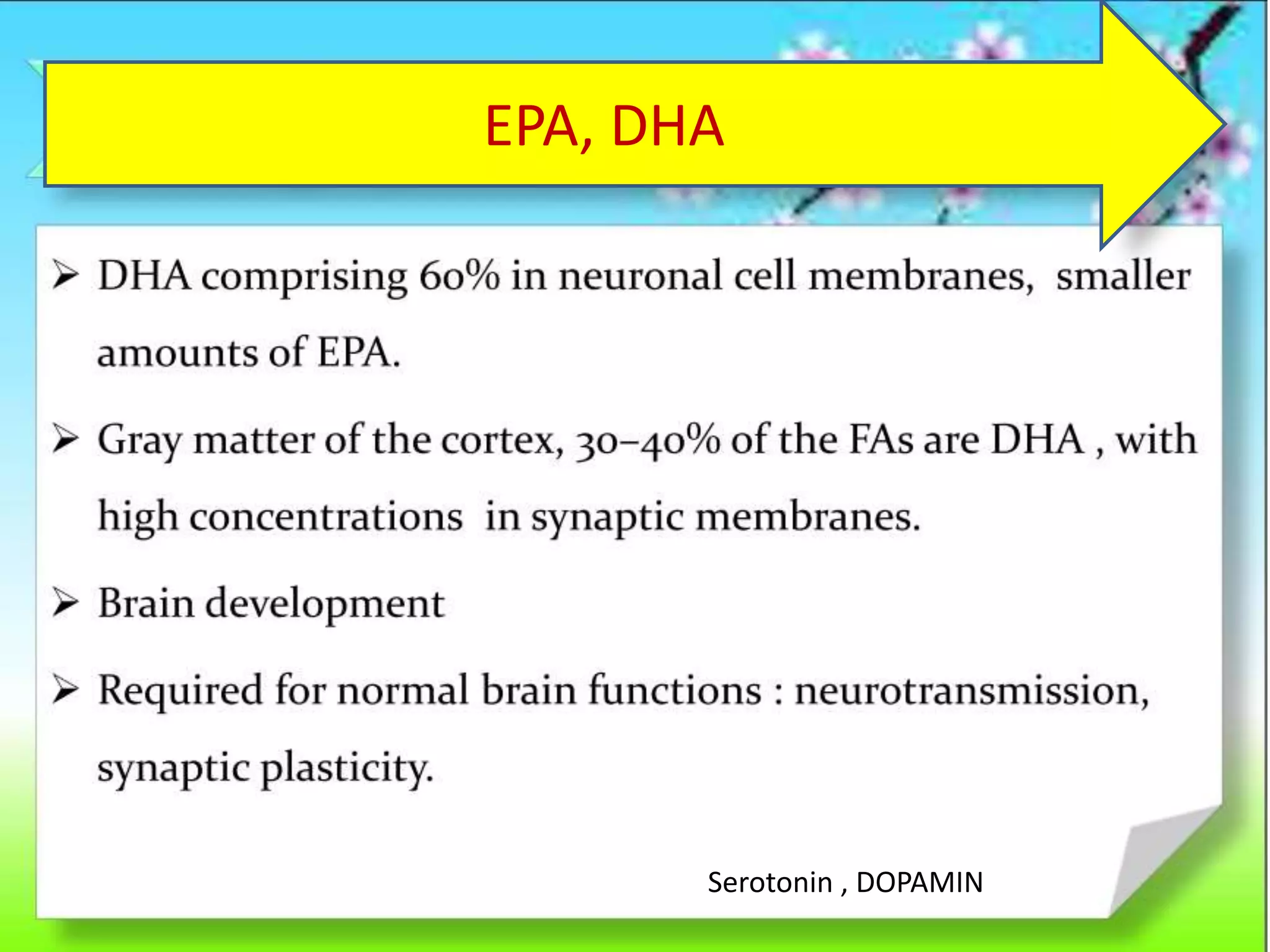
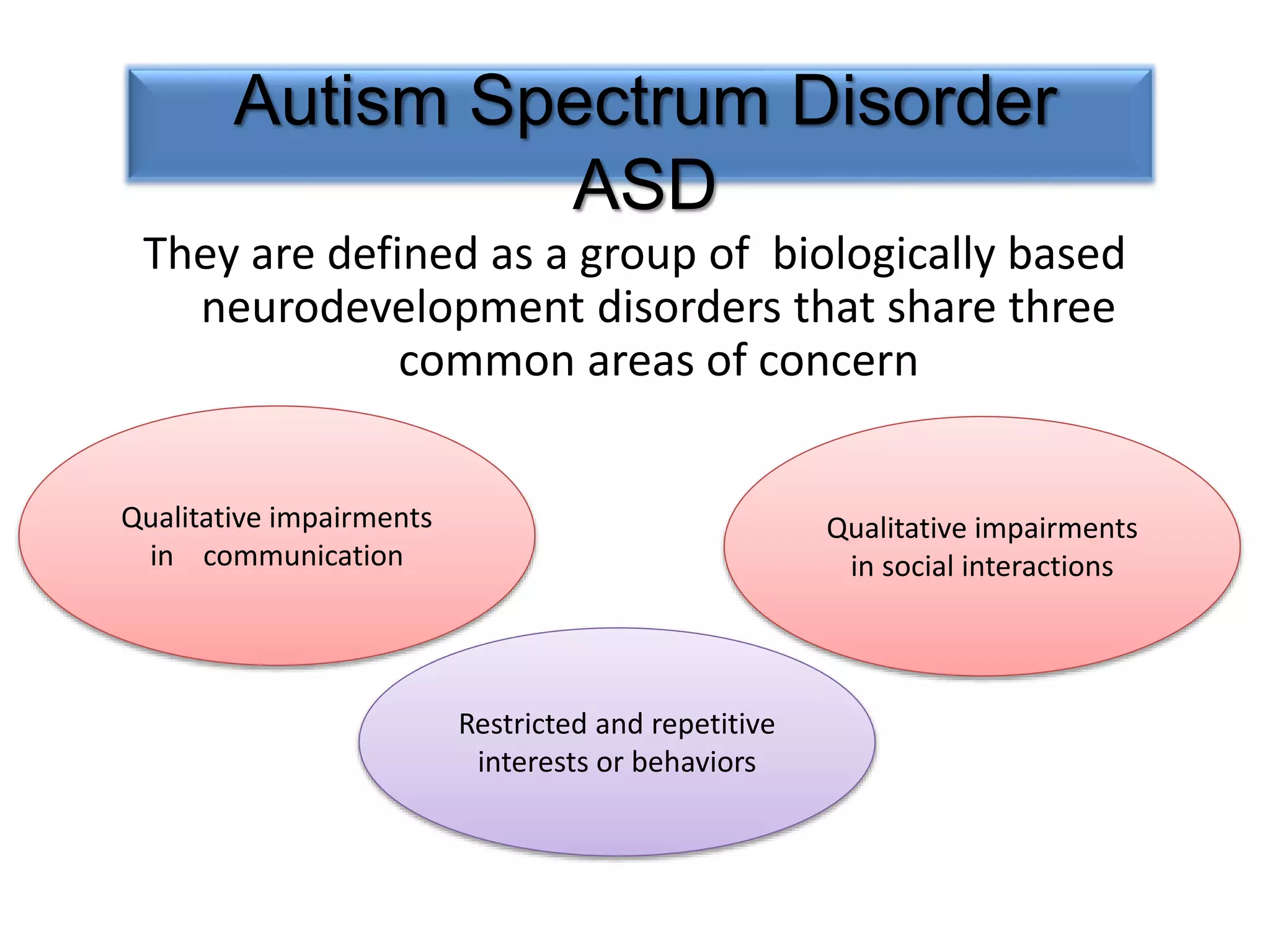
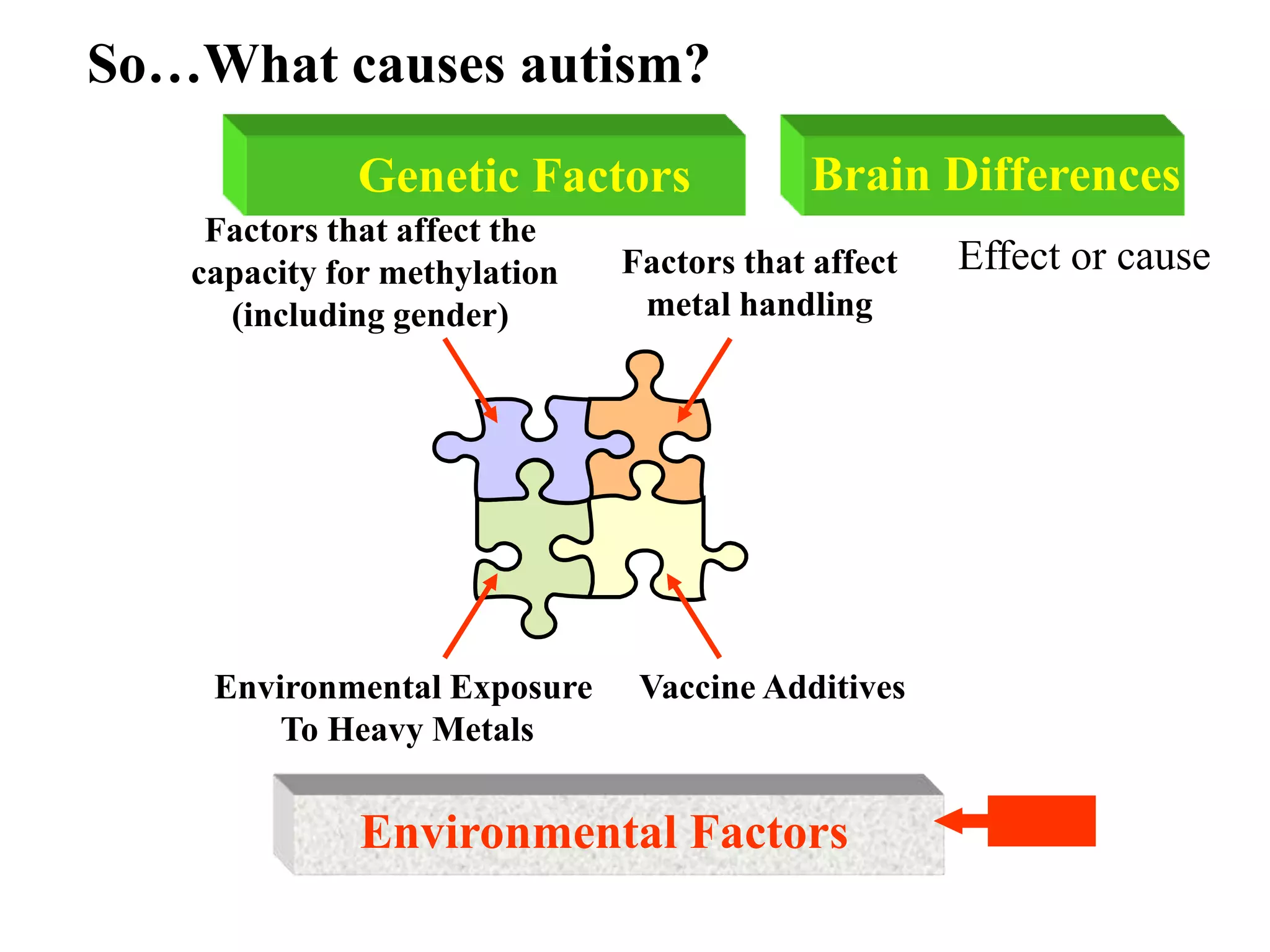
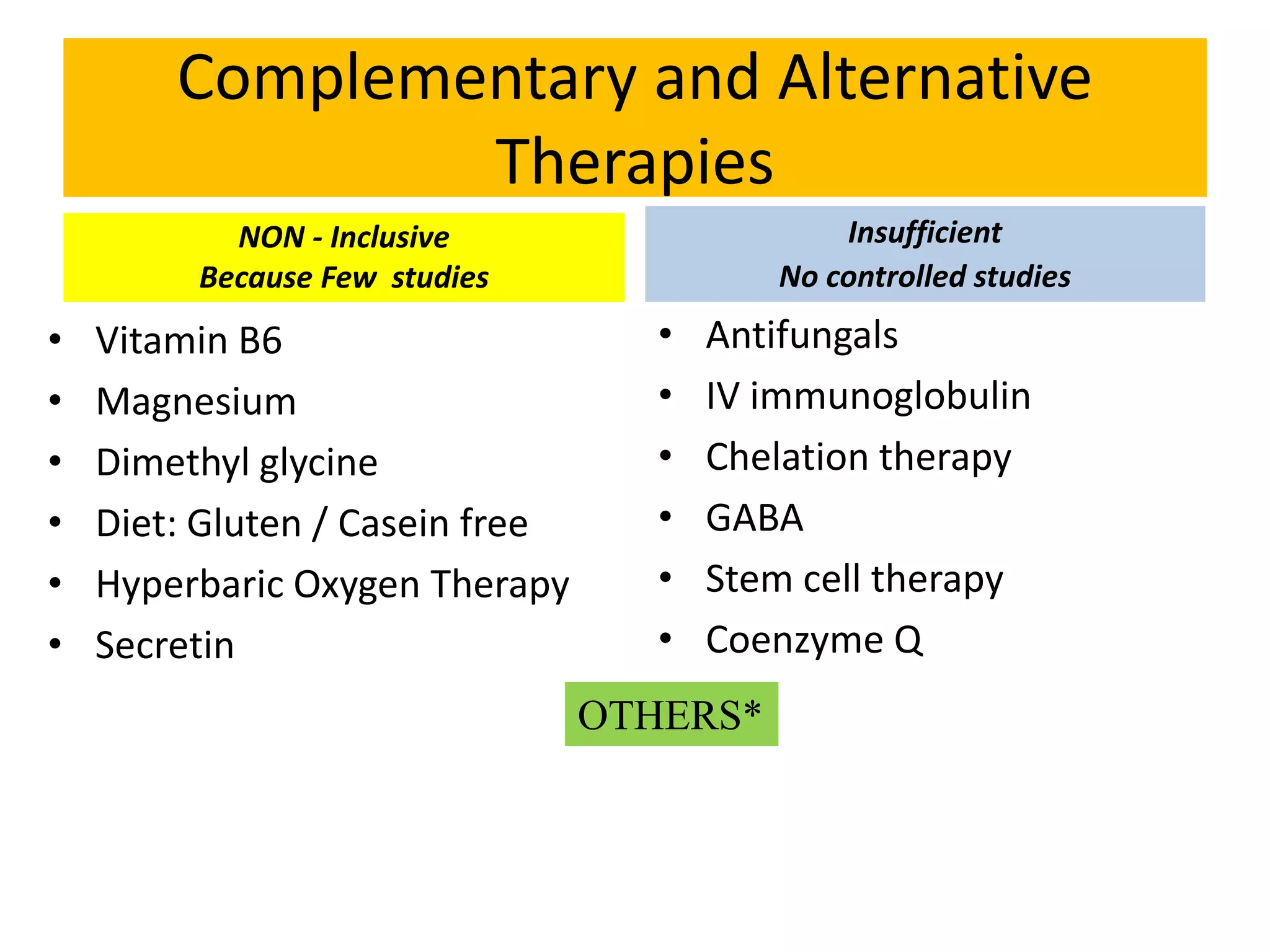
