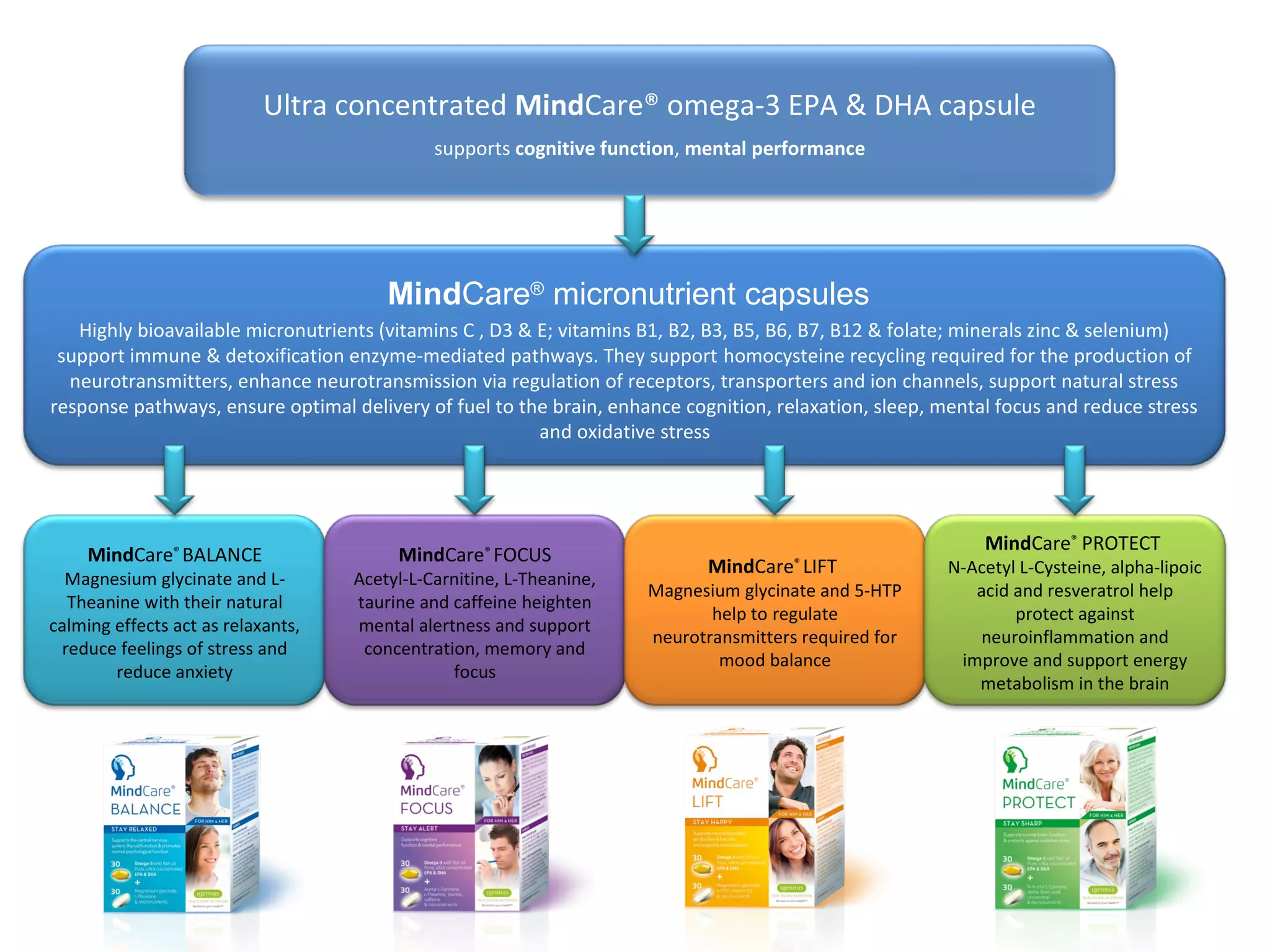
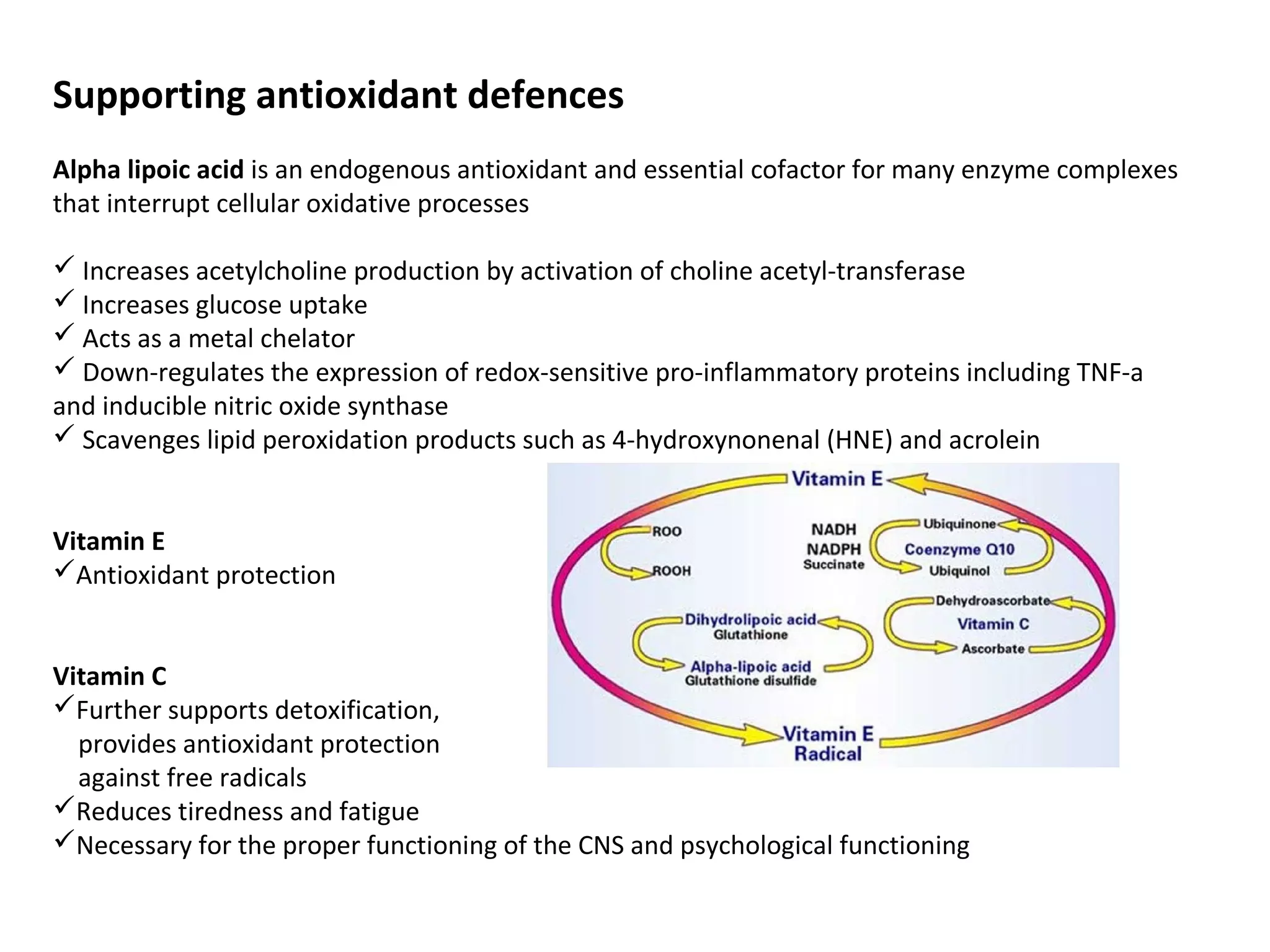
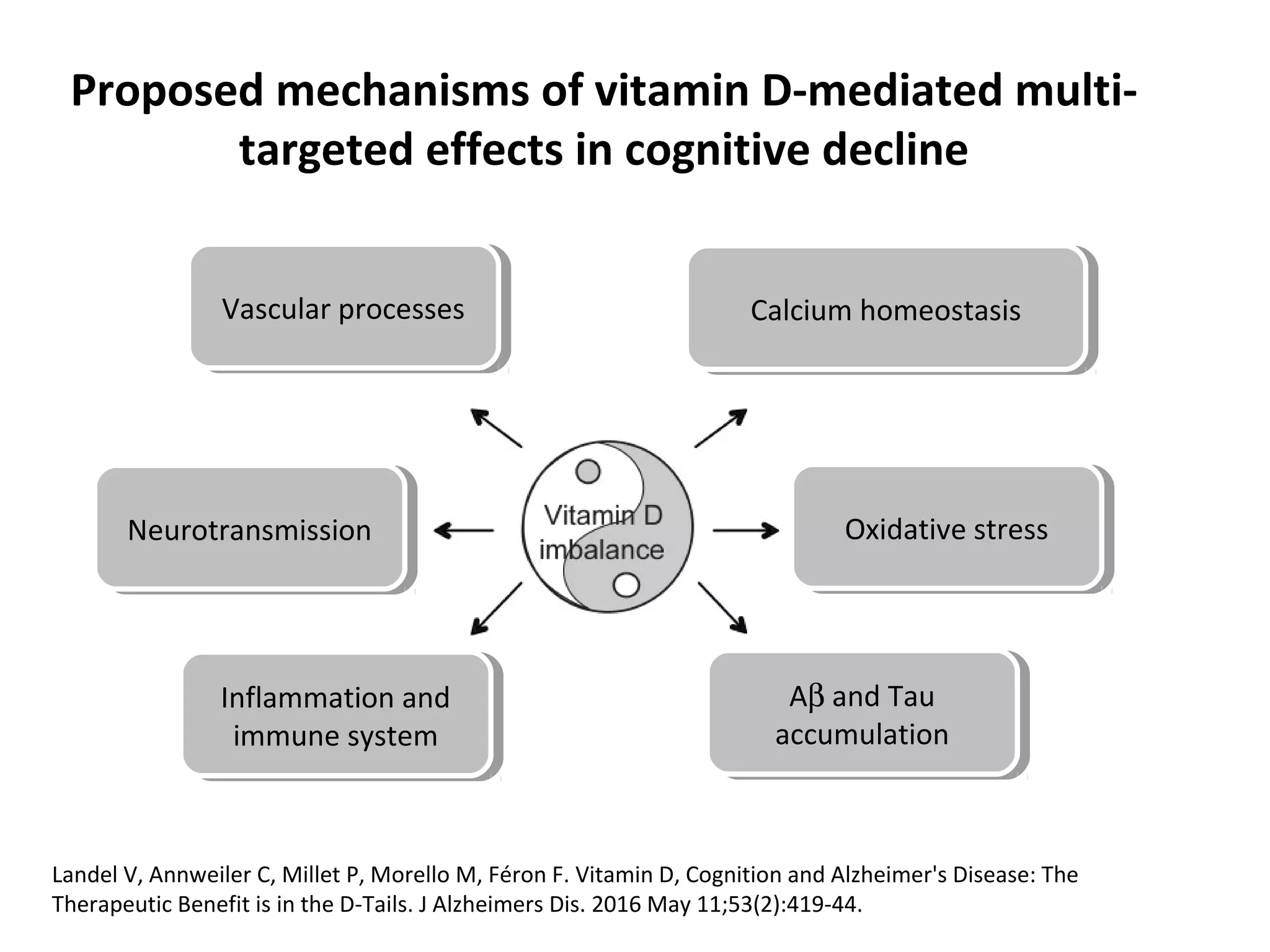
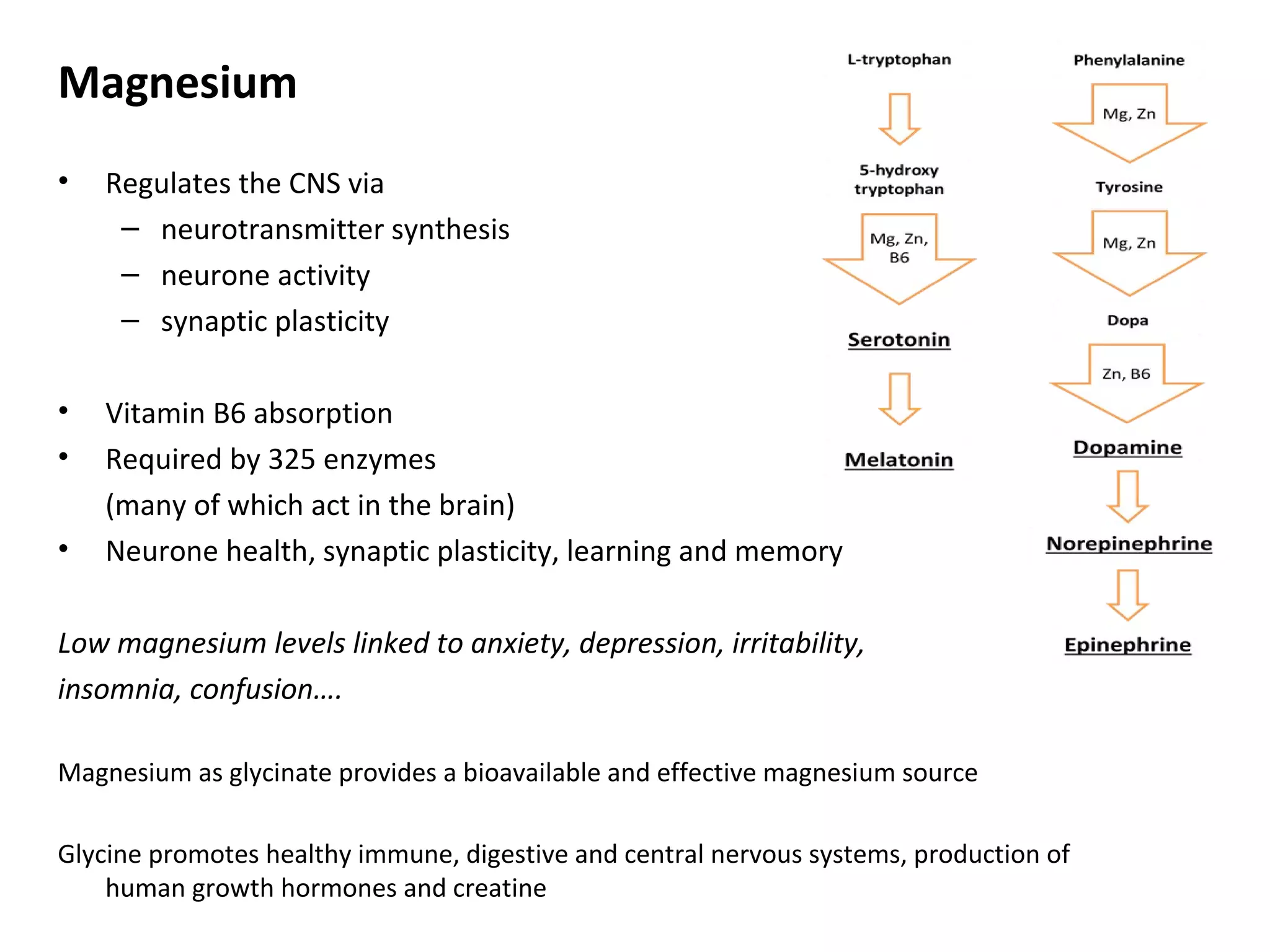
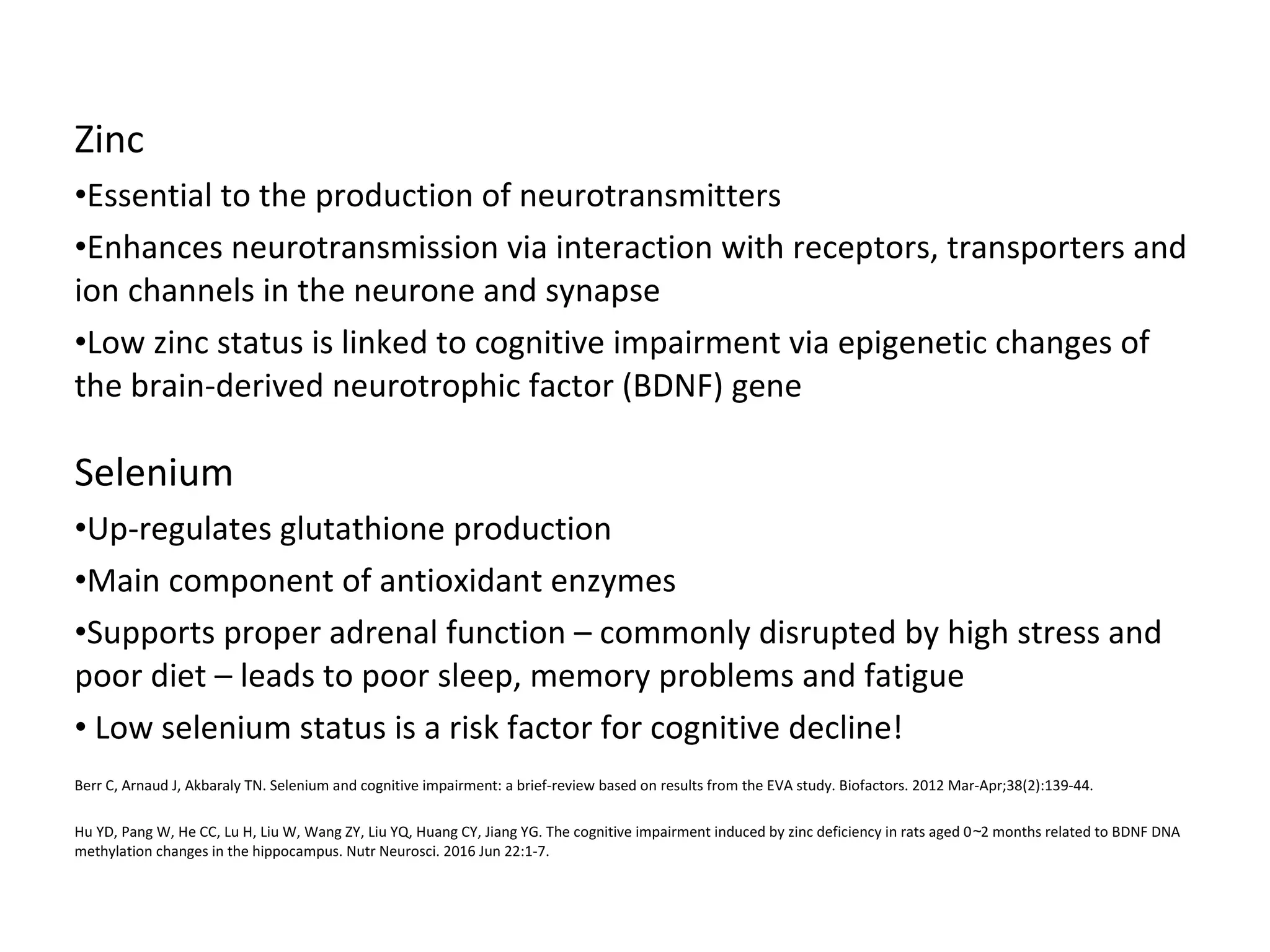
