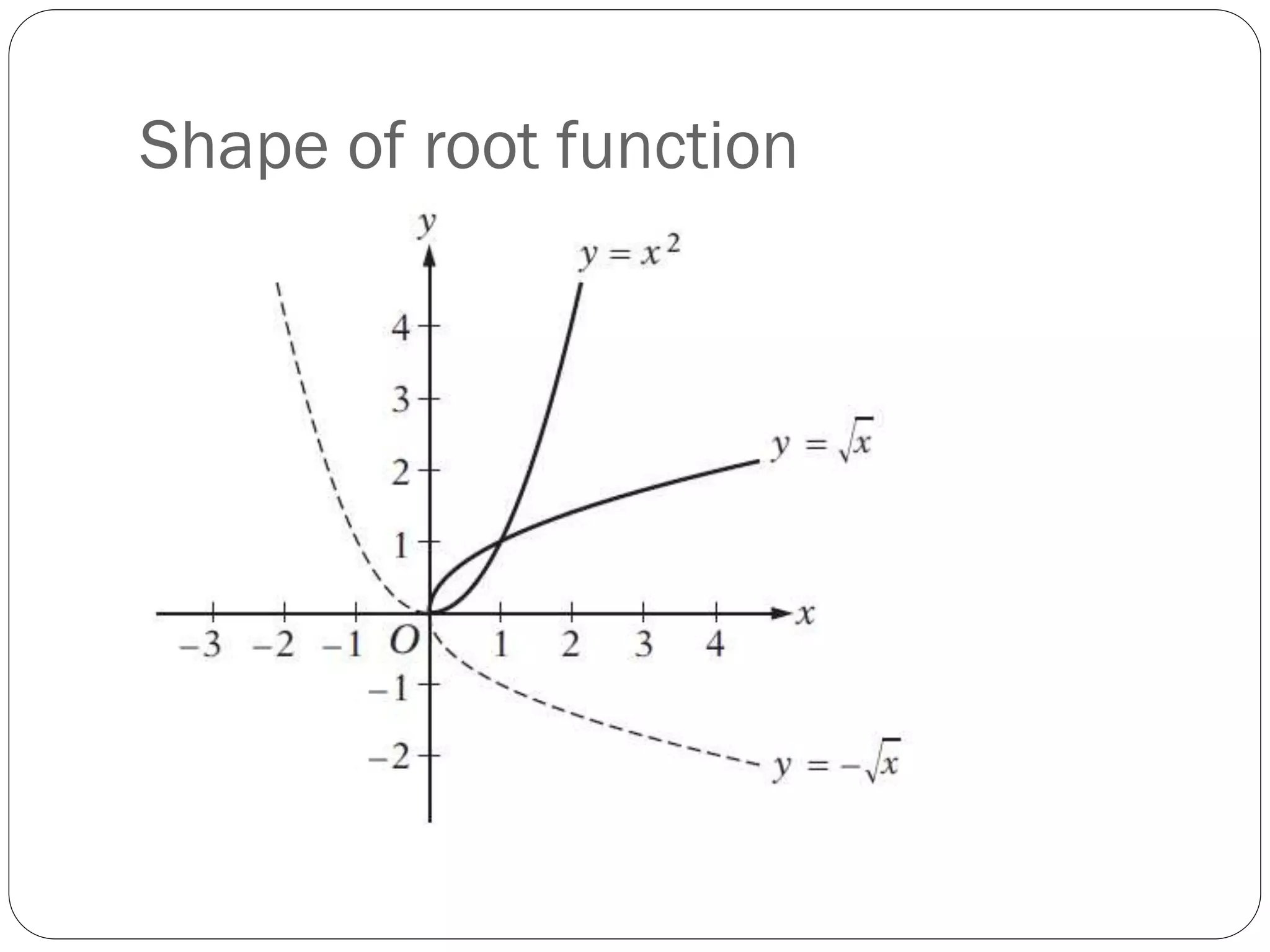
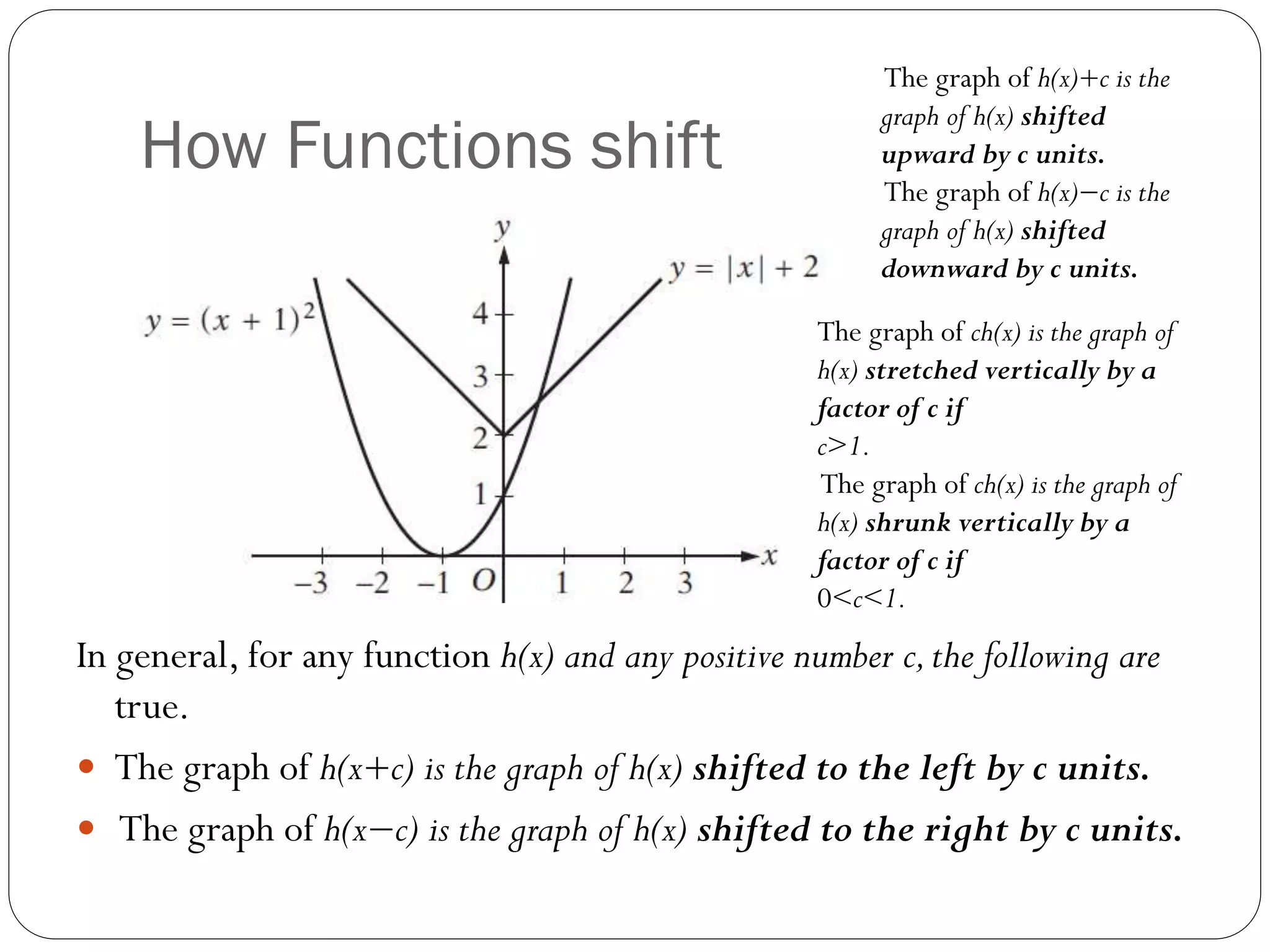
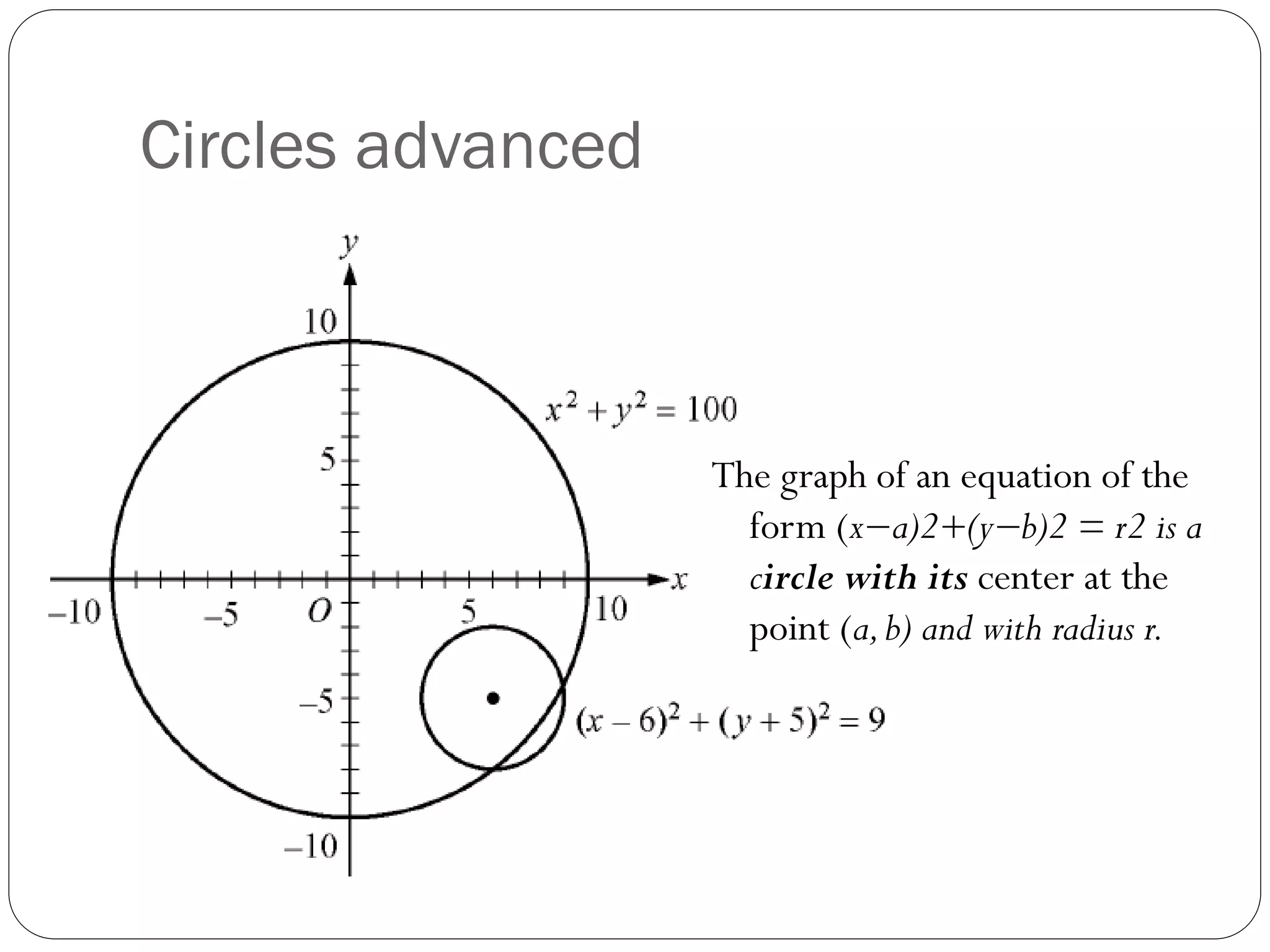
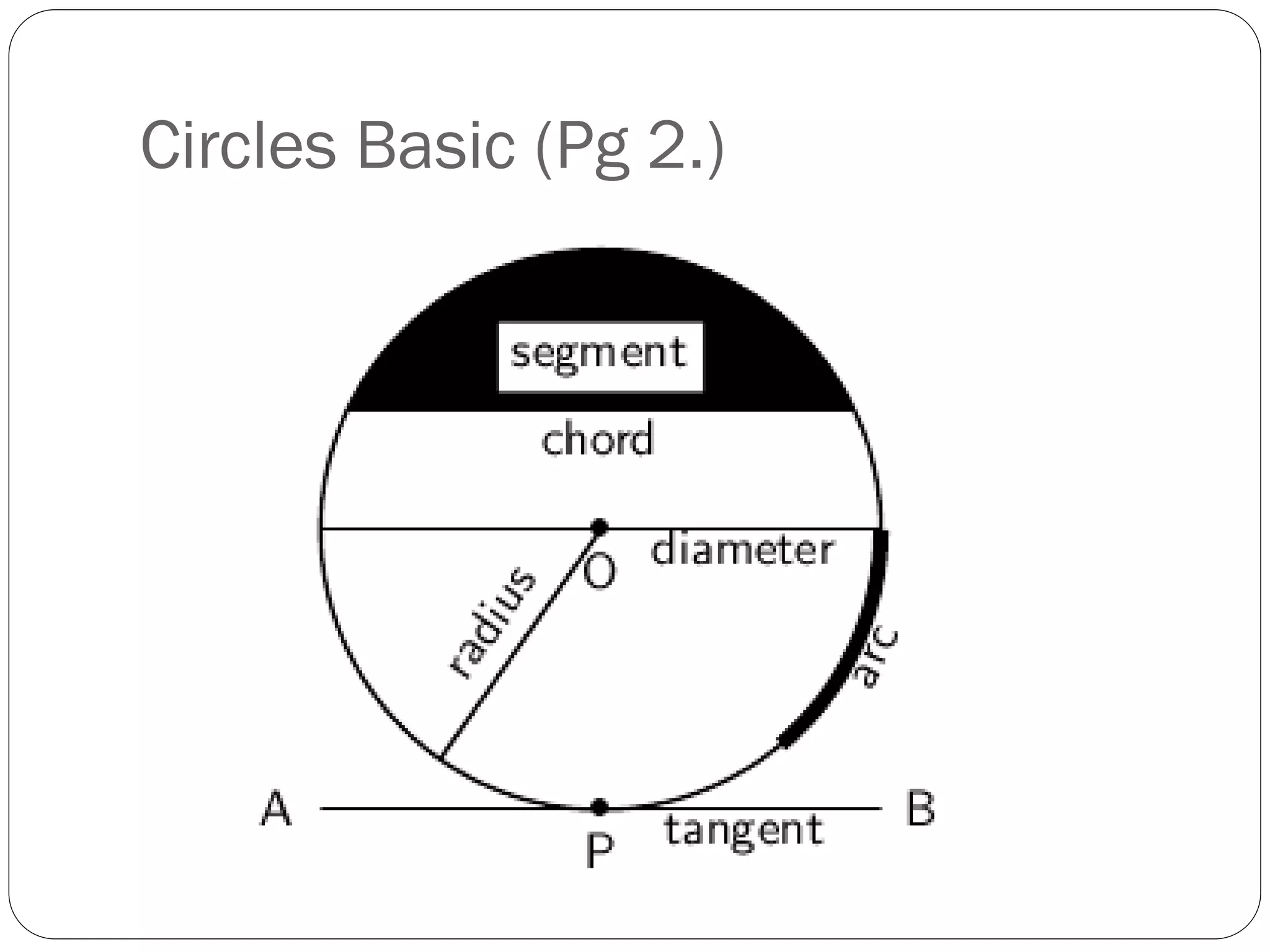