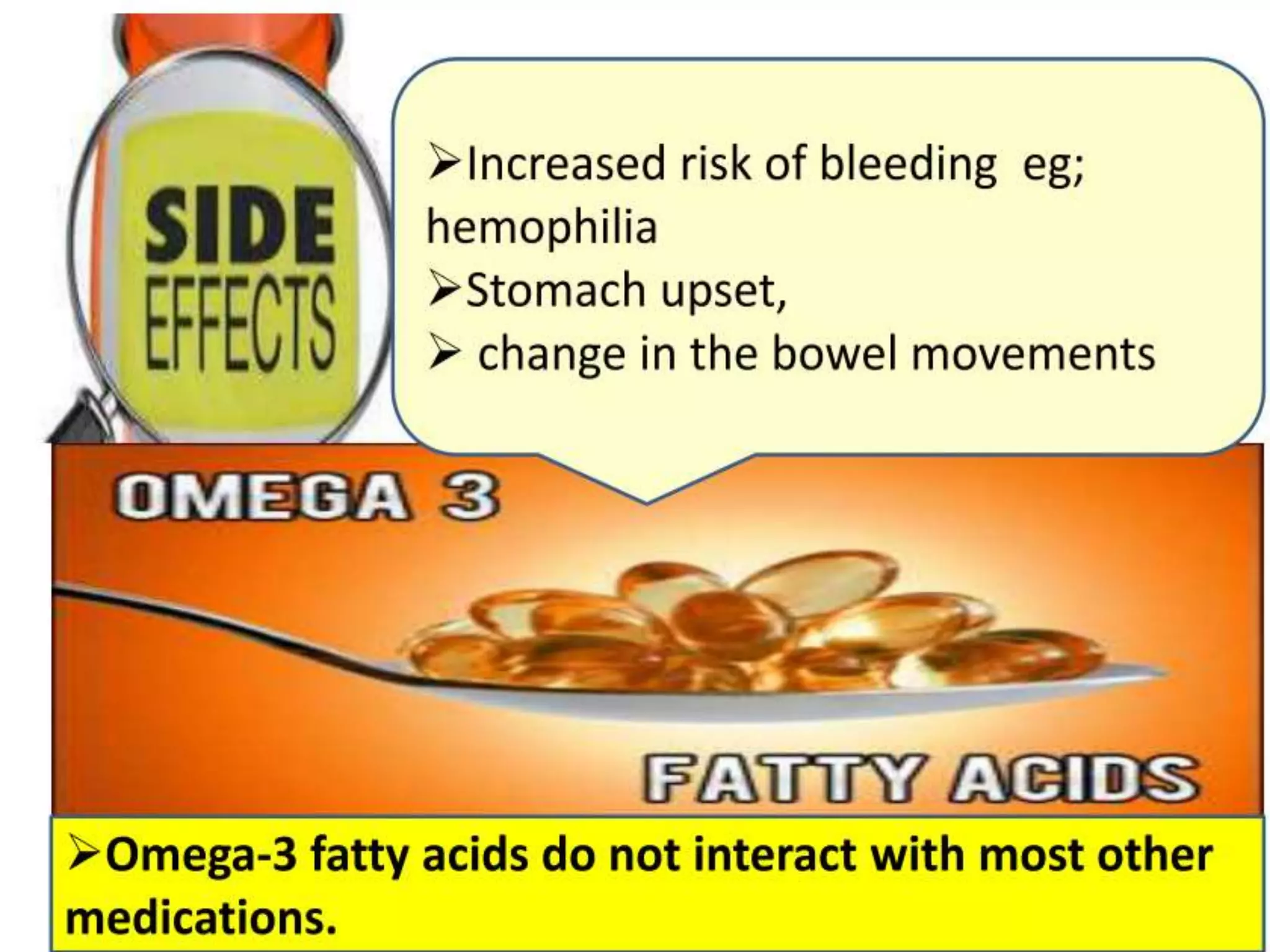
This document discusses the various benefits of omega-3 fatty acids in pediatric neurology, highlighting their essential role in brain development, cognitive function, and the treatment of neurological disorders such as ADHD, autism, and depression. It emphasizes the importance of dietary intake for pregnant mothers and infants while suggesting omega-3 as a complementary treatment option. Additionally, emerging evidence indicates that deficiencies in omega-3 are linked to multiple neurological and developmental issues in children.