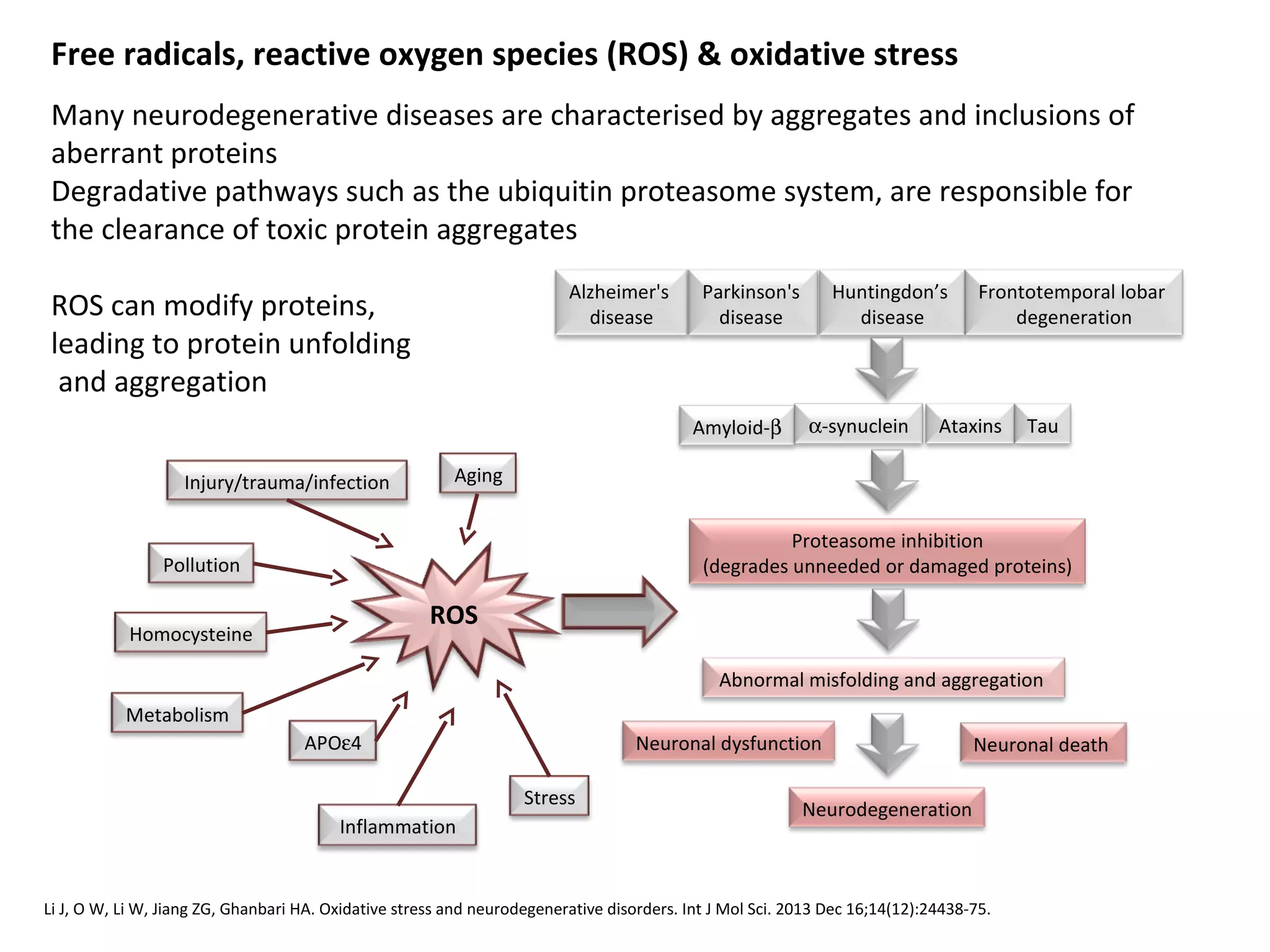
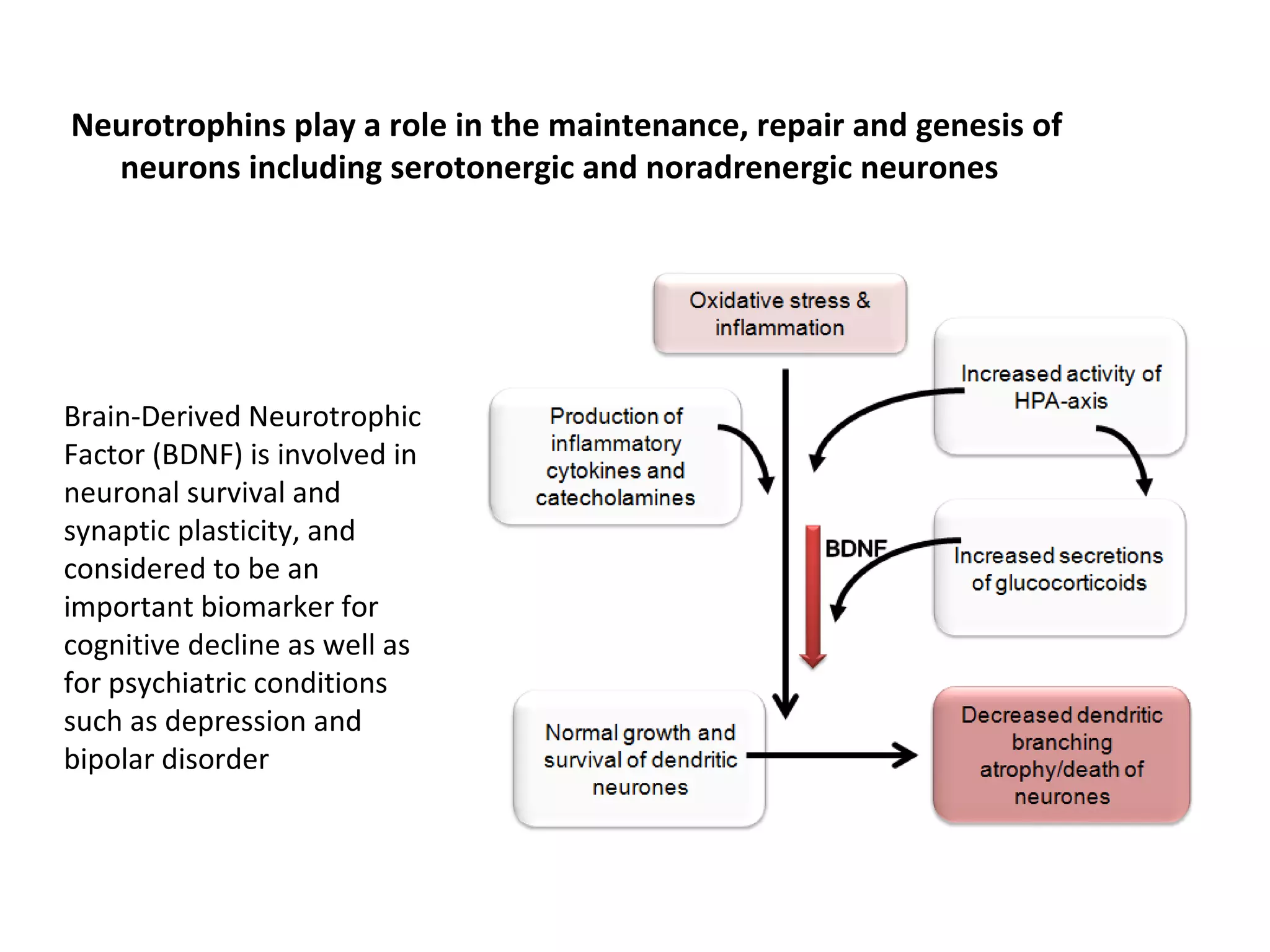
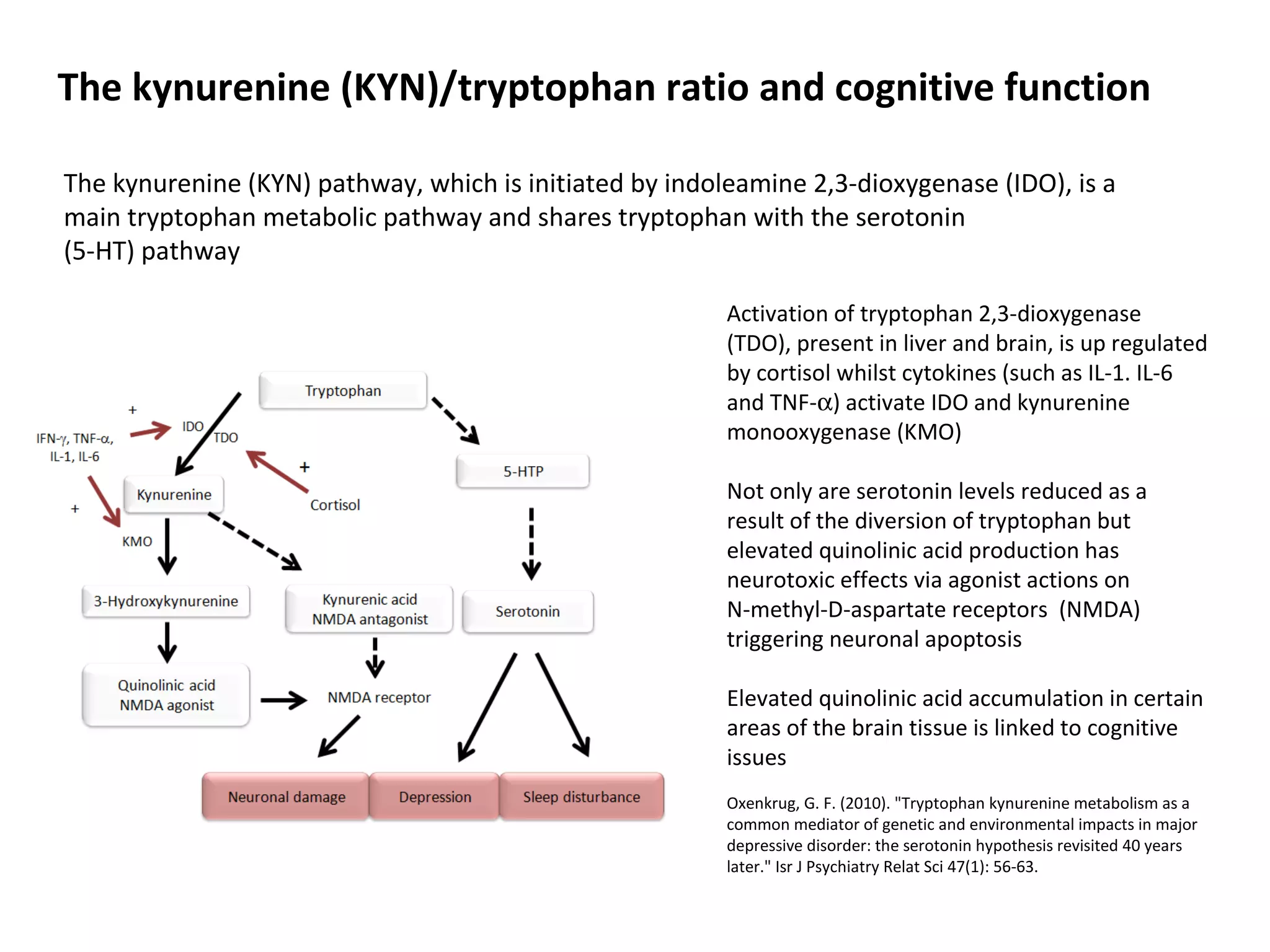
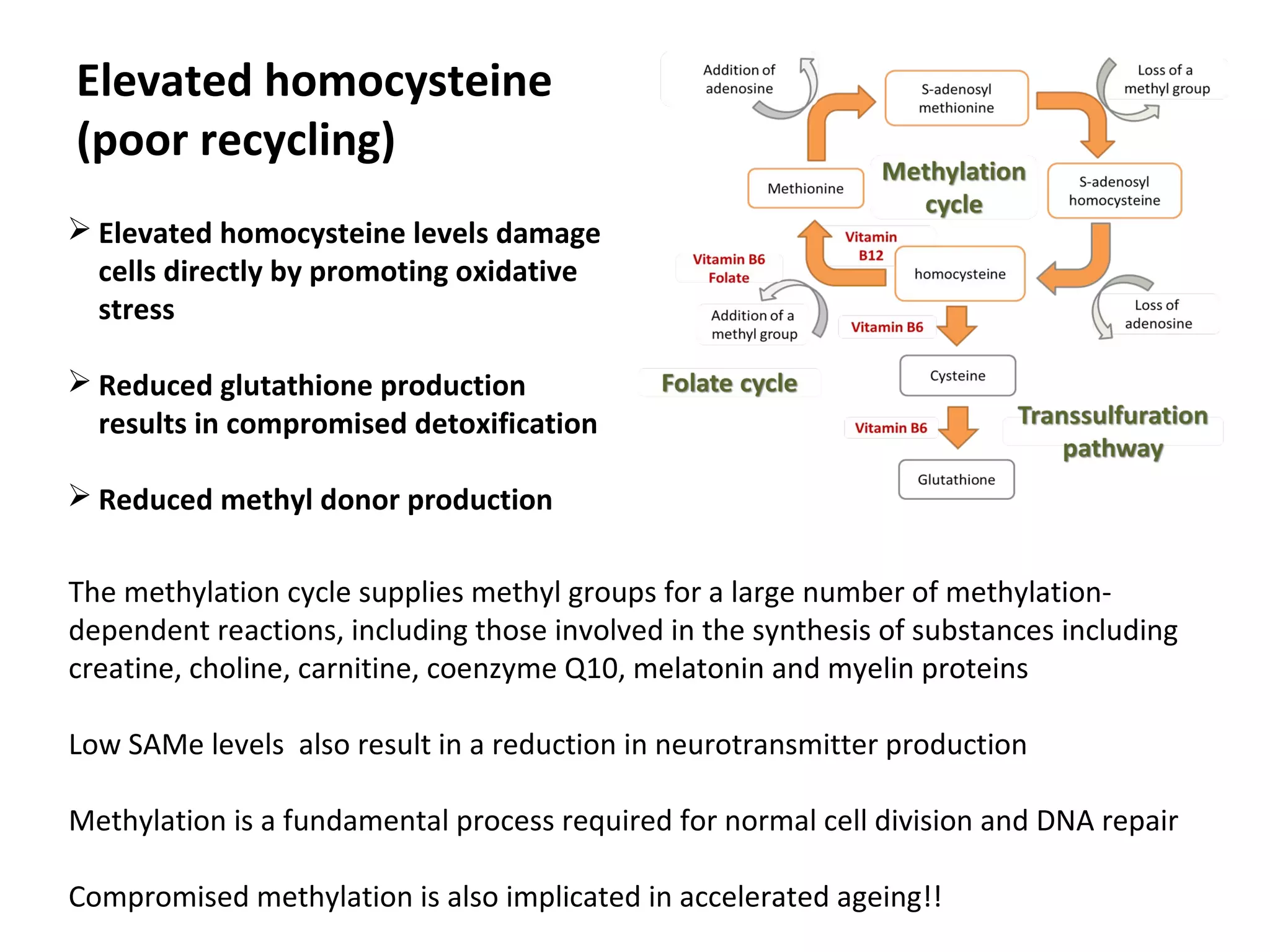
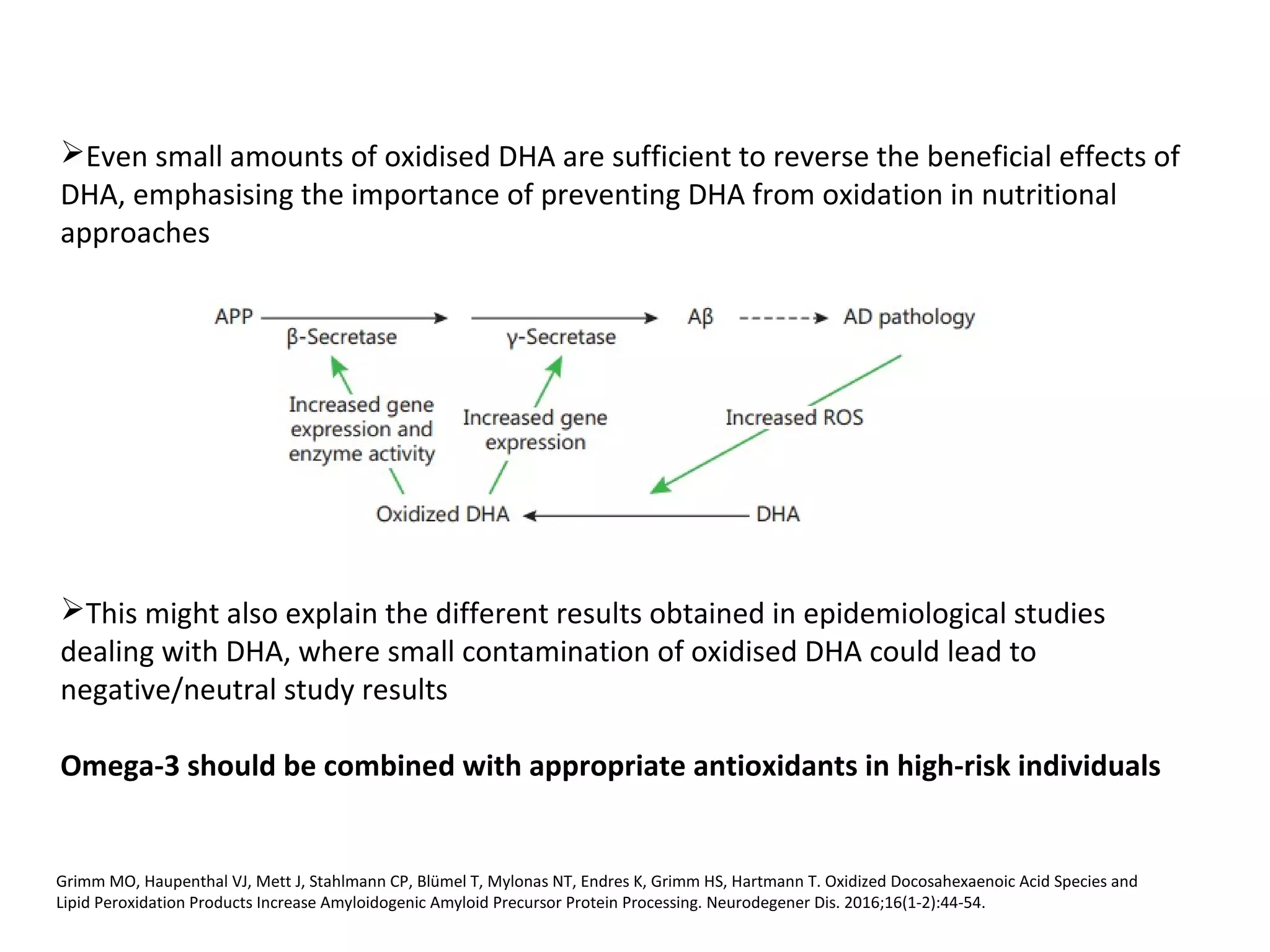