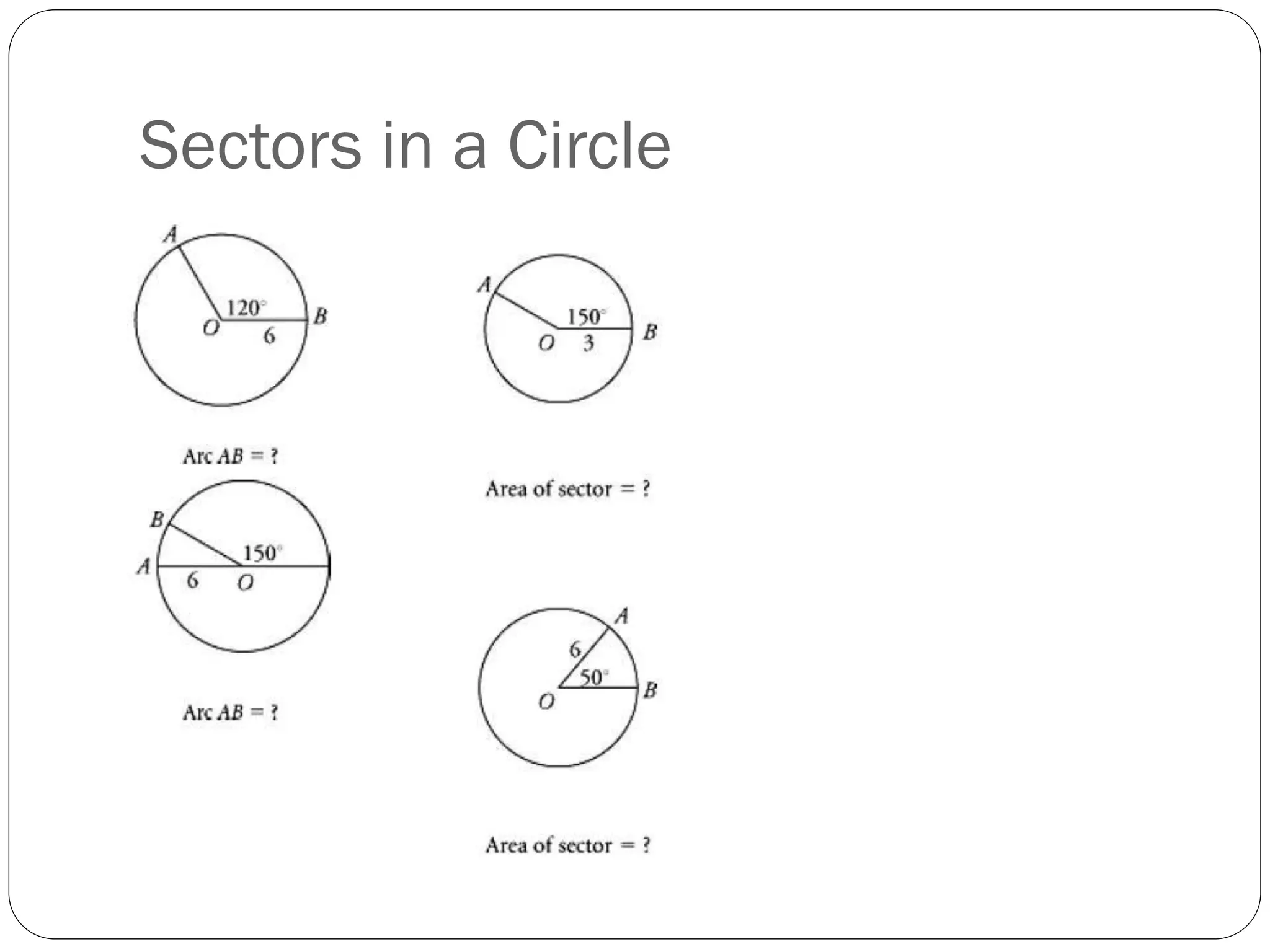
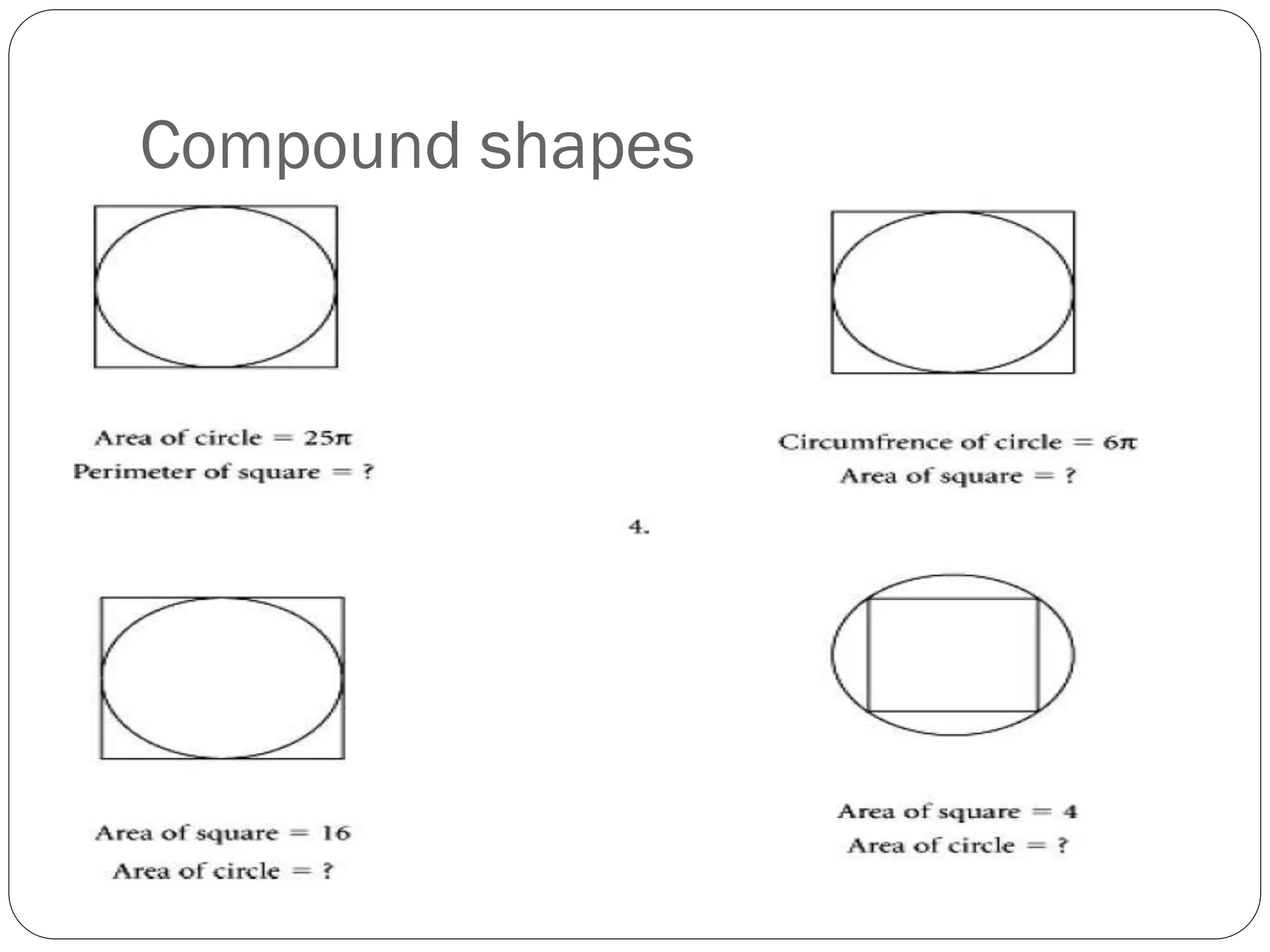
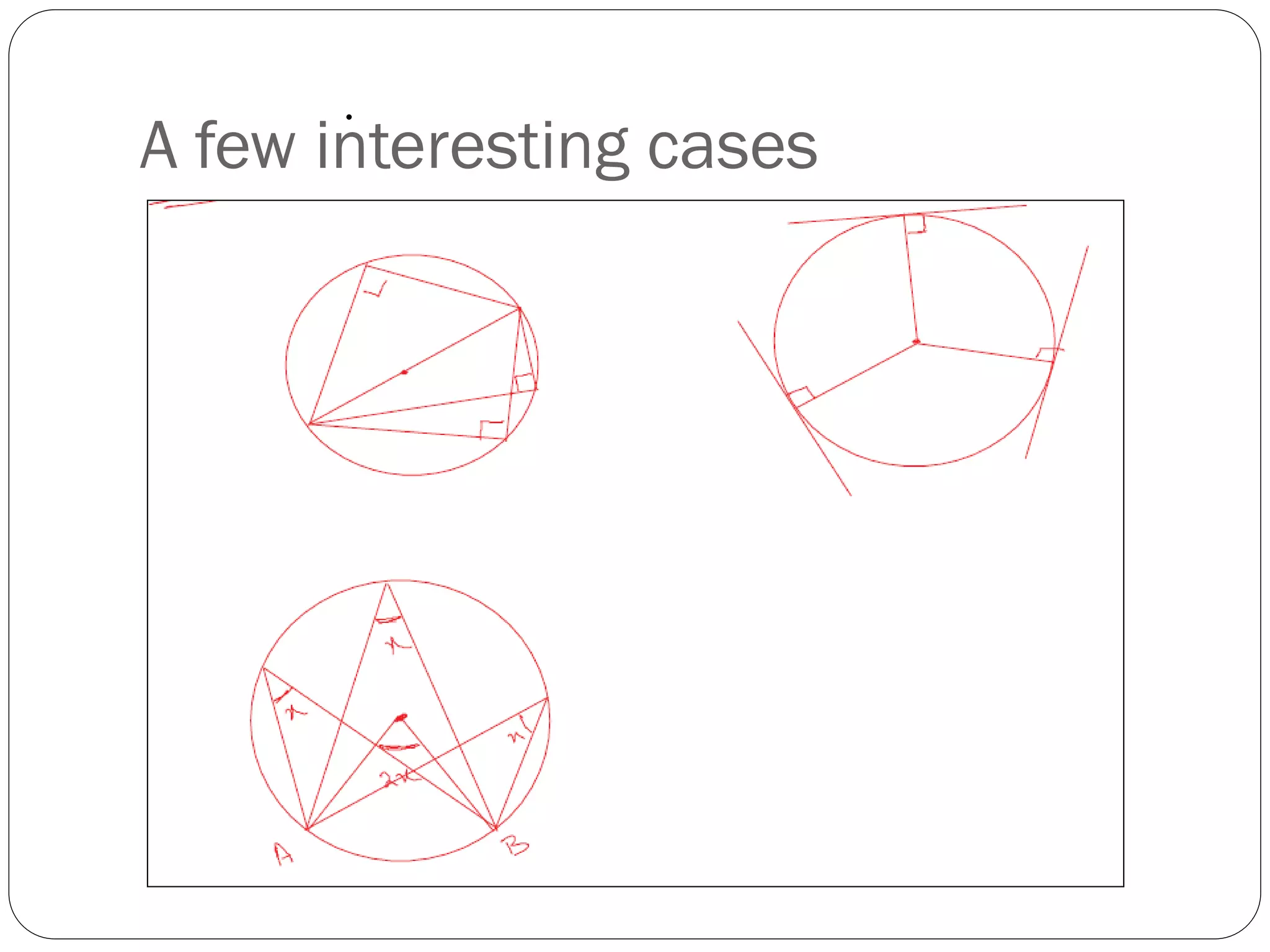
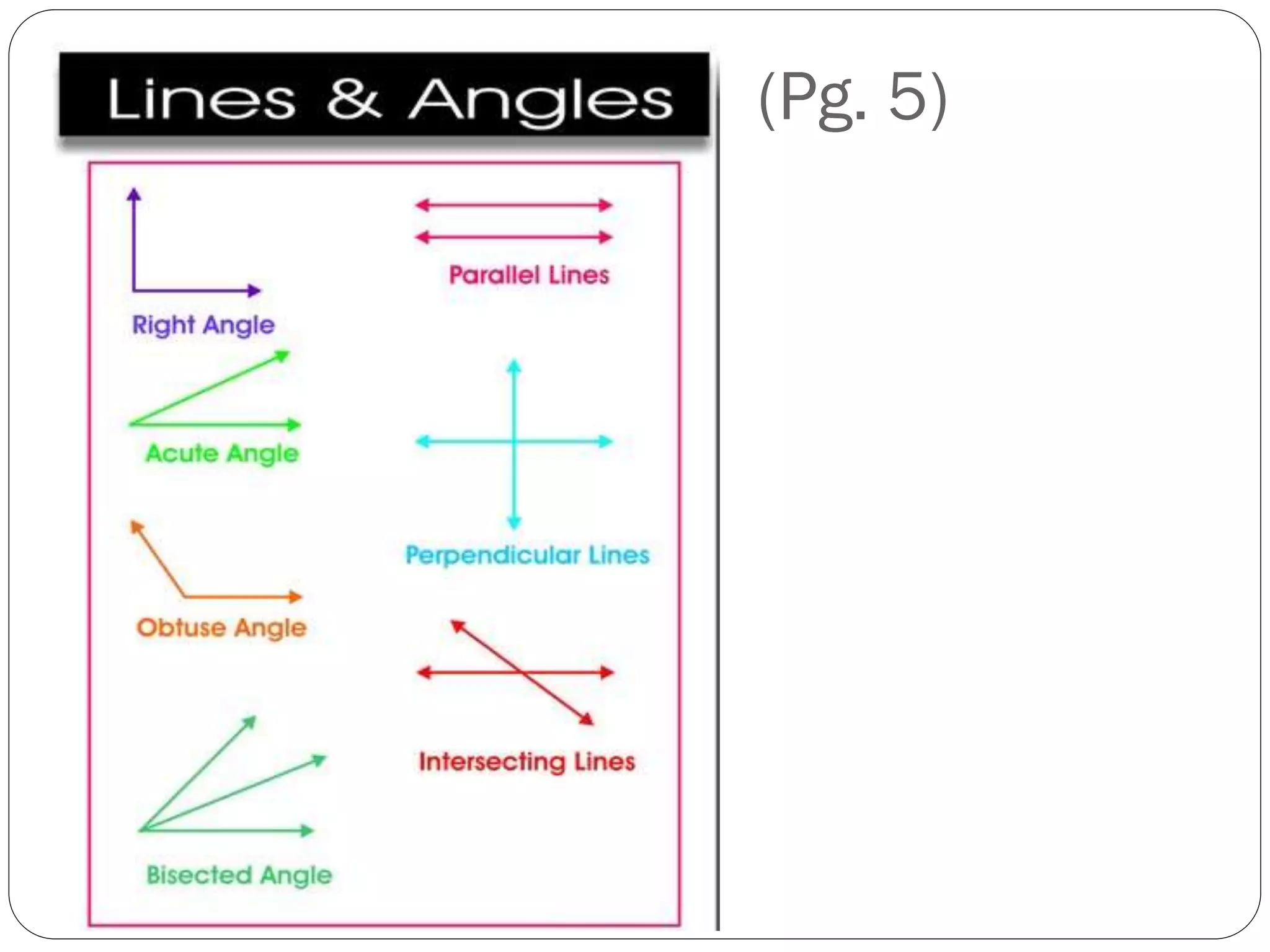
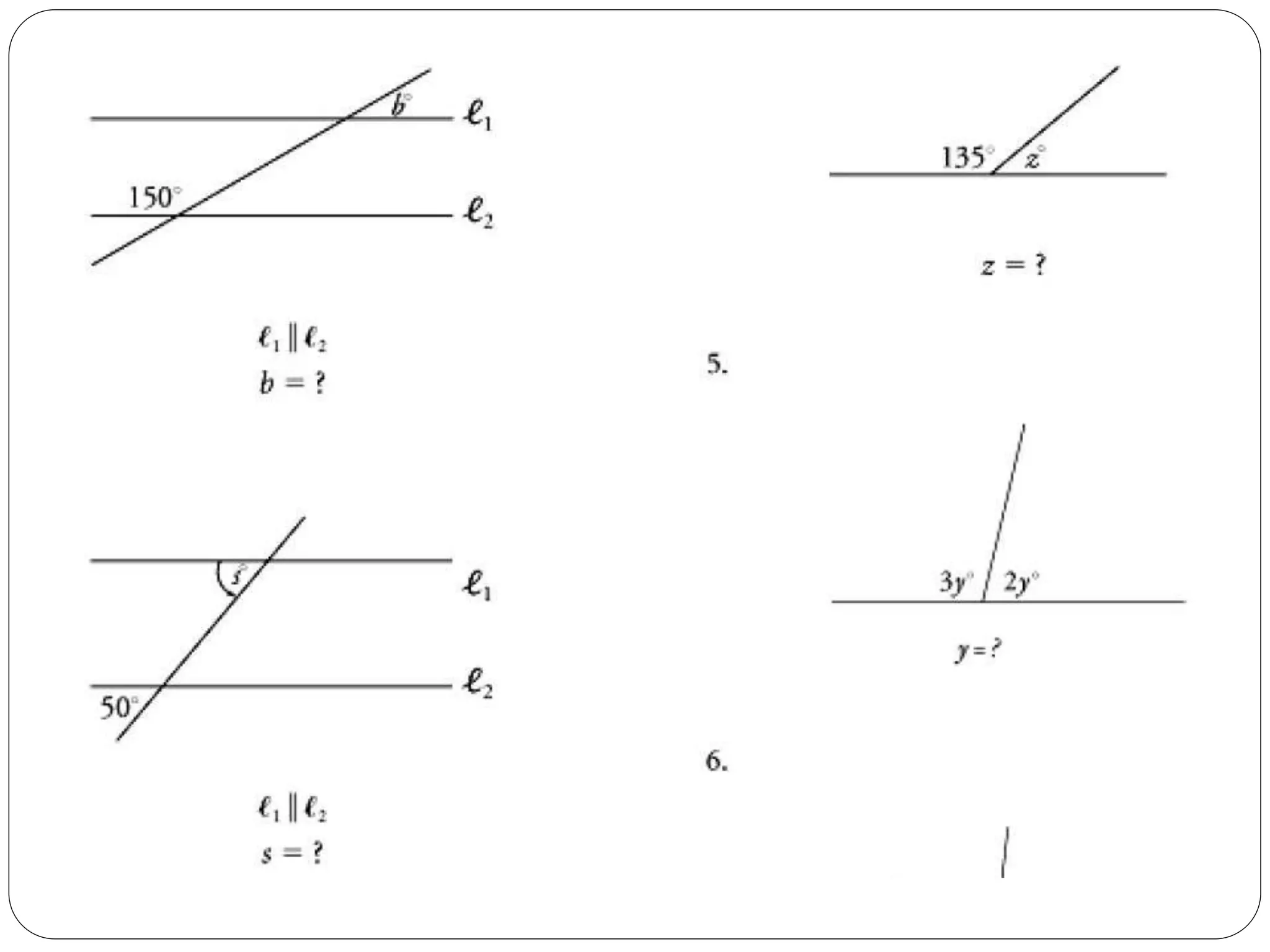
