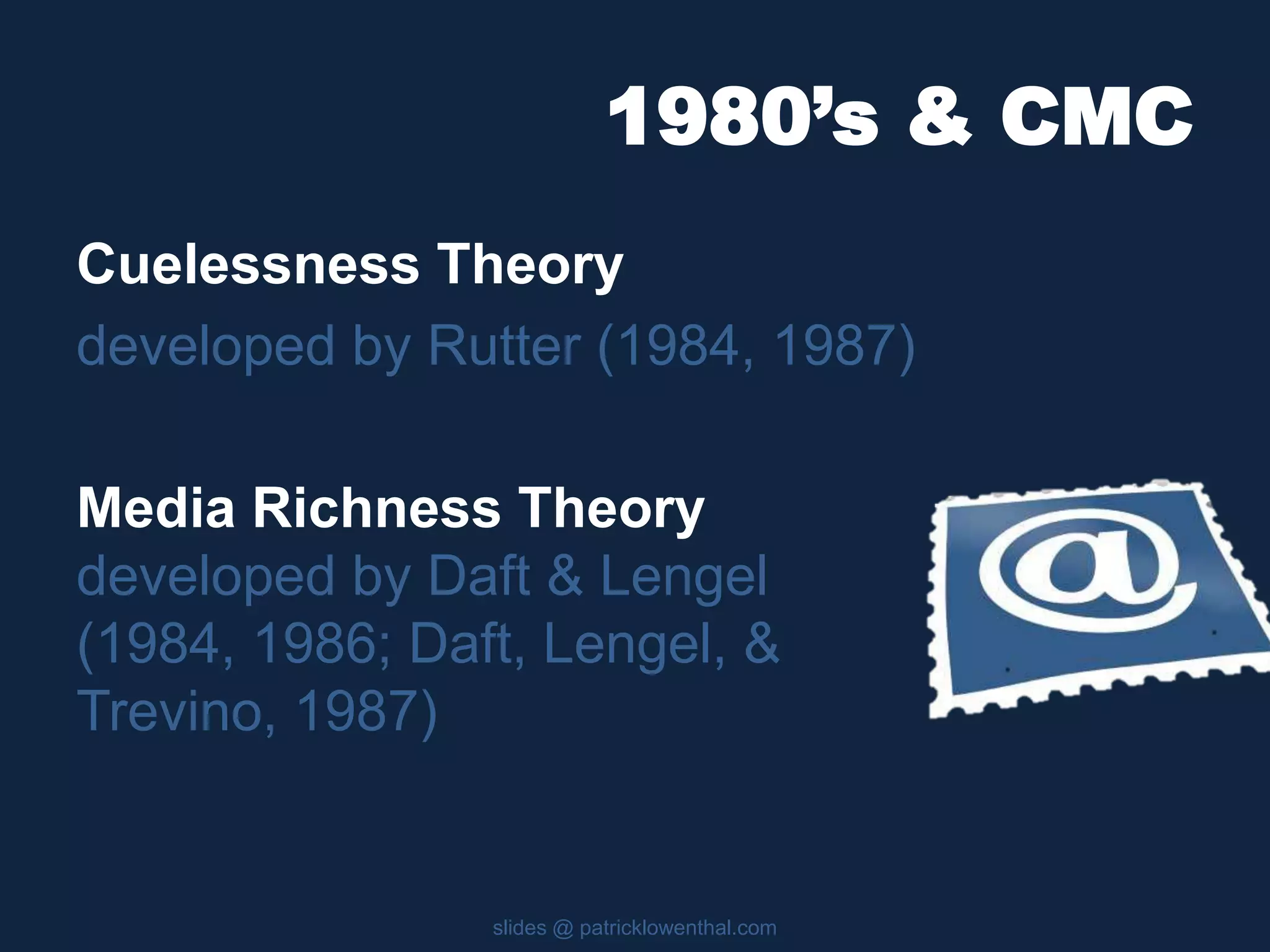
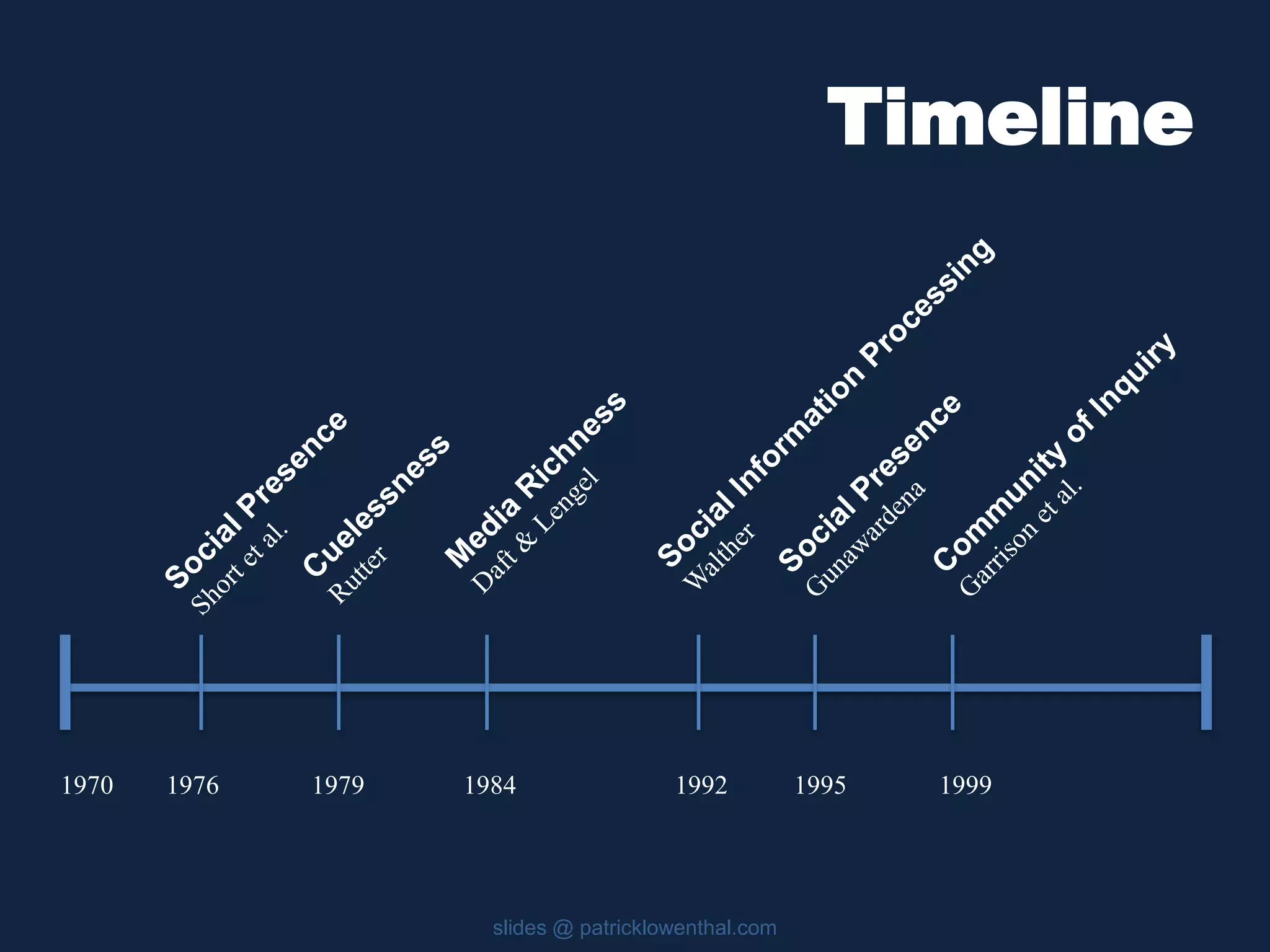
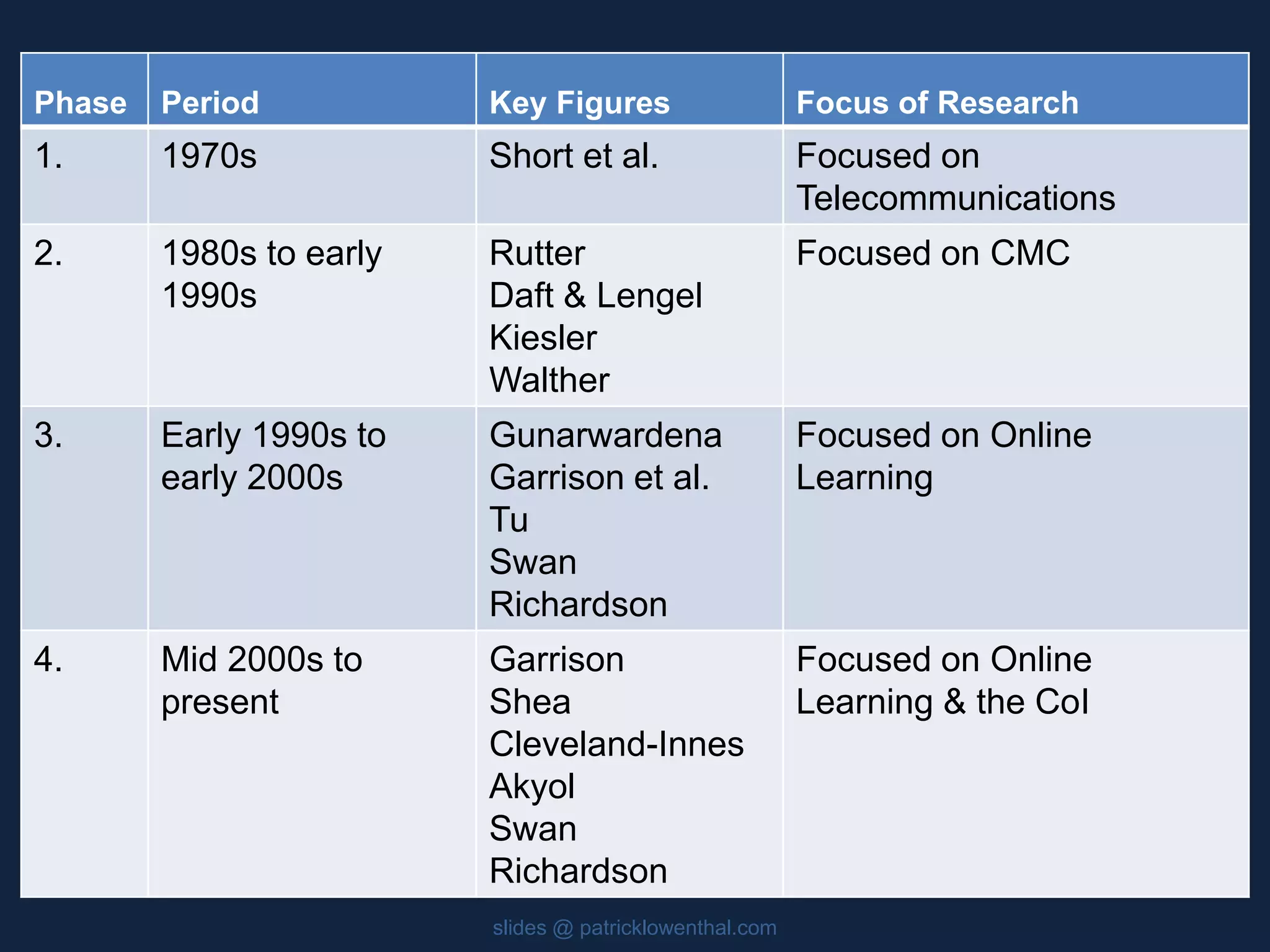
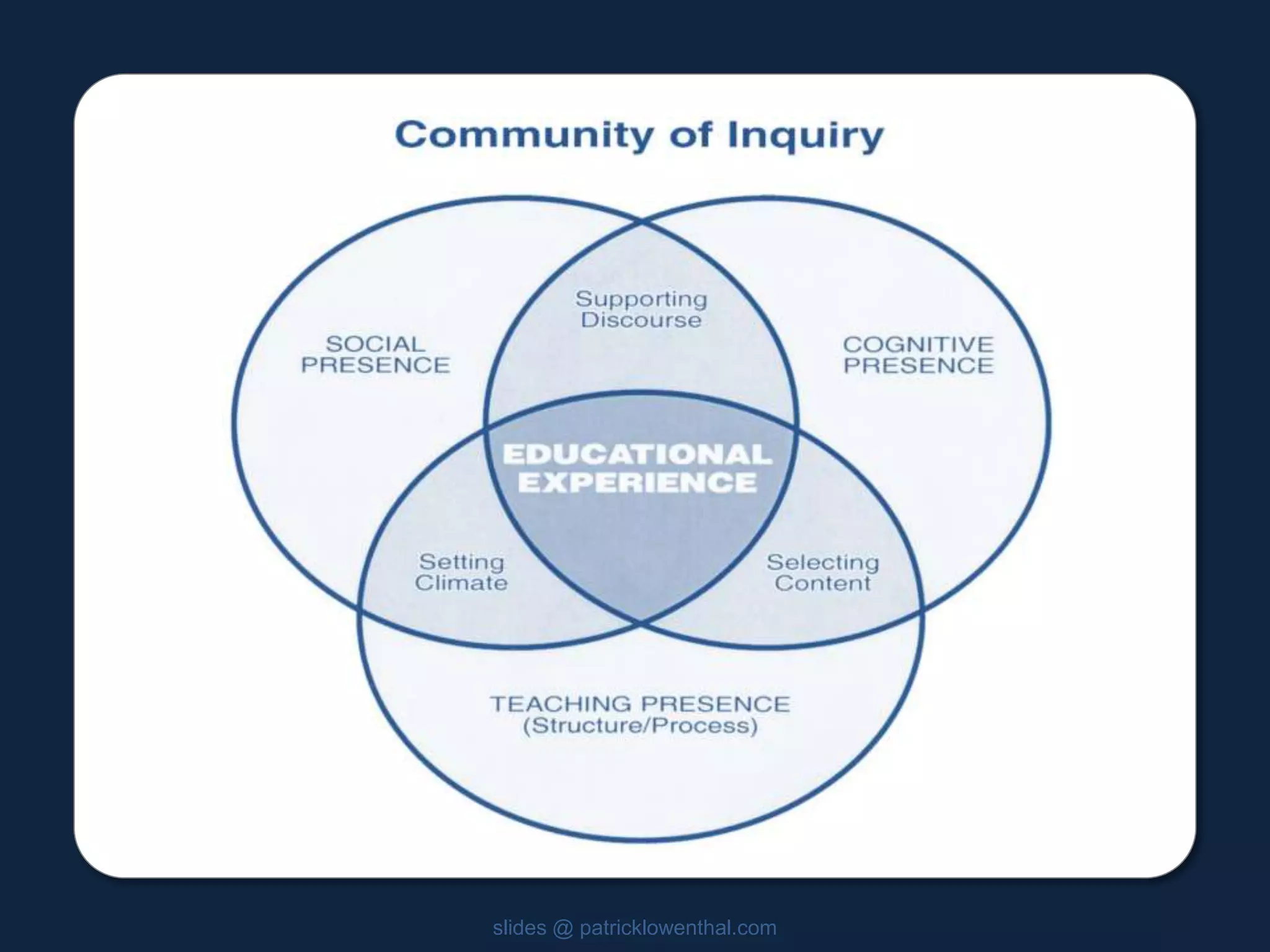