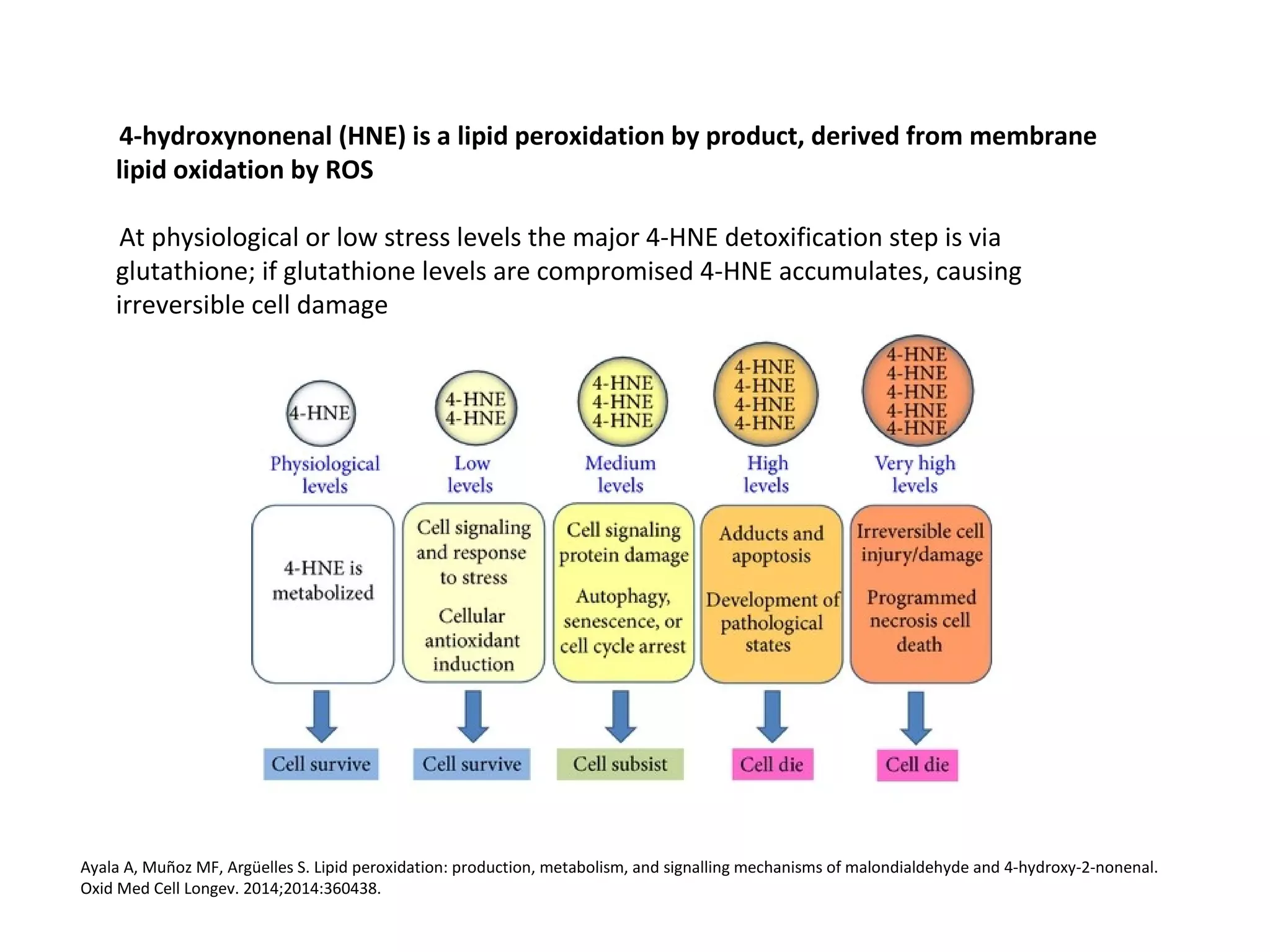
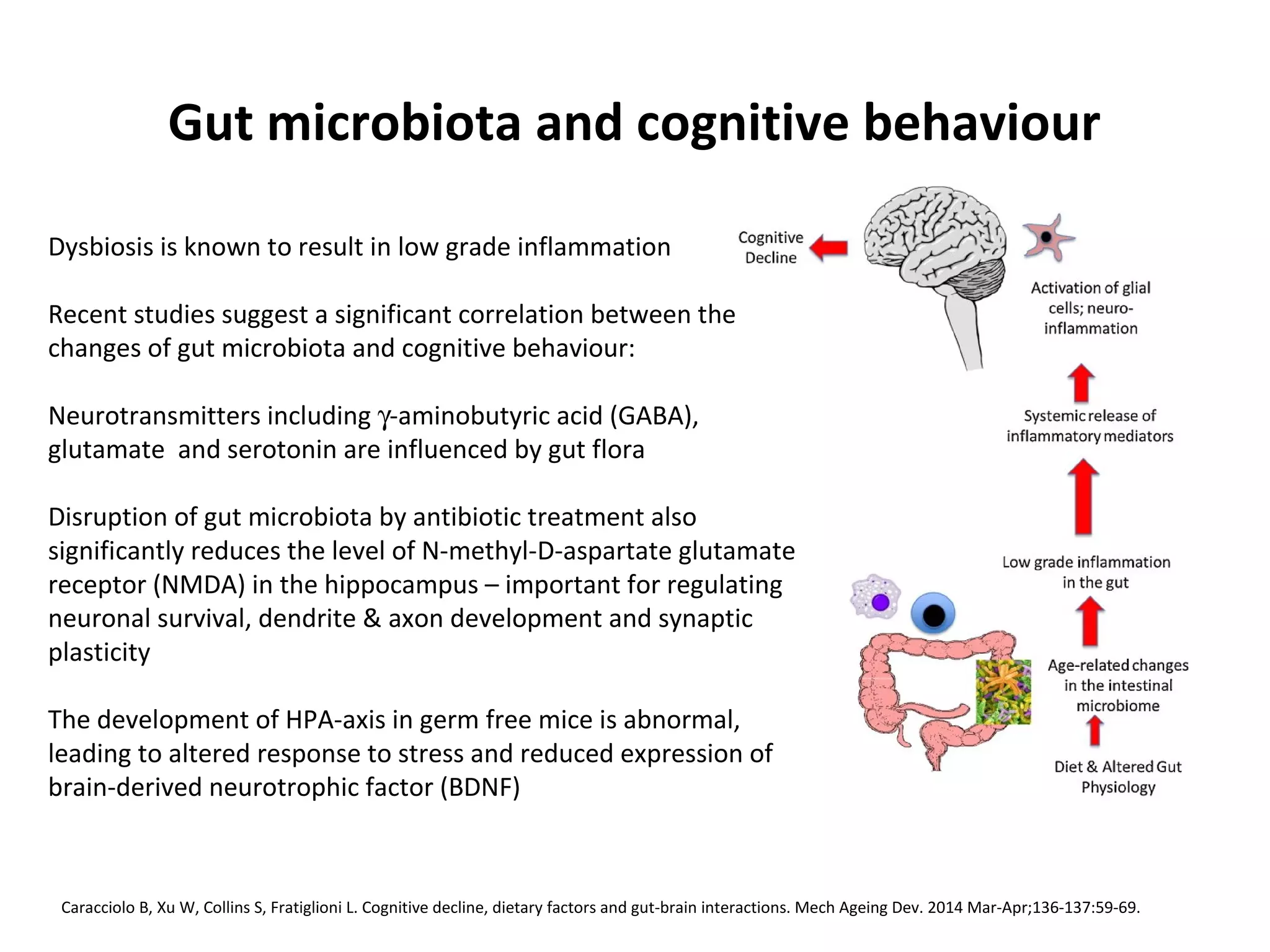
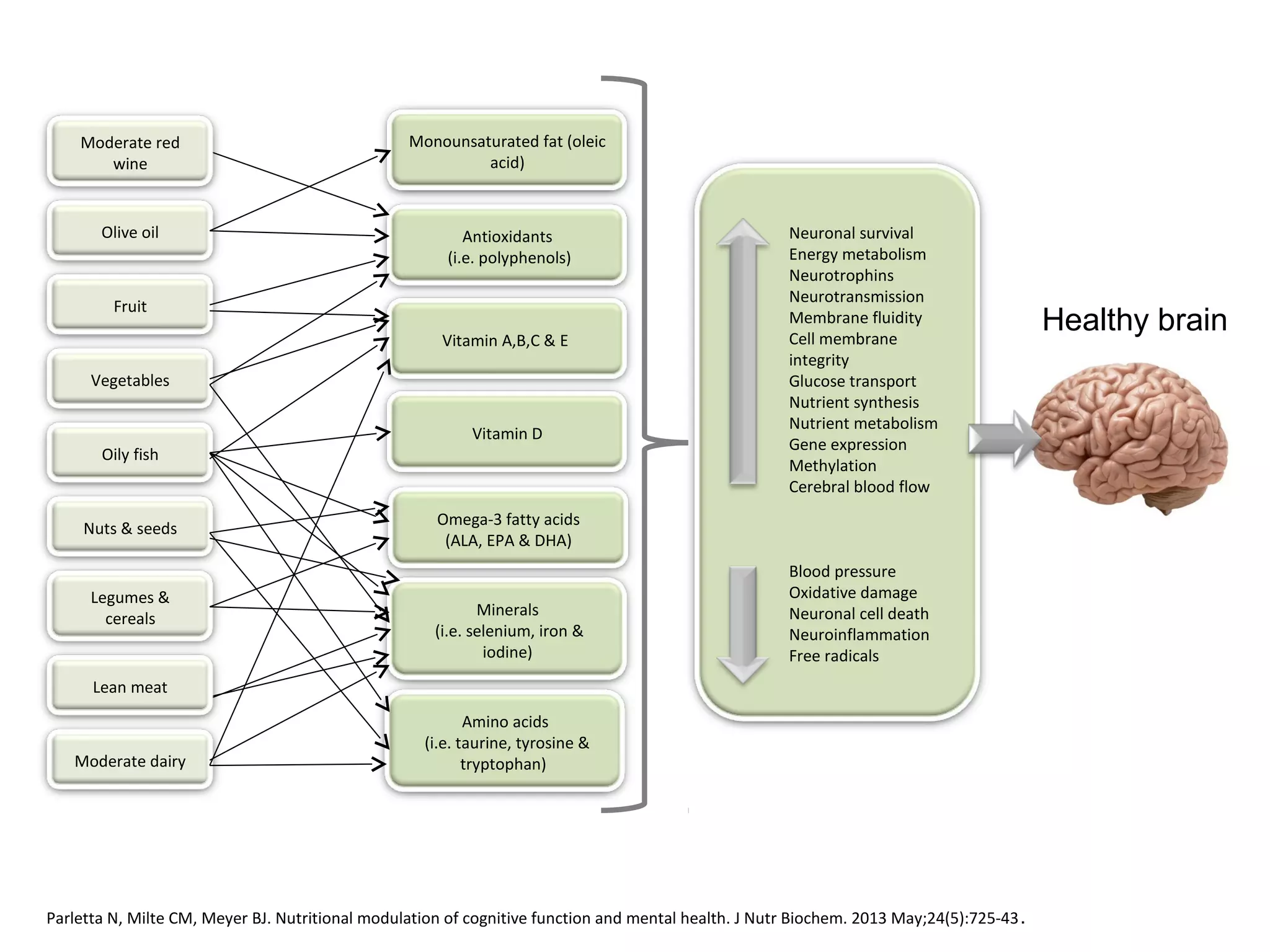
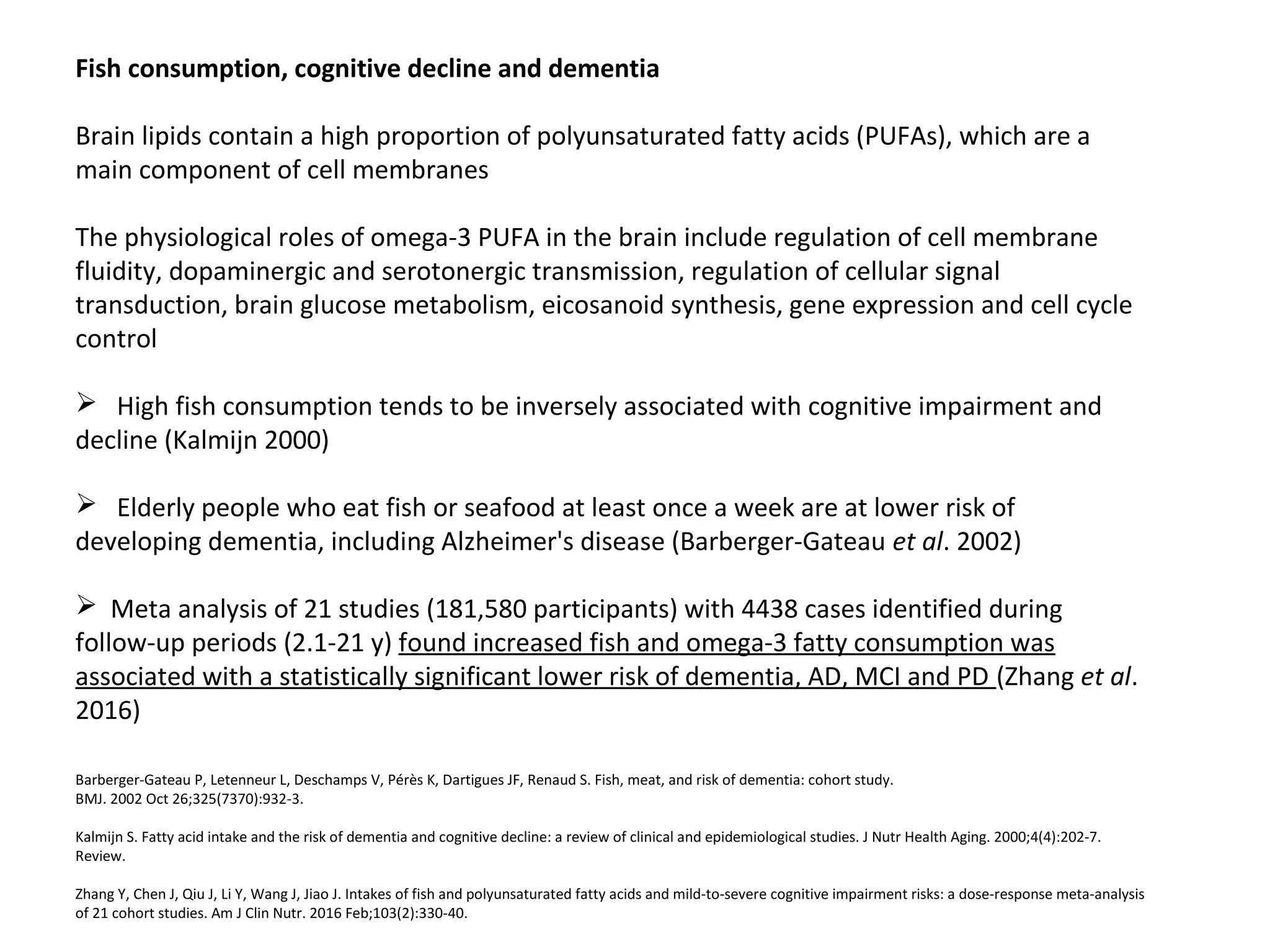
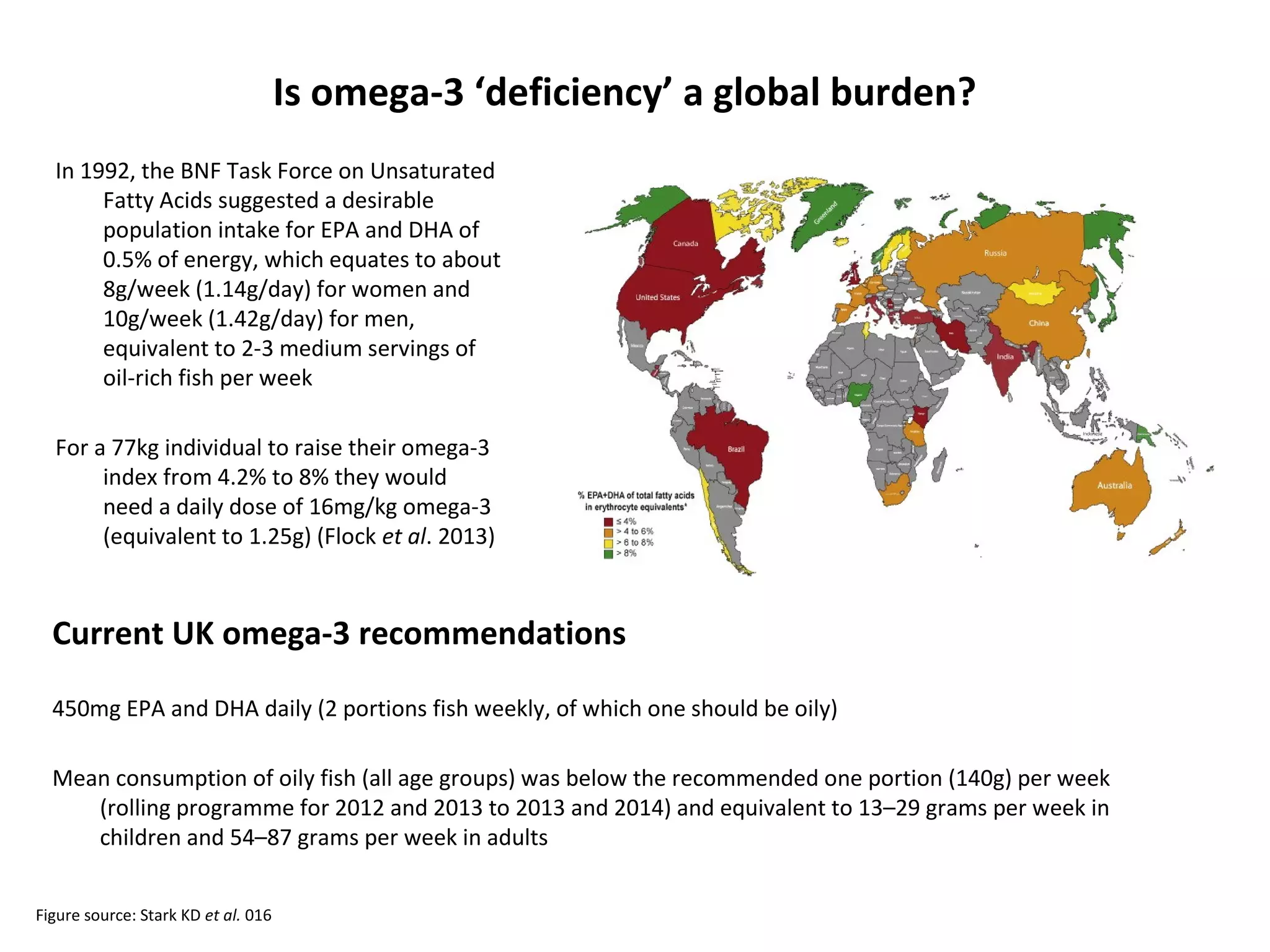
The document discusses the relationship between dietary factors and cognitive decline, emphasizing that dementia is characterized by a gradual decline in cognitive abilities. It outlines modifiable risk factors for cognitive decline, including elevated homocysteine levels and poor dietary habits, and advocates for early intervention through dietary changes as a potential preventative strategy. Furthermore, it highlights the importance of specific nutrients, such as B vitamins and omega-3 fatty acids, in influencing cognitive health and offers insights on the role of oxidative stress and gut microbiota in this context.