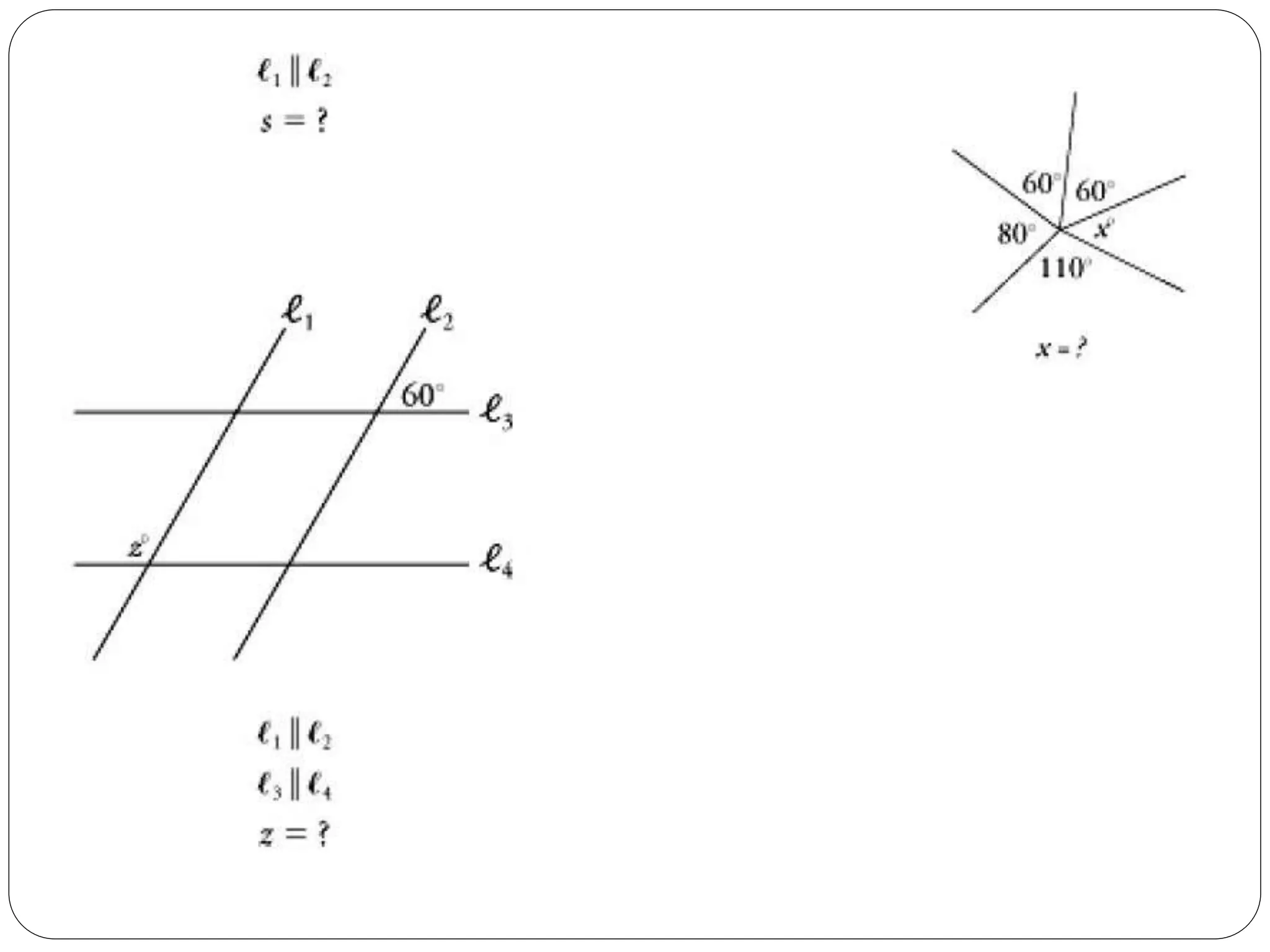
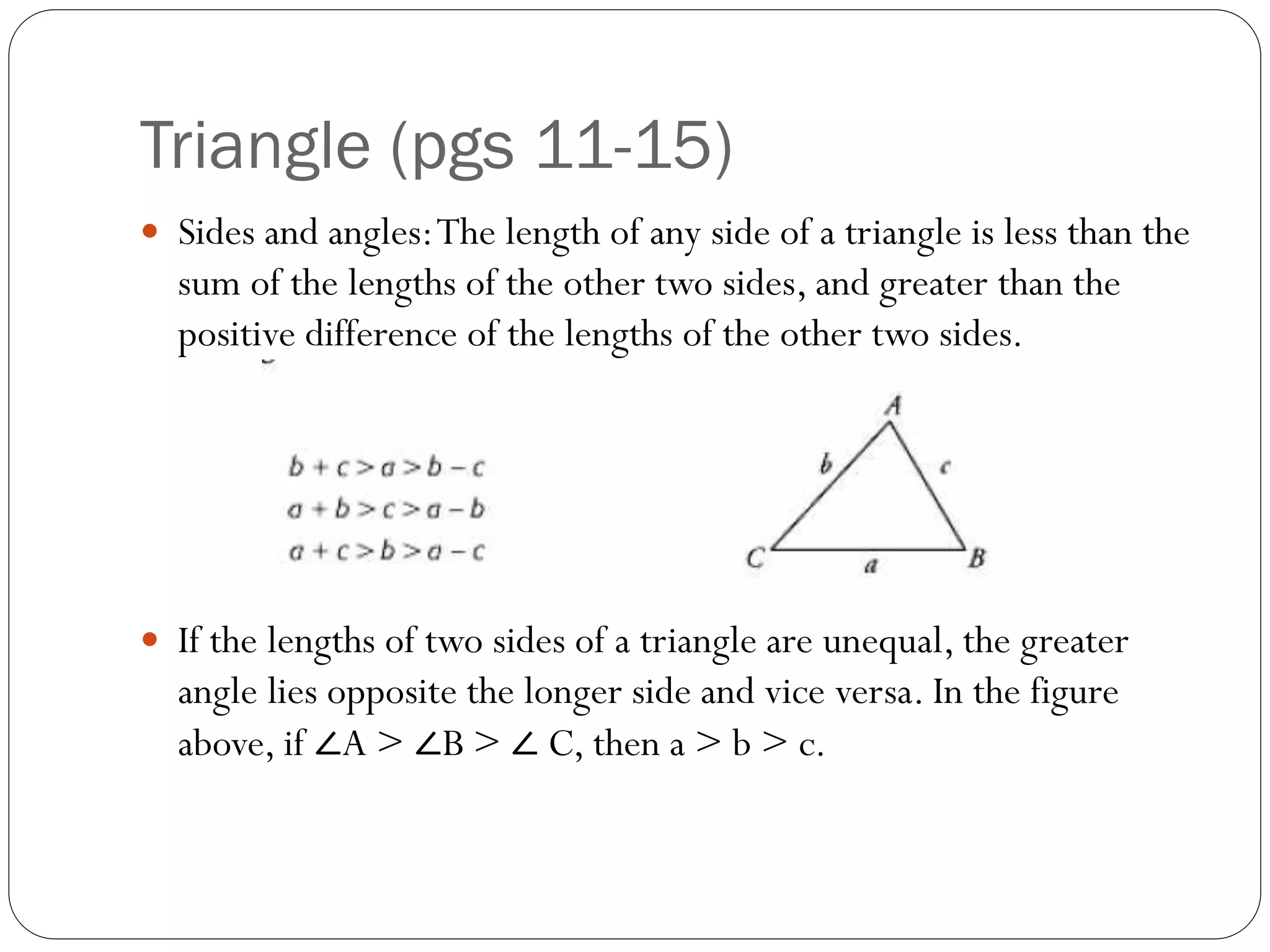
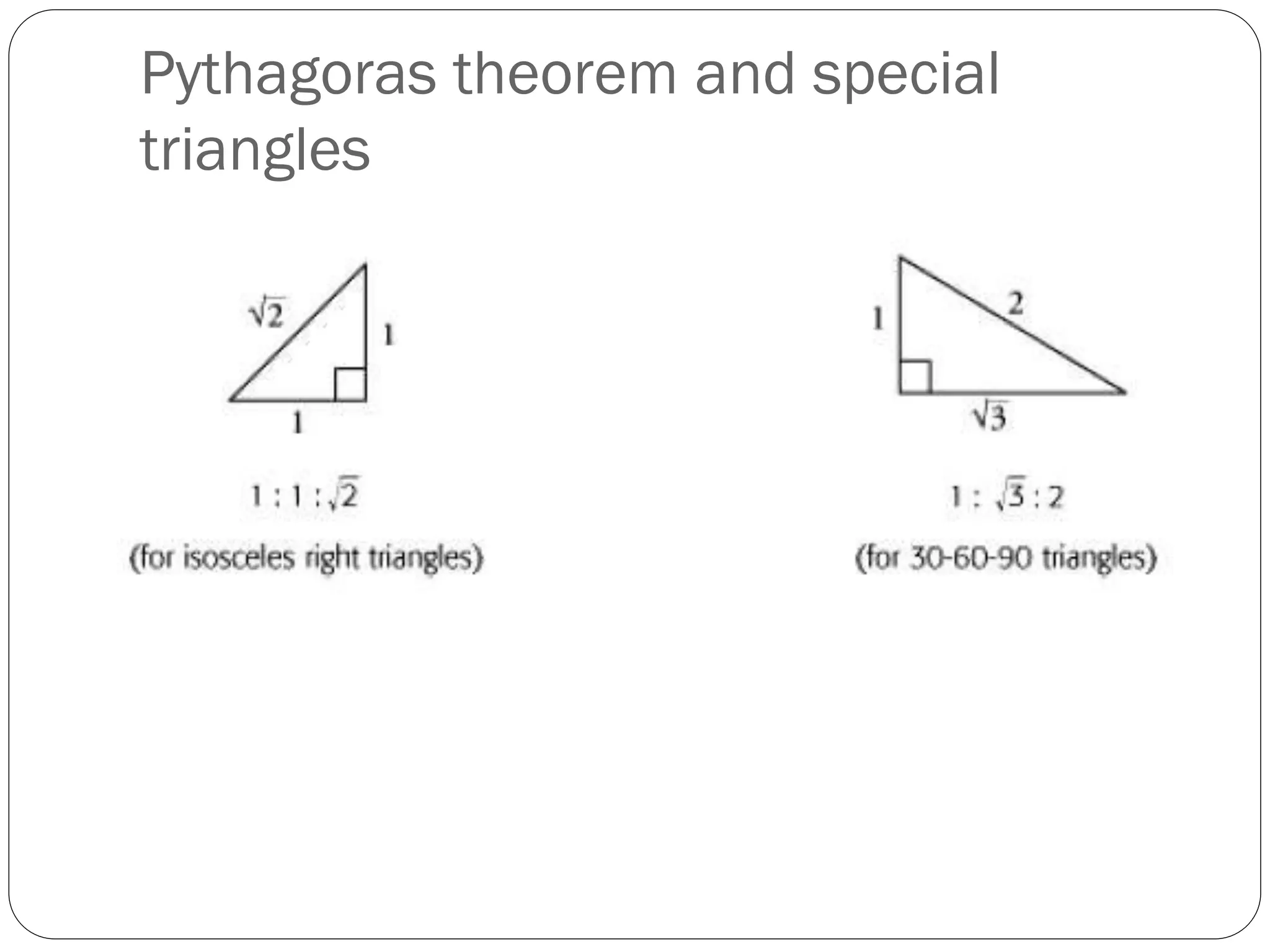
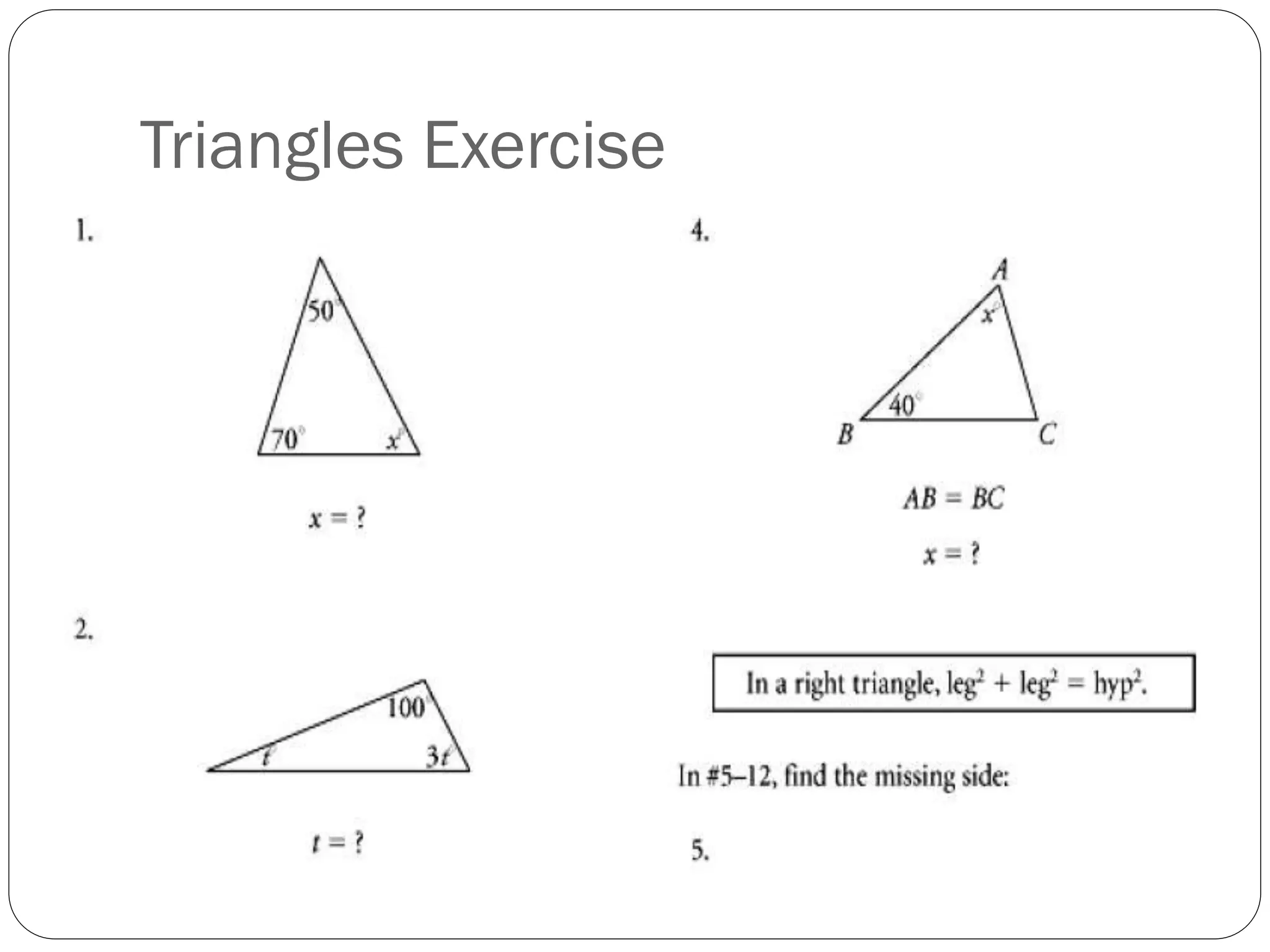