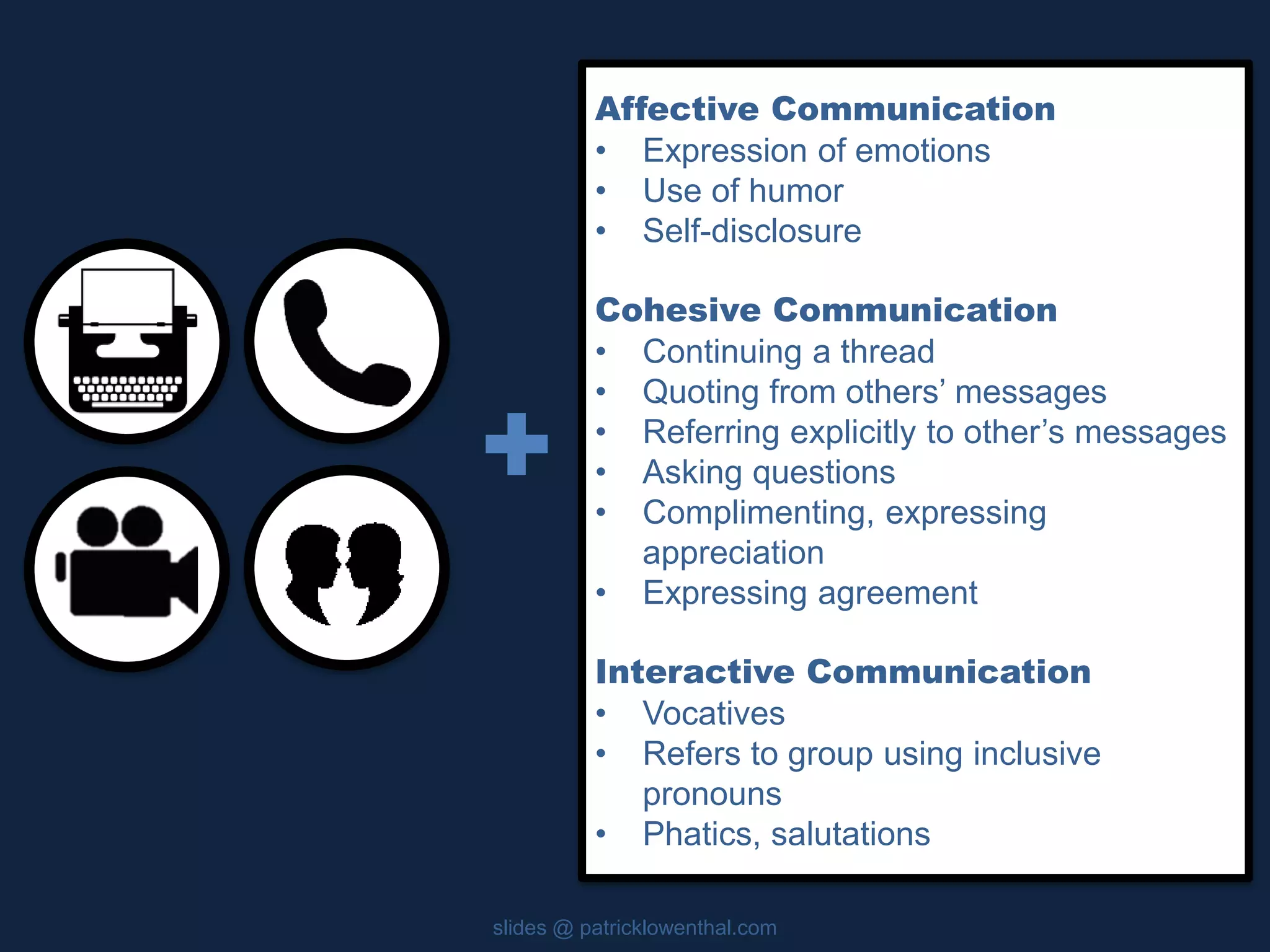
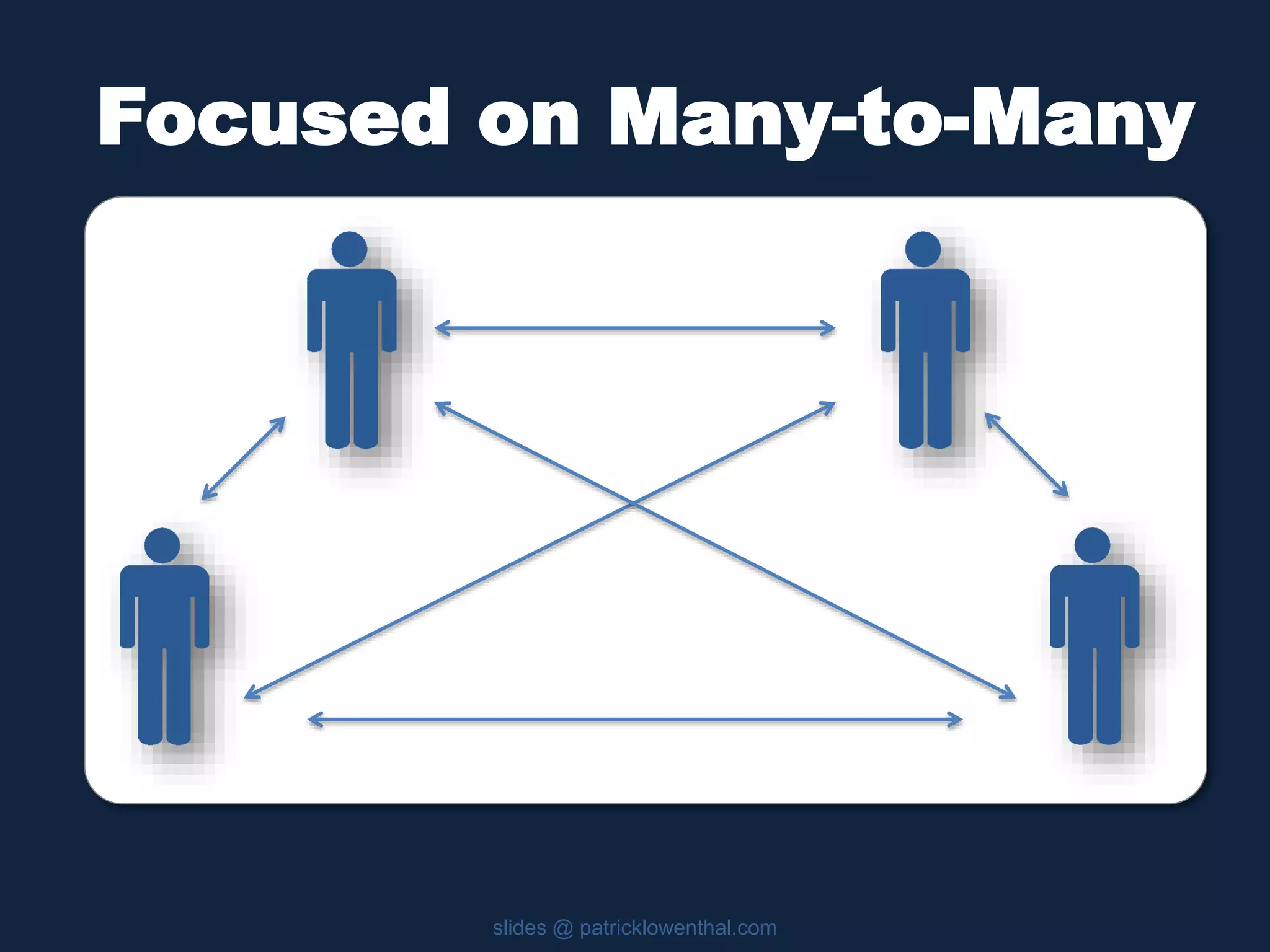
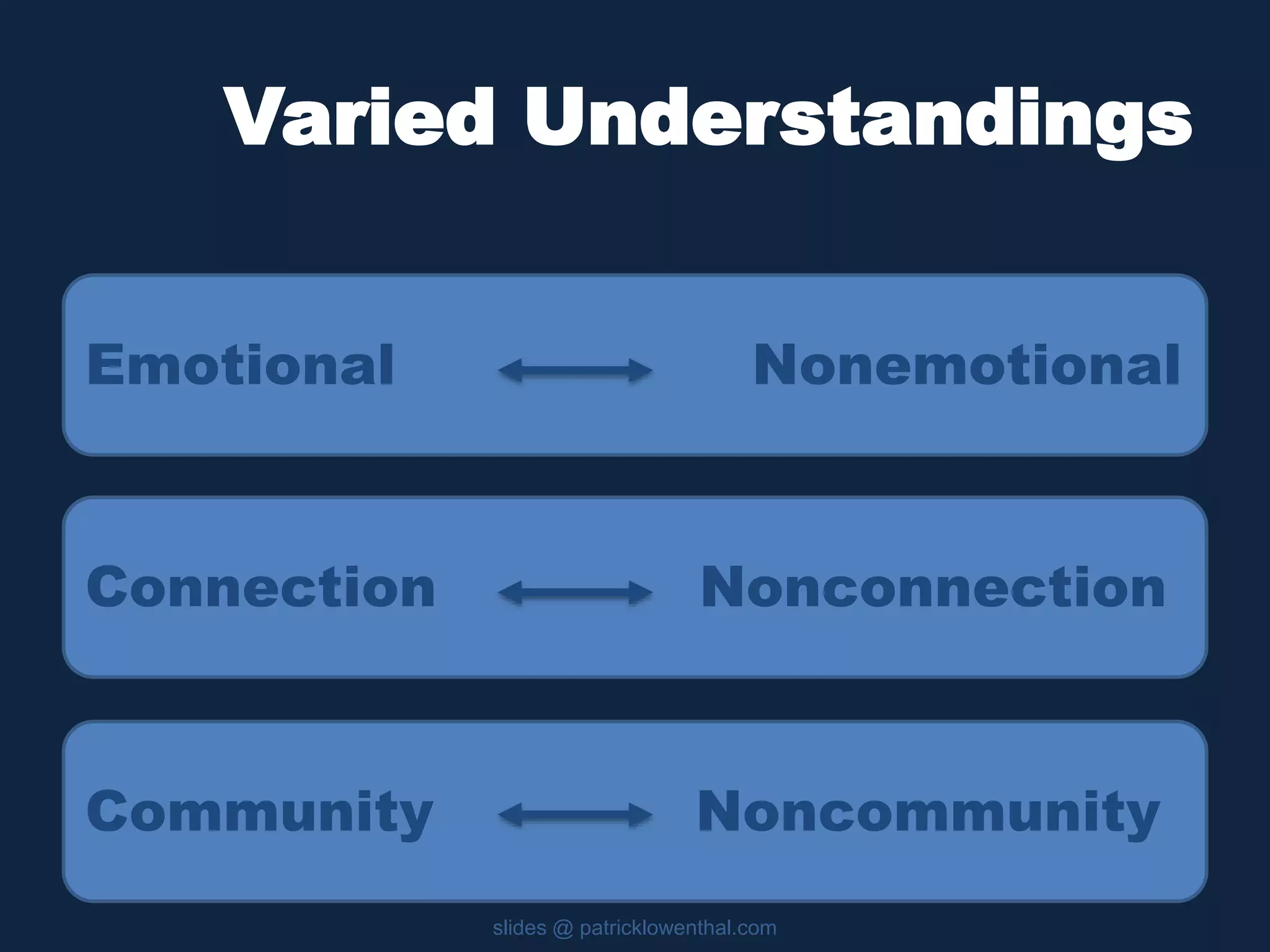
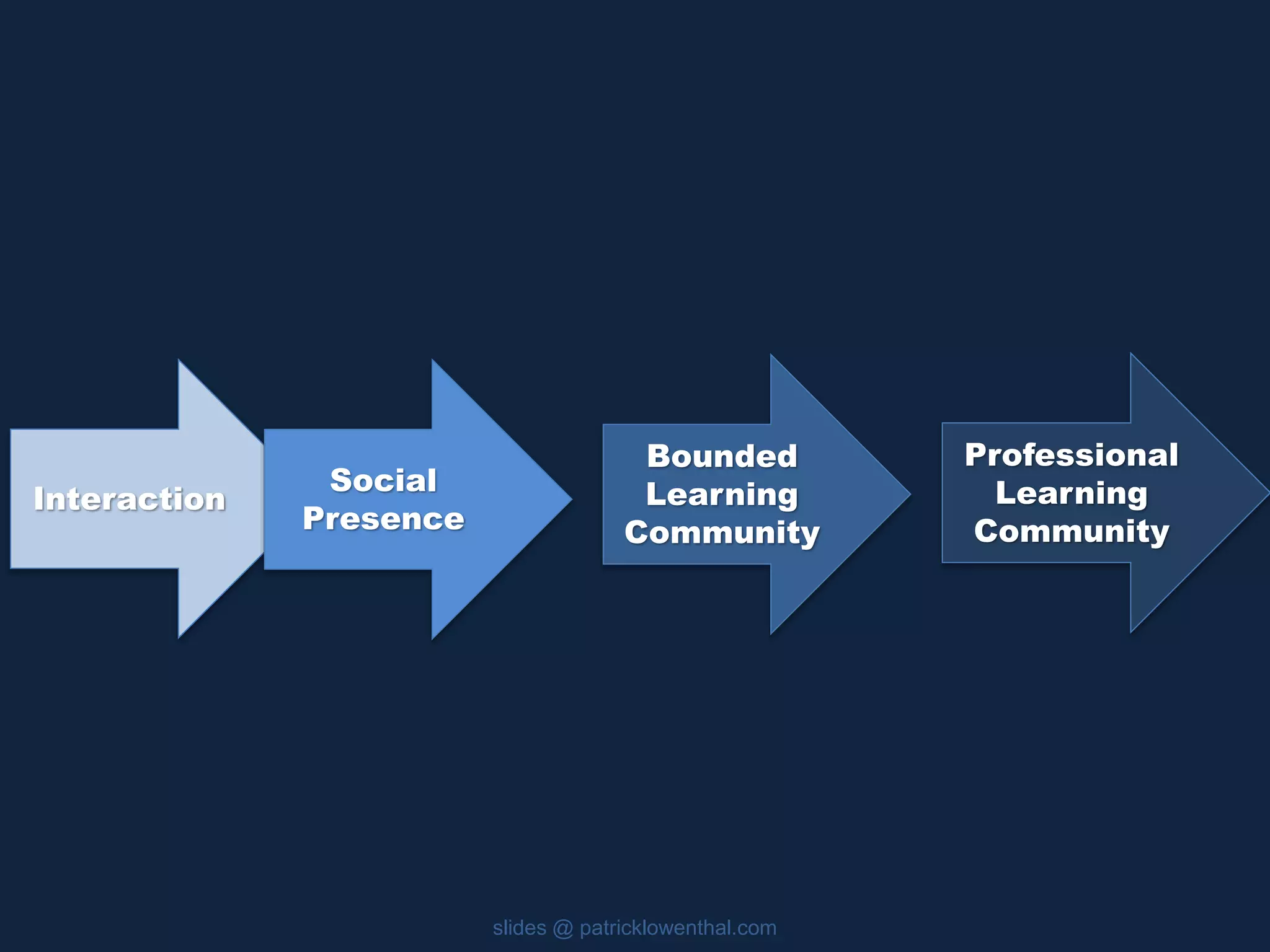