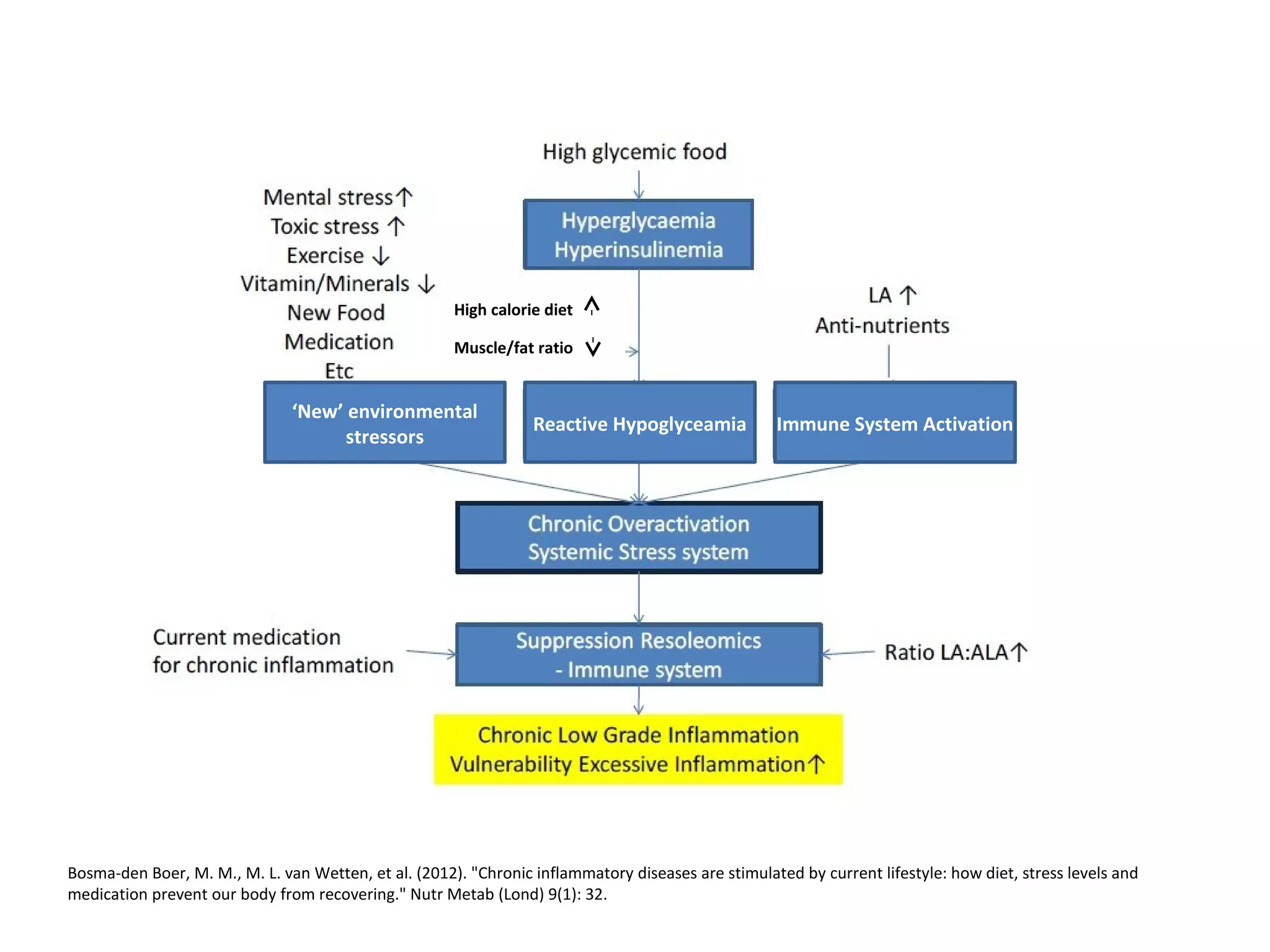





![Cytokines
(IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α)
Acute Phase Proteins
C-reactive protein (CRP),
Serum amyloid A (SAA)
PLA2/COX2/LOX
NFκB
Receptor mediated pathways
(Toll like receptors [TLR], TNF-α, IL-
1)
Inflammation stimulus (i.e.
tissue injury, infection, heat
stress, psychological stress)
Prostaglandins
Leukotrienes
Thromboxanes
INFLAMMATION
Saturated fatDysbiosis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nutritionalstrategiesforcdac1nbshortversion-161027124335/75/Nutritional-strategies-for-cognitive-decline-22-2048.jpg)


![Randomised controlled trials to assess the effect on cognition of a nutritional intervention using
Mediterranean diet (supplemented with extra-virgin olive oil [EVOO] or mixed nuts) in comparison
with a low-fat control diet
2013 - PREDIMED-NAVARRA trial - 6.5 years nutritional intervention - 522 participants at high
vascular risk (44.6% men, age 74.6 ± 5.7 years at cognitive evaluation)
Measurements: cognitive performance as a main outcome and cognitive status (normal, mild
cognitive impairment [MCI] or dementia) as a secondary outcome. Global cognitive performance was
examined by Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) and Clock Drawing Test (CDT)
2015 -Prevención con Dieta Mediterránea nutrición intervención trial - 6.5 years nutritional
intervention 447 participants at high cardiovascular risk (47.9% men, mean age 66.9 years at cognitive
evaluation)
Rates of cognitive change over time based on a neuropsychological test battery: Mini-Mental State
Examination, Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test (RAVLT), Animals Semantic Fluency, Digit Span subtest
from the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, Verbal Paired Associates from the Wechsler Memory
Scale, and the Colour Trail Test
In older populations, compared to a low fat diet, a Mediterranean diet supplemented with olive oil
or nuts is associated with improved cognitive function.
Martinez-Lapiscina, E.H.; Clavero, P.; Toledo, E.; Estruch, R.; Salas-Salvado, J.; San Julian, B.S.; Sanchez-Tainta, A.; Ros, E.; Valls-Pedret, C.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A. Mediterranean diet improves cognition: The
PREDIMED-NAVARRA randomised trial. J. Neurol. Neurosur. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 1318–1325.
Valls-Pedret, C.; Sala-Vila, A.; Serra-Mir, M.; Corella, D.; de la Torre, R.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Martínez-Lapiscina, E.H.; Fitó, M.; Pérez-Heras, A.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; et al. Mediterranean diet and age-related
cognitive decline: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 1094–1103.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nutritionalstrategiesforcdac1nbshortversion-161027124335/75/Nutritional-strategies-for-cognitive-decline-25-2048.jpg)
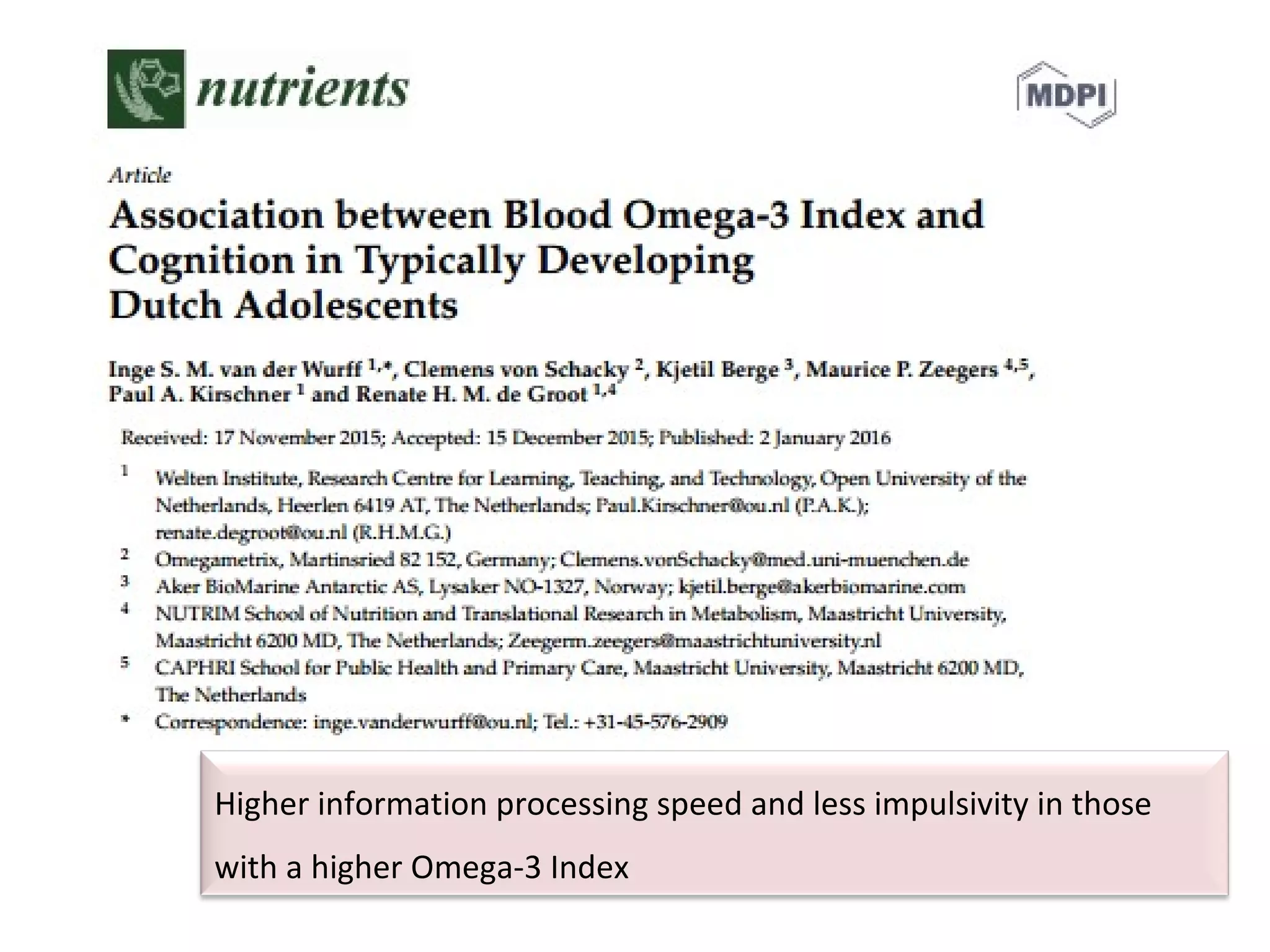
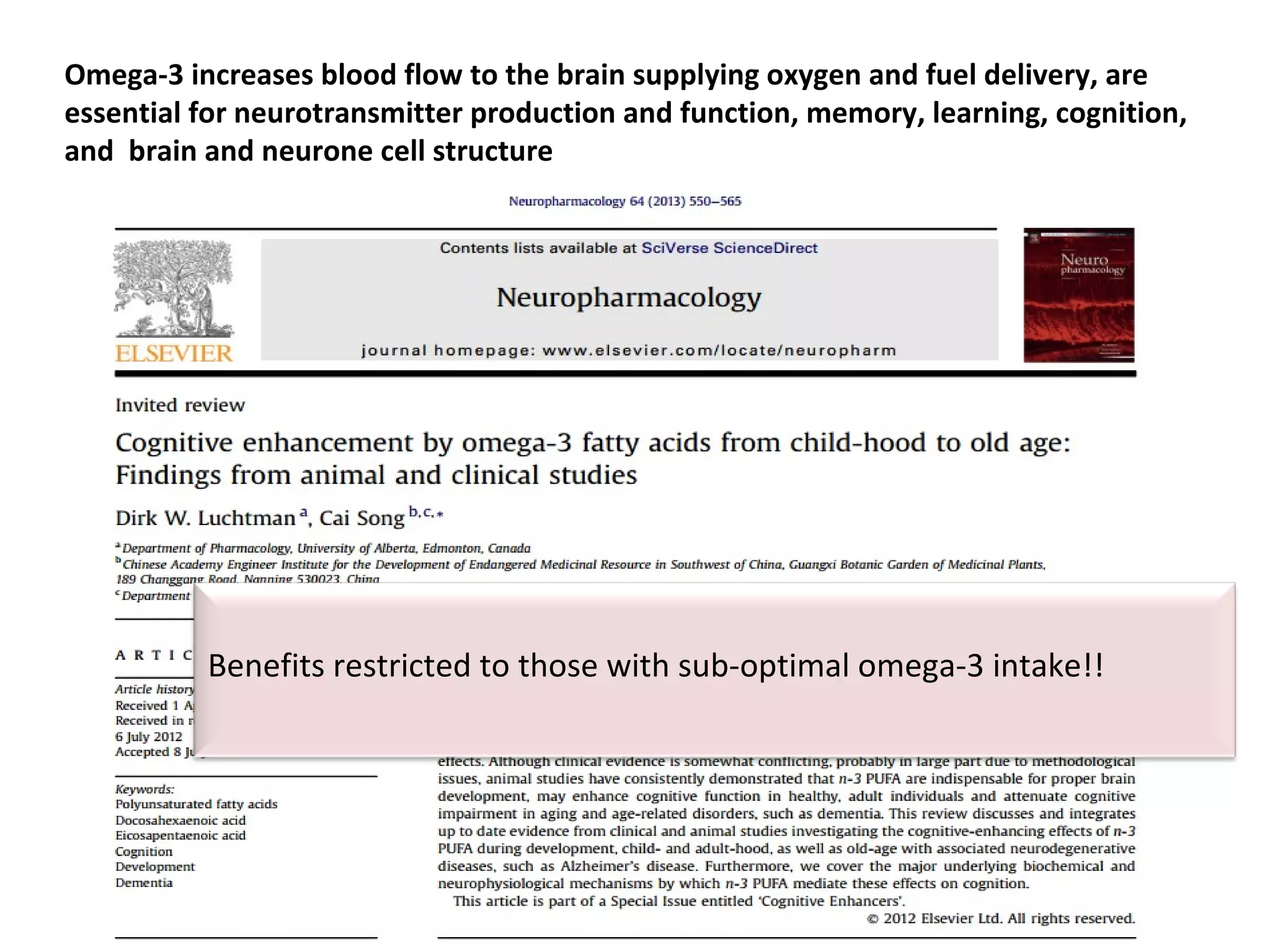
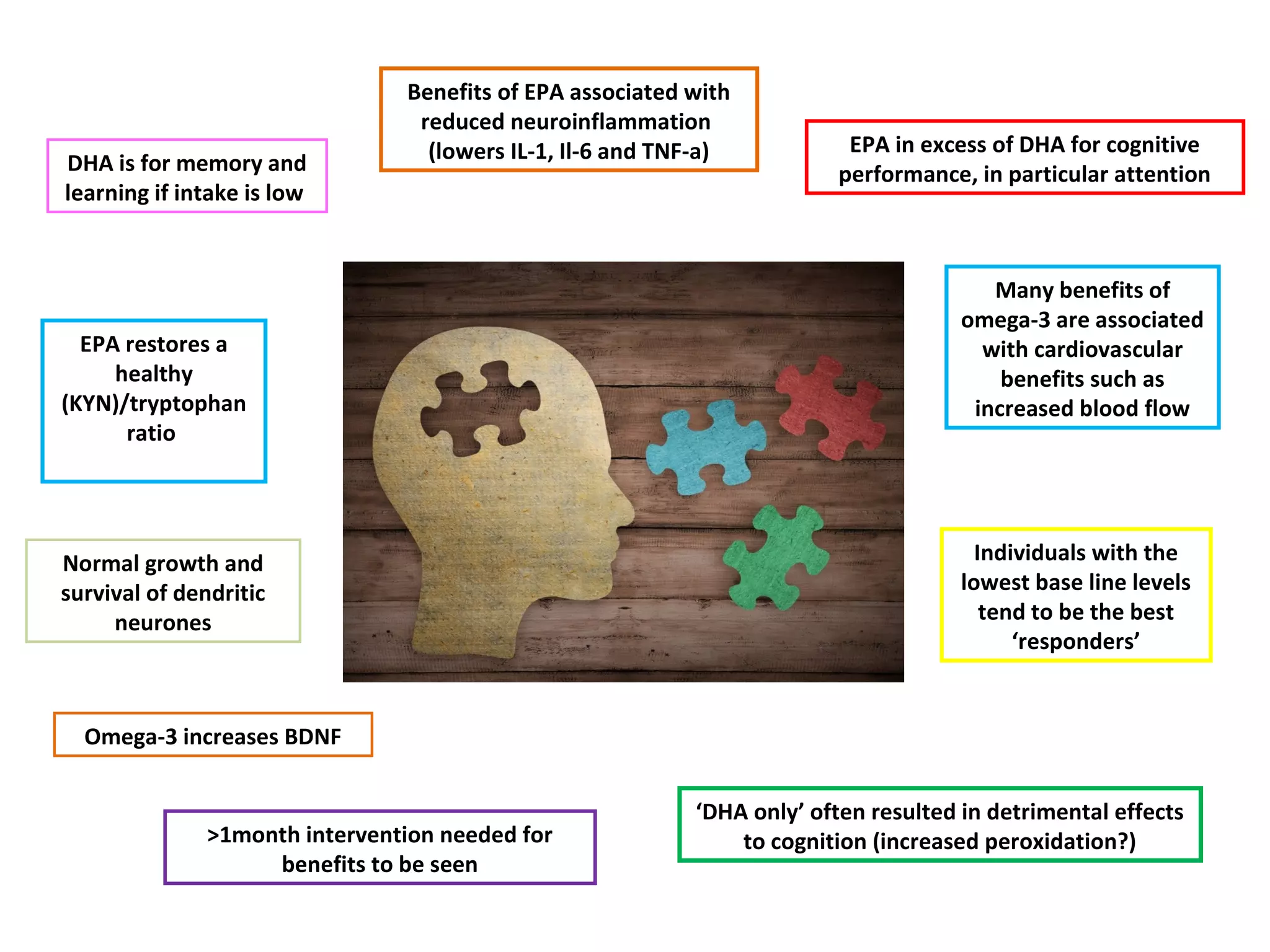
![Omega-3 and cognitive decline
• Meta-analysis examined the neuropsychological benefit of omega-3 in
