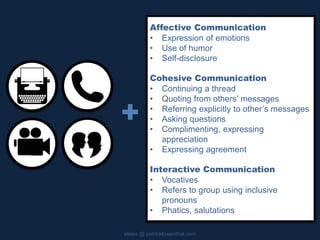
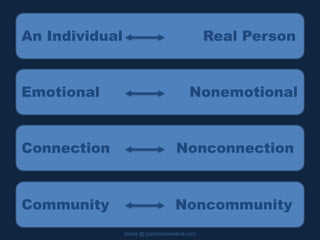
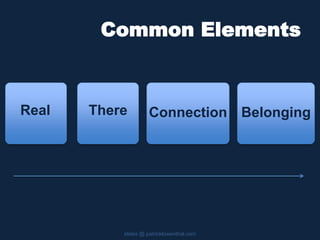
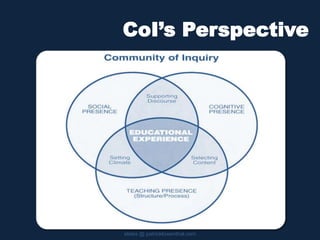
This document discusses building community and social presence in online classrooms. It provides a history of social presence theory and how definitions of social presence have evolved over time. Bounded online learning communities are described as having required participation, fixed time periods, and explicit efforts to connect students. Benefits of online communities include providing social context for learning, bridging school and work environments, and helping students feel more connected. The document cautions that online communities can privilege certain types of students and discusses striving for good instruction that is effective, efficient and engaging.