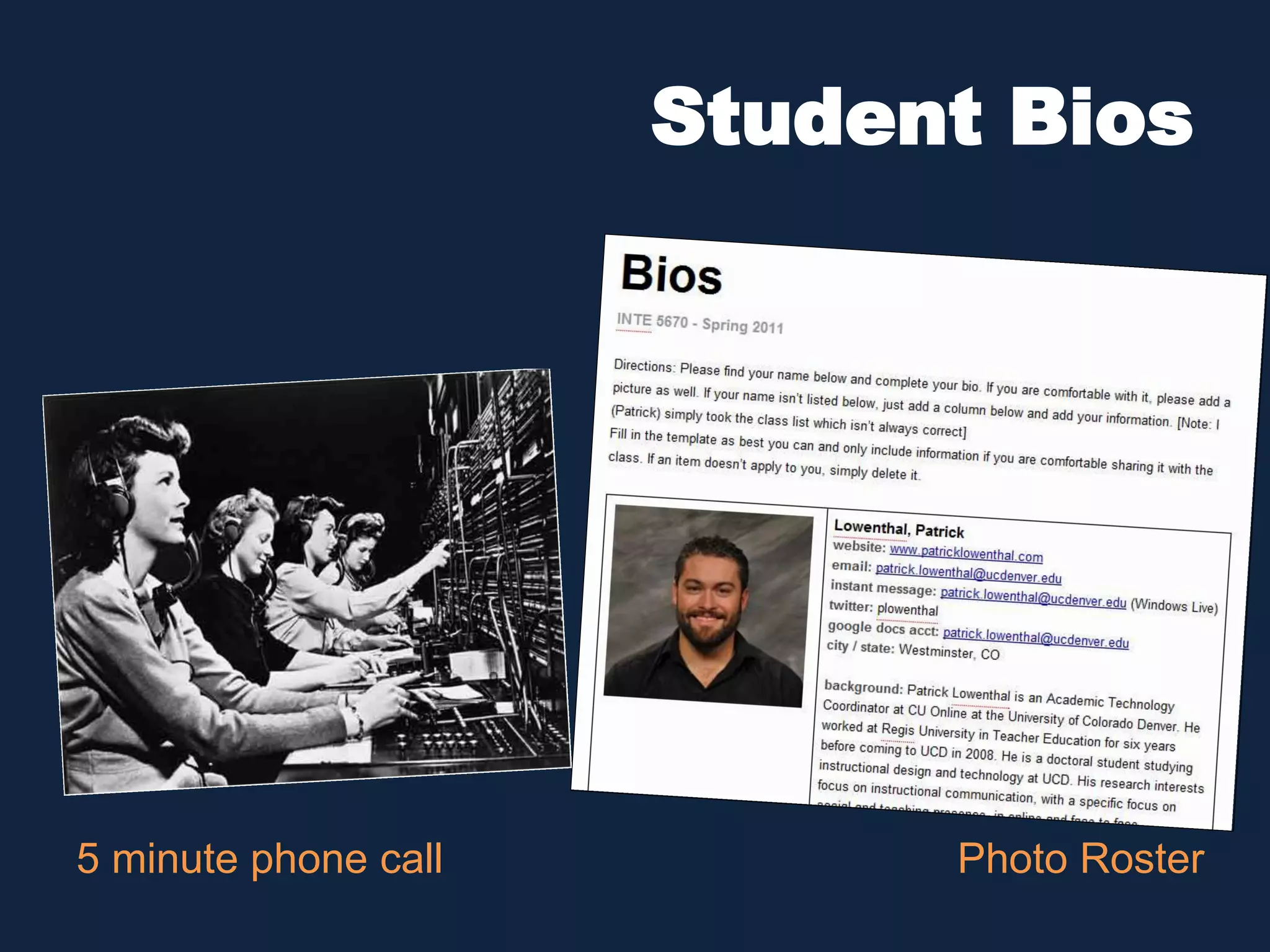
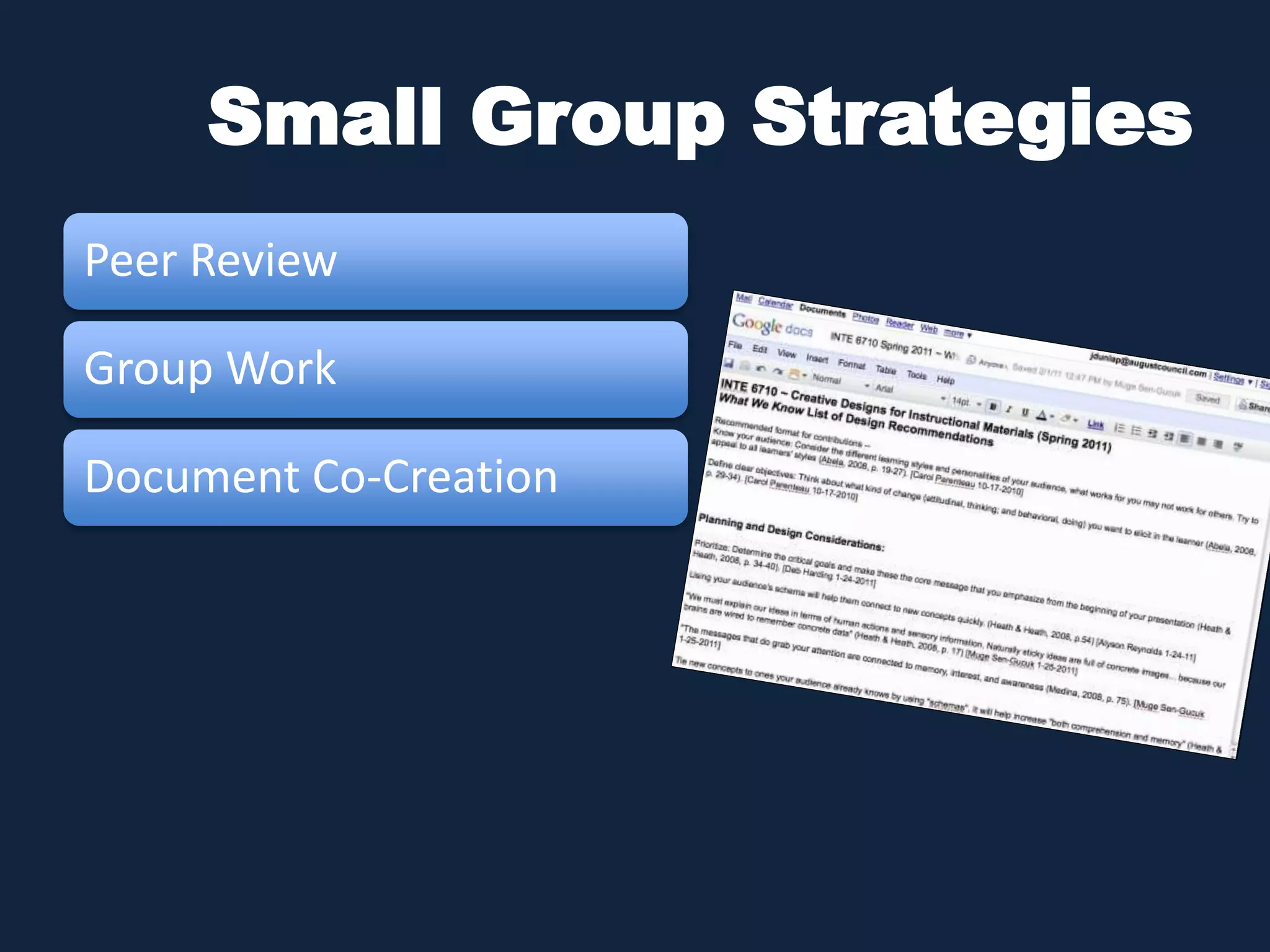
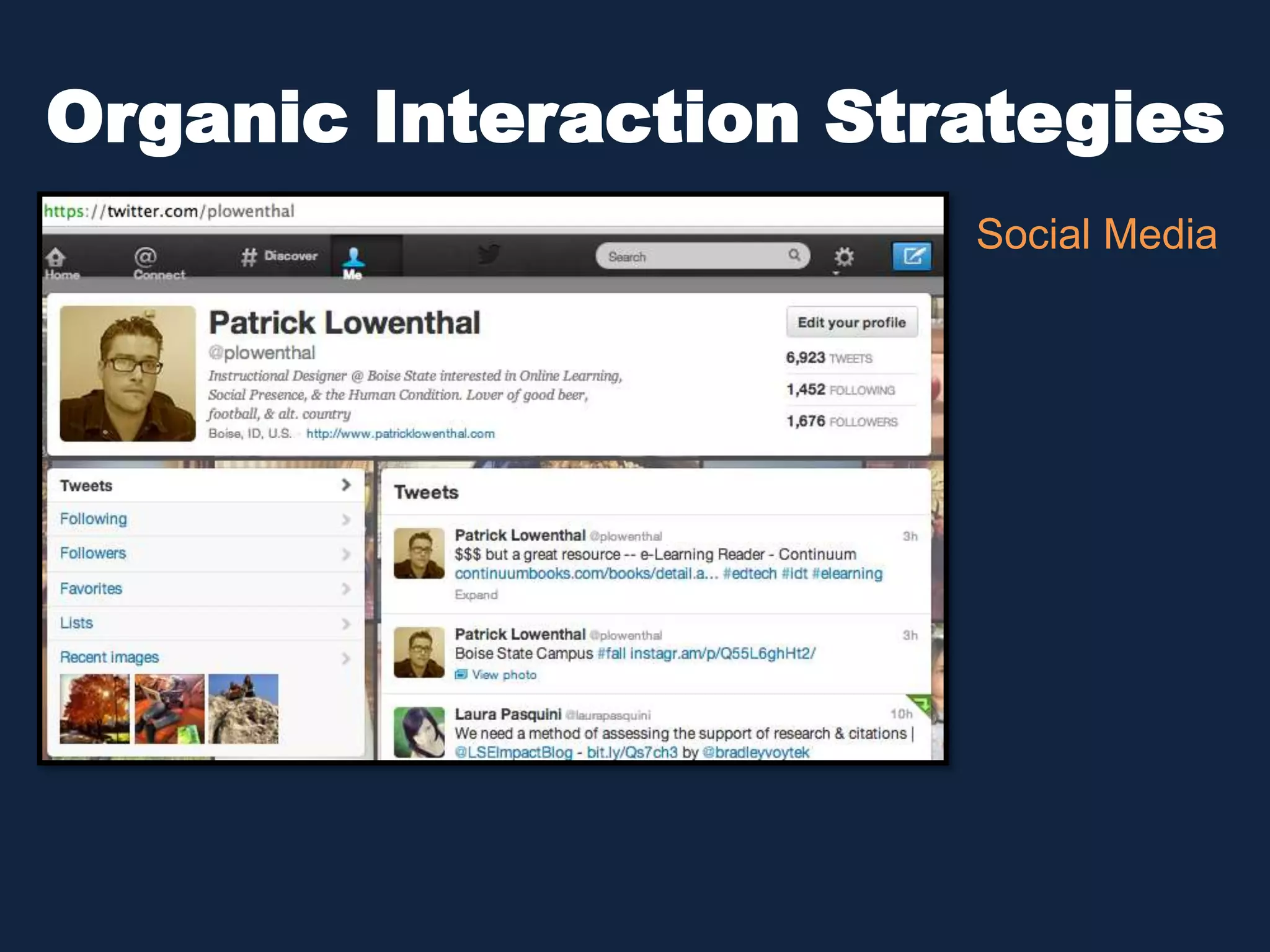
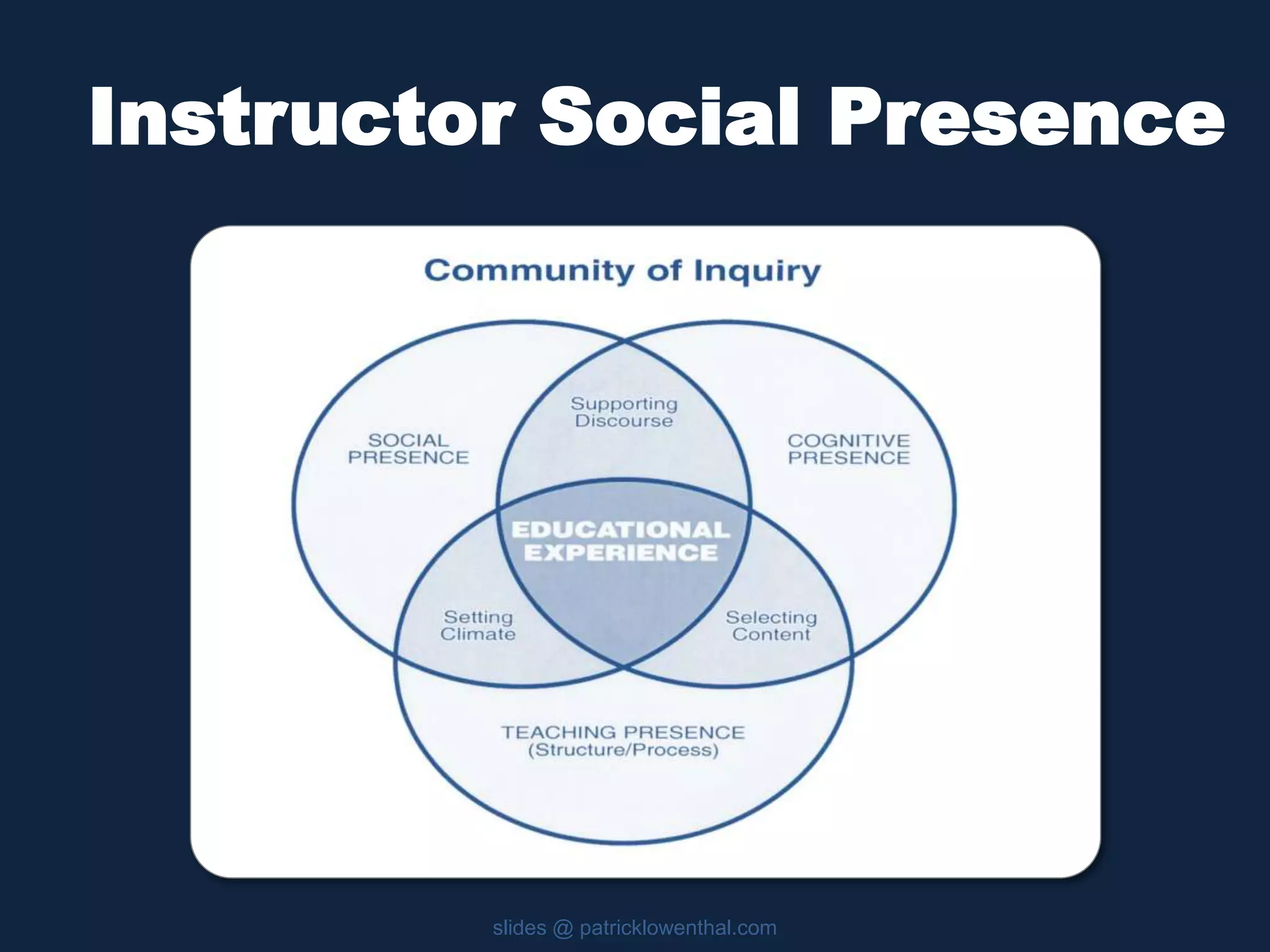
