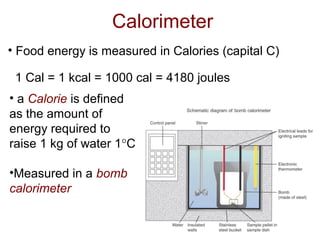
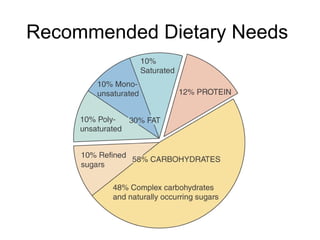
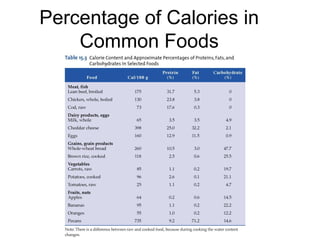
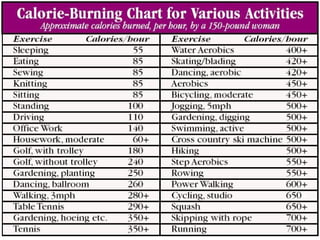
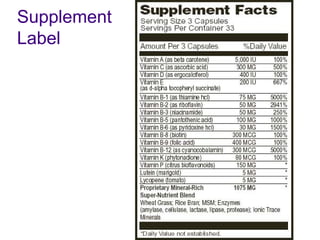
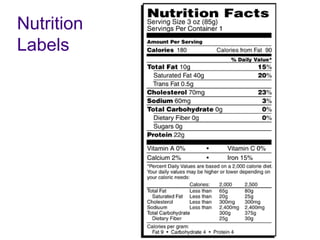
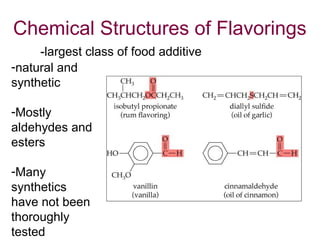
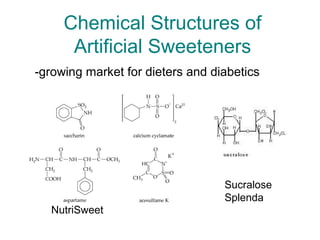
1) The body stores energy by breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins from food into smaller components that it can use to power cellular processes or store for later use as fat or glycogen.
2) When 180 grams of glucose are fully converted to CO2 and H2O, approximately 672 Calories of energy are released.
3) The two essential fatty acids that the body cannot synthesize are omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids.
4) A complete protein is one that contains all the essential amino acids that the body requires but cannot synthesize.