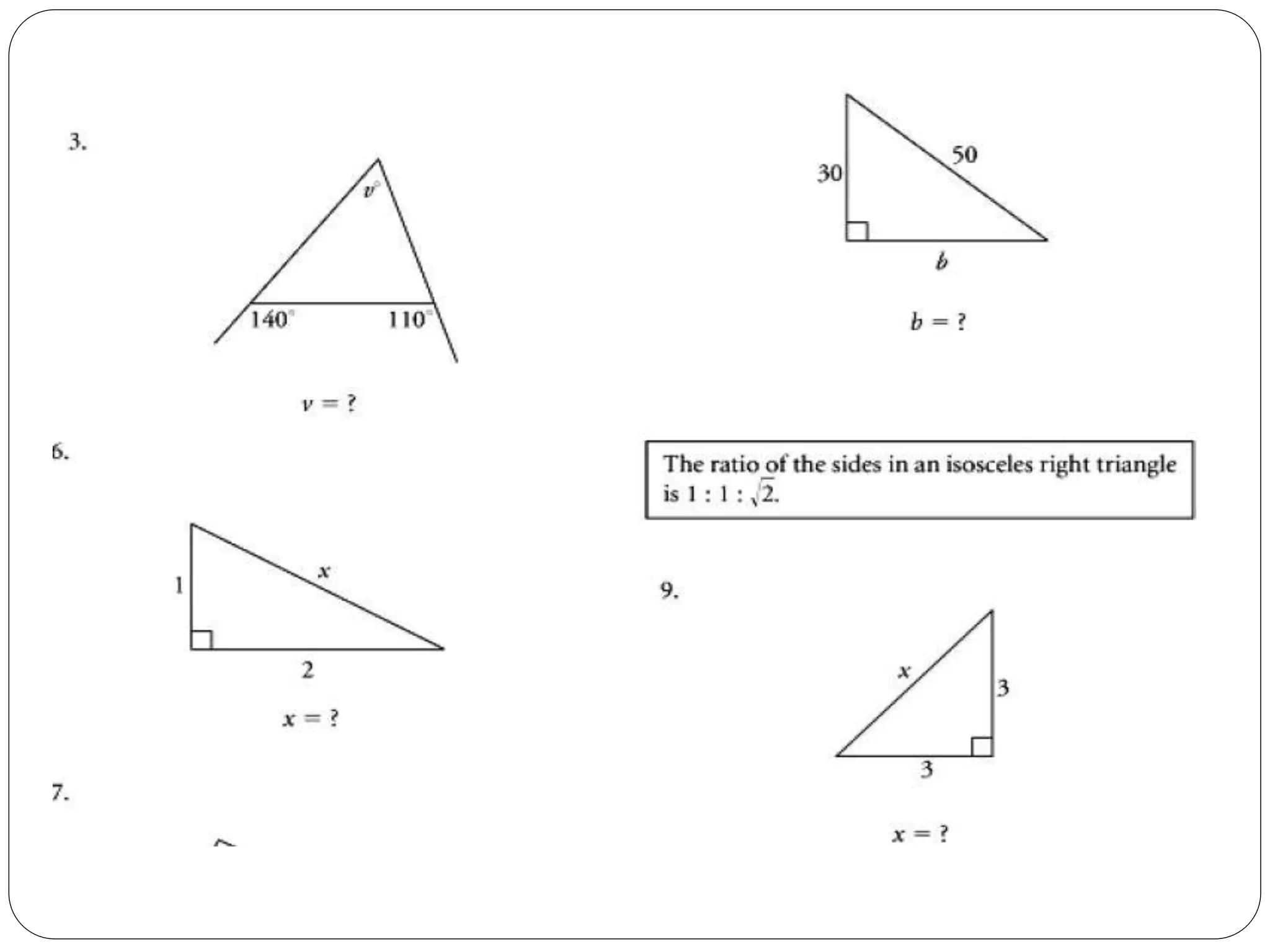
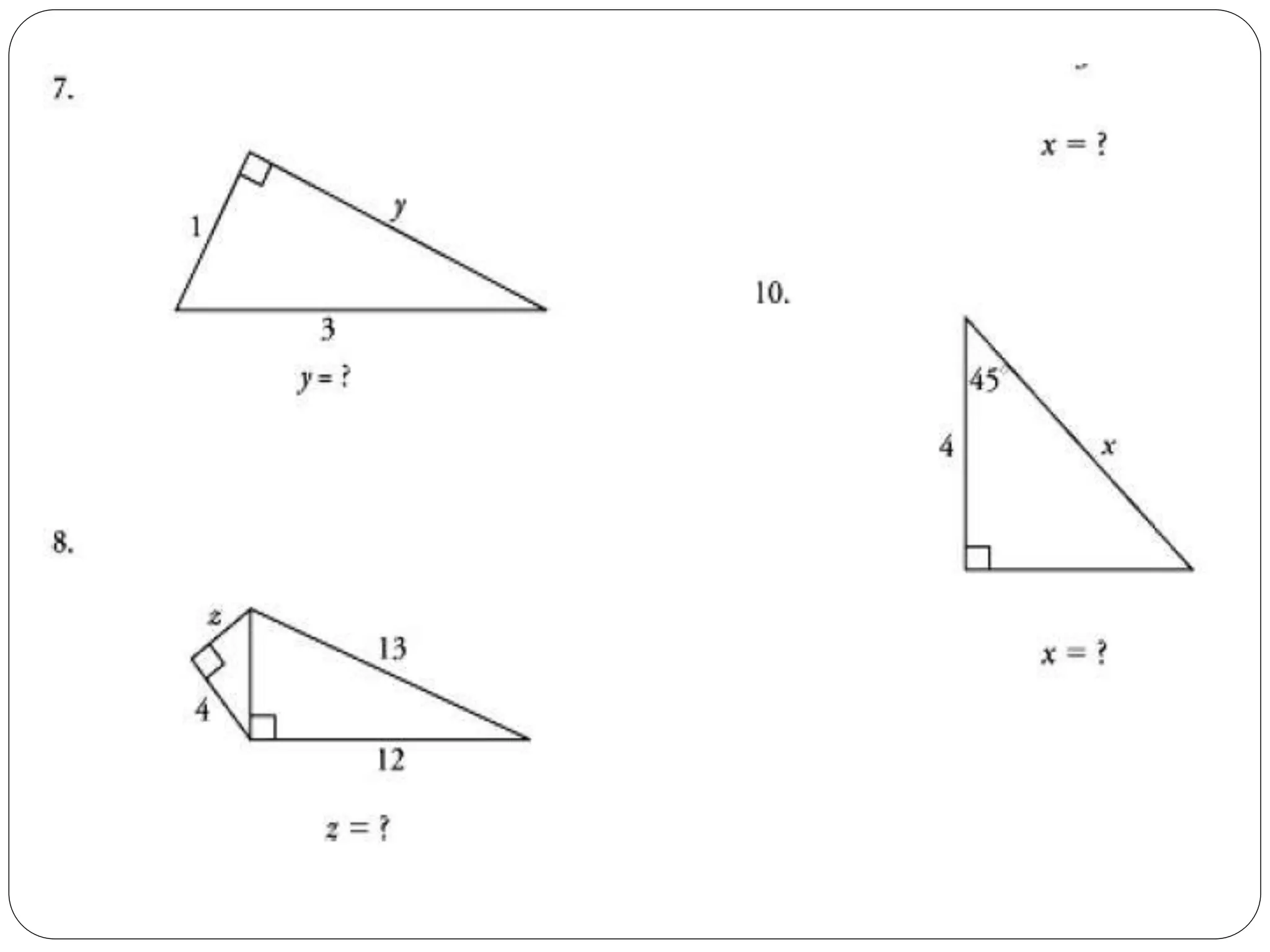
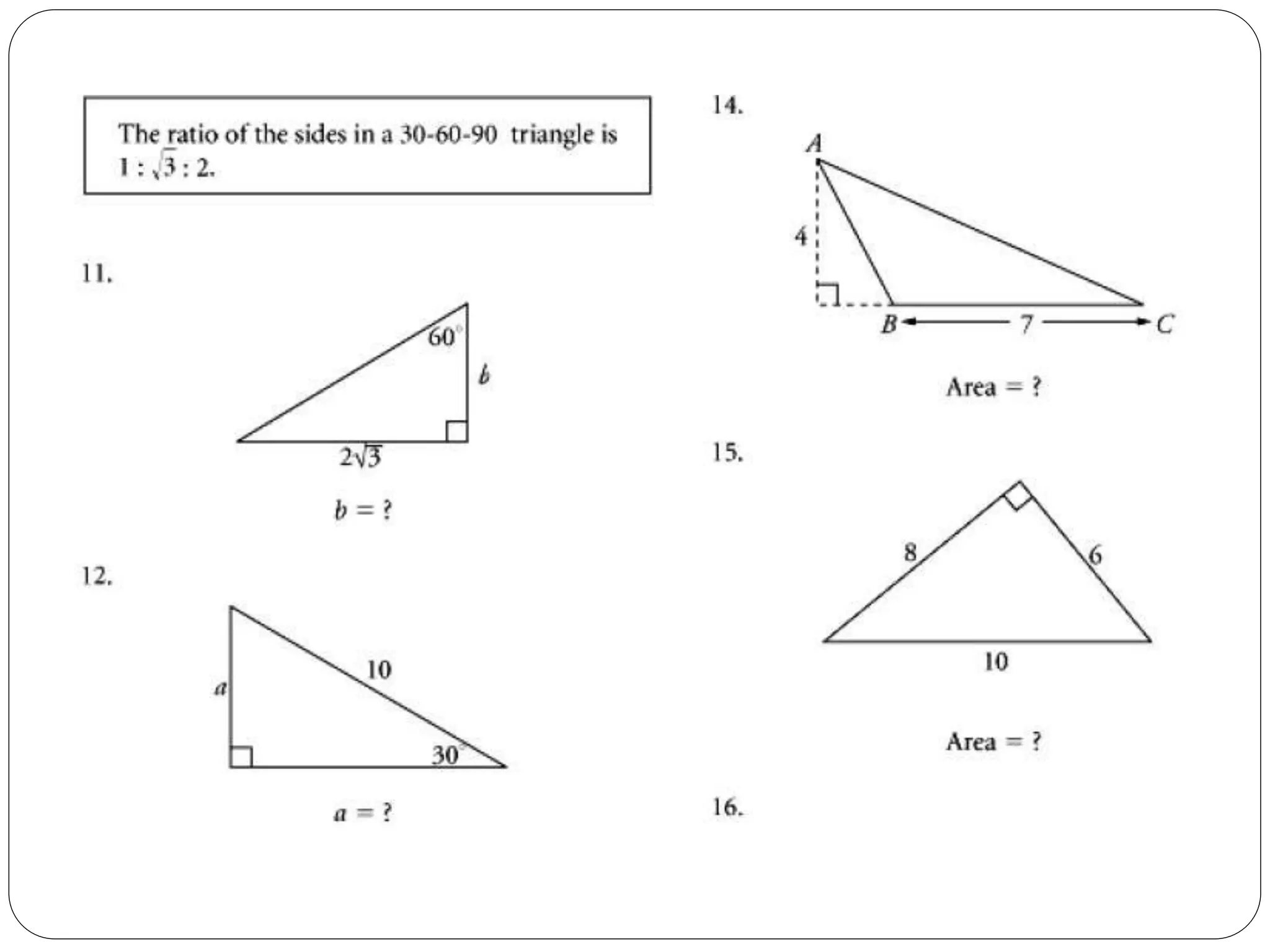
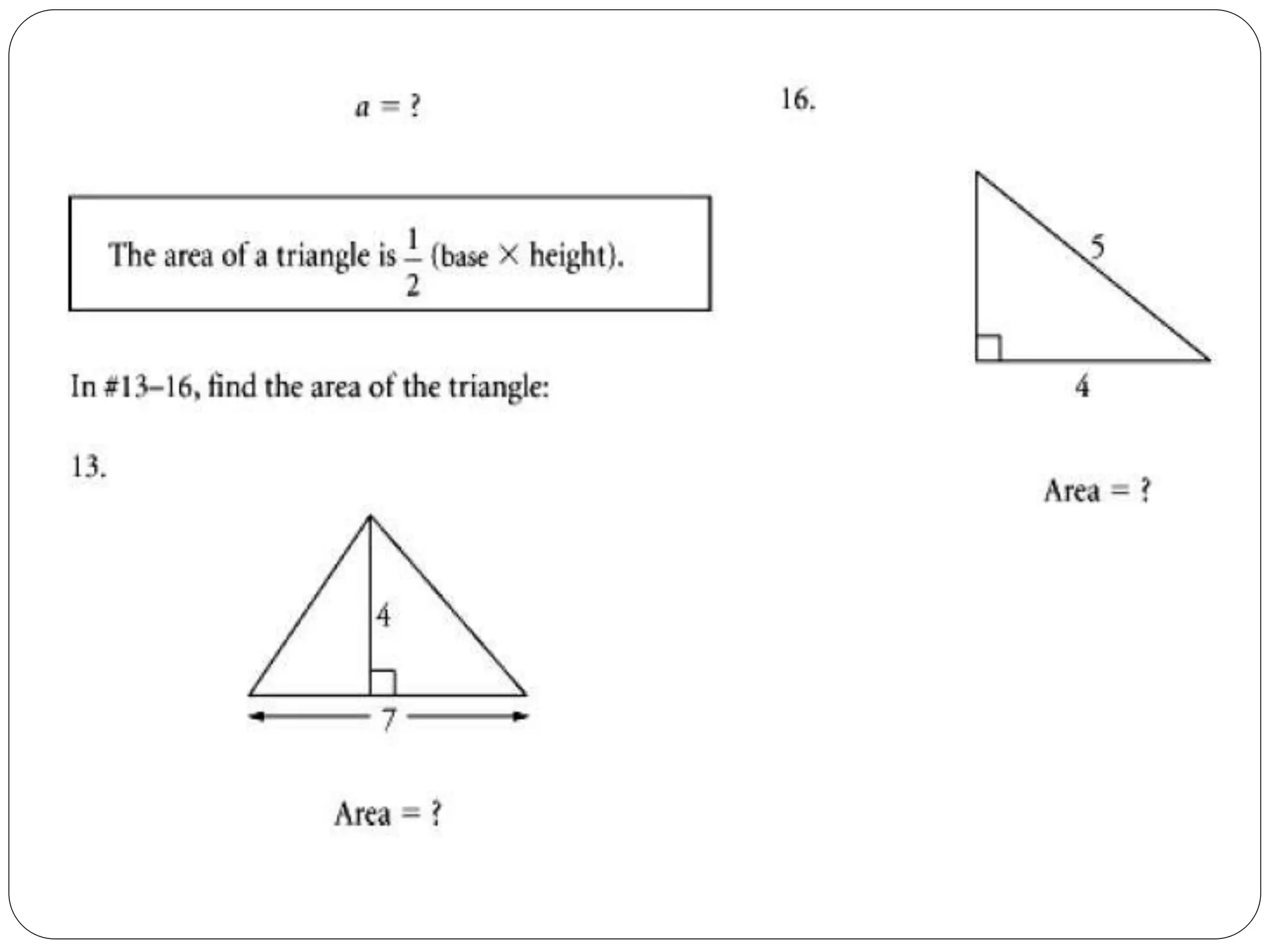