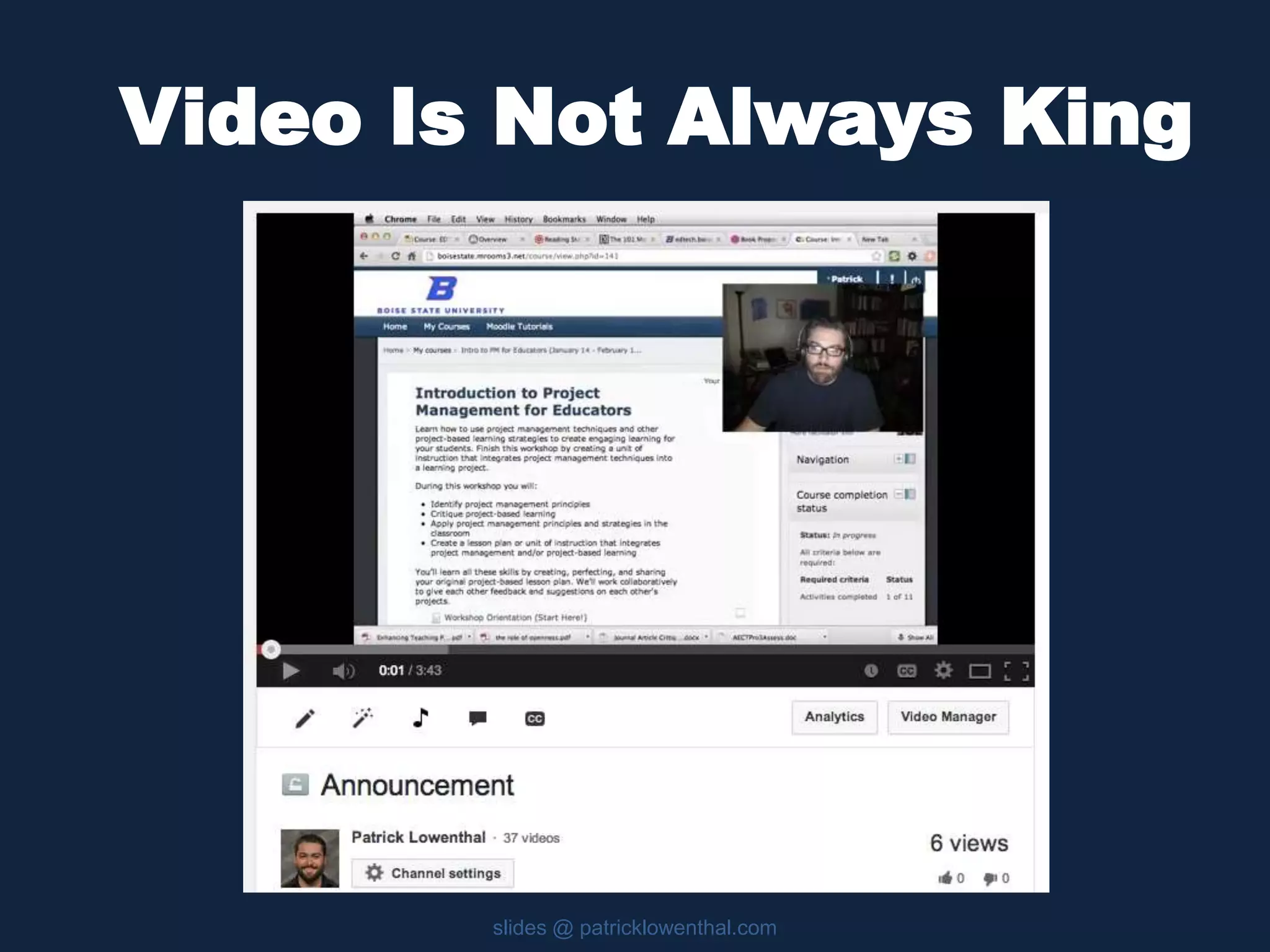
This document discusses the history and evolution of social presence theory in online courses. It begins with an overview of the origins of social presence theory focusing on 1-on-1 communication. It then outlines how understanding of social presence has evolved over time to focus on many-to-many communication and learning communities. Various definitions of social presence are provided from different scholars. The remainder of the document discusses strategies to build social presence in online courses through teacher/student bios, orientation, feedback, discussions, small groups and more organic interactions. Recent work on social presence focusing on the instructor's role, location-based presence and alternatives to video are also mentioned.