randomized RCTs including healthy people, Alzheimer's disease and milder forms
of cognitive impairment (e.g. cognitive impairment no dementia [CIND])
• ApoE-ε4 status (genetic risk factor for AD) appears to be a predictor of response to
omega-treatment (no protective response)
• Omega-3 fatty acid treatment was associated with a small, but significant, benefit
for immediate recall and attention and processing speed in subjects with CIND but
not in healthy subjects or those with AD (similar findings from OmegAD study)
“Nevertheless, the present findings suggest that the effects of omega-3 on
cognitive decline are not uniform, and that there is a need to identify potentially
responsive populations”
Furthermore it is likely that nutrients work synergistically rather than in isolation!
Mazereeuw G, Lanctôt KL, Chau SA, Swardfager W, Herrmann N. Effects of ω-3 fatty acids on cognitive performance: a meta-analysis. Neurobiol
Aging. 2012 Jul;33(7):1482.e17-29.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nutritionalstrategiesforcdac1nbshortversion-161027124335/75/Nutritional-strategies-for-cognitive-decline-31-2048.jpg)









![Ingredient features
Folate ([6S]-5-methyltetrahydrofolate) vs folic acid
Quatrefolic®
provides the metabolic reduced folate form utilised and stored in the human body, as (6S)-5-
methyltetrahydrofolate, and may benefit certain genetic defects that influence folate metabolism.
Quatrefolic®
overcomes accumulation of unmetabolised folic acid (UMFA) arising from standard folic acid
supplementation, which has no biological function and whose effects are not yet known.
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin-5-phosphate)
As with many B-vitamins, riboflavin must be converted to its active form – riboflavin-5-phosphate – in order for
it to be utilised by the body.
As absorption of riboflavin occurs in the upper gastrointestinal tract, a compromised digestive system can
adversely affect the body's ability to convert riboflavin to riboflavin-5-phosphate.
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxal-5-phosphate)
Vitamin B6 exists in 6 forms but only the pyridoxal-5-phosphate form has cofactor activity.
Several inborn errors of B6 metabolism exist, which can compromise vitamin B metabolism to pyridoxal-5-
phosphate.
Pyridoxal-5-phosphate is required for approximately 100 enzymes that are important in the metabolism of
neurotransmitters and other neuroprotective compounds.
Sweeney MR, Staines A, Daly L, Traynor A, Daly S, Bailey SW, Alverson PB, Ayling JE, Scott JM: Persistent circulating unmetabolised folic acid in a setting of
liberal voluntary folic acid fortification. Implications for further mandatory fortification? BMC public health 2009, 9:295.
Surtees et al. “Inborn errors affecting vitamin B6 metabolism” Future Neurol 2006, 5:615
Powers HJ: Riboflavin (vitamin B-2) and health. The American journal of clinical nutrition 2003, 77:1352-1360.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nutritionalstrategiesforcdac1nbshortversion-161027124335/75/Nutritional-strategies-for-cognitive-decline-48-2048.jpg)