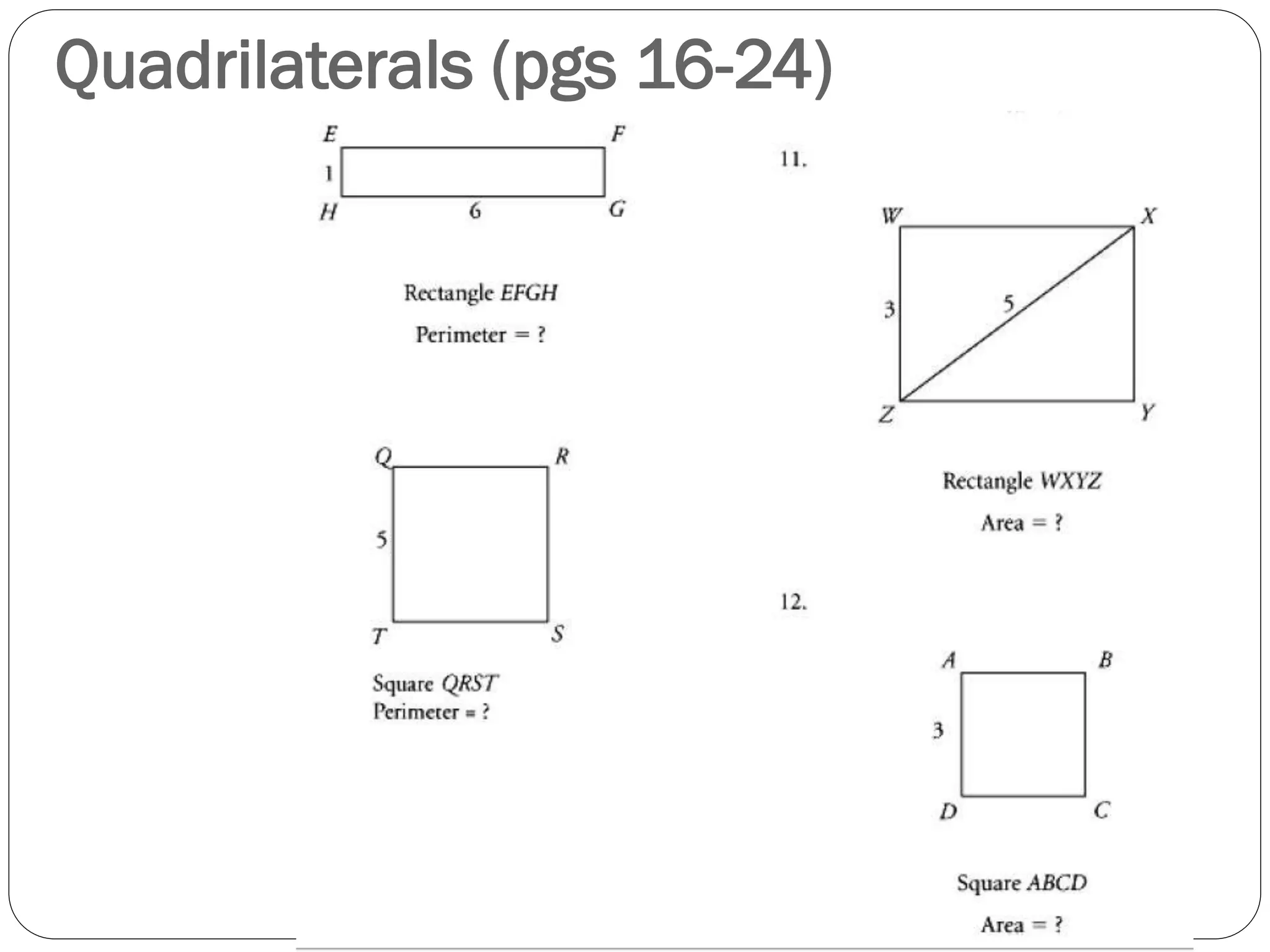
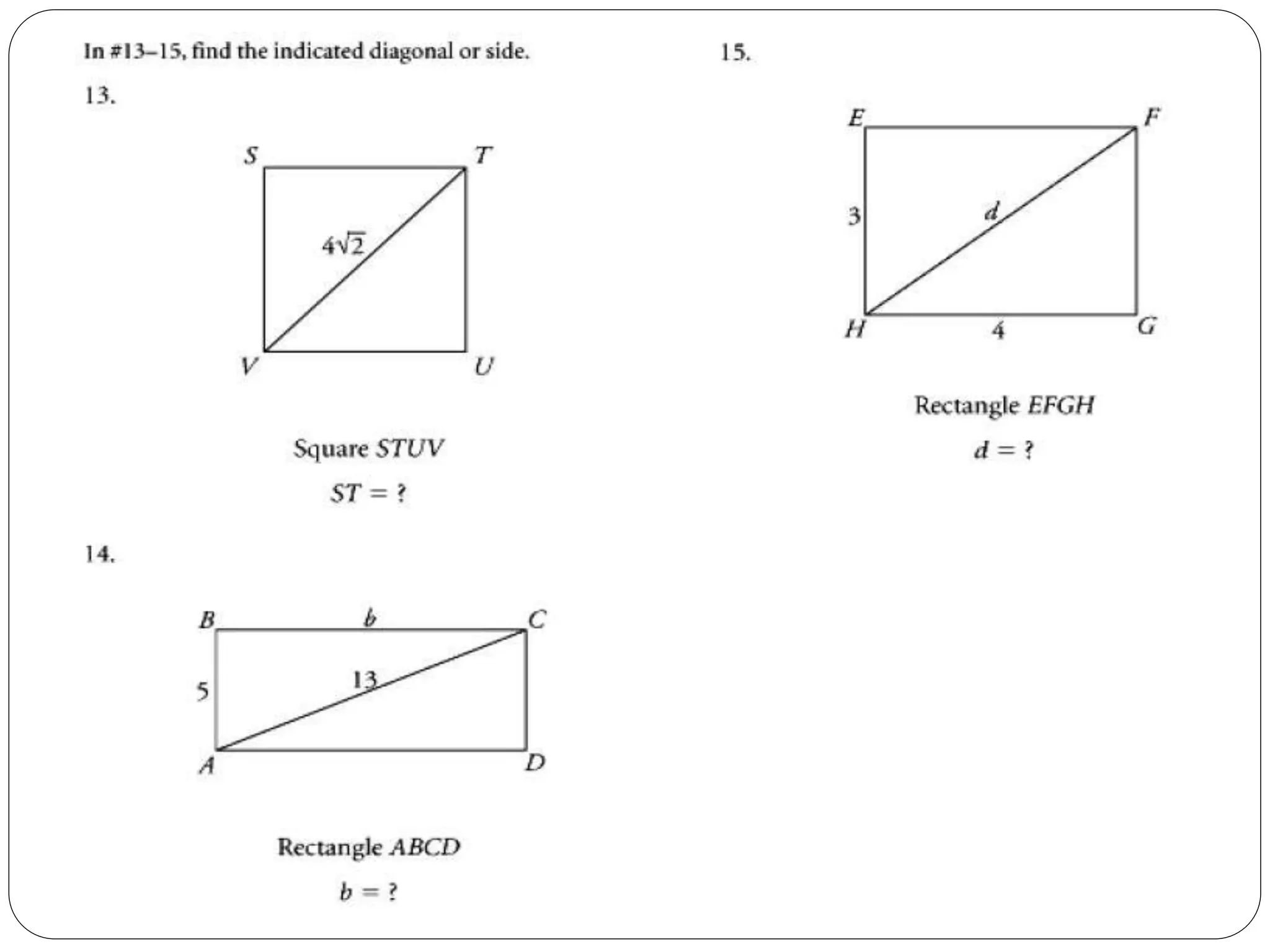
This document provides an agenda for a geometry review session. It begins with a brief review of algebra concepts like identities, linear equations, quadratics, exponents, and inequalities. The bulk of the document then outlines the geometry concepts to be covered, including coordinate geometry, graphing functions, circles, lines and angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, and solids. Circle topics include finding areas and circumferences, as well as sectors. Triangle topics include side and angle properties, the Pythagorean theorem, and special right triangles. Solids problems involve calculating volumes and surface areas.