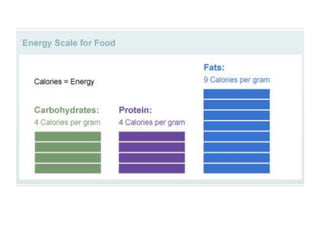
The document discusses macronutrients - protein, carbohydrates, and fats - which provide calories and energy for the body. Protein builds muscle, carbohydrates are the primary energy source, and fats are also an energy source and important for cell function. Common food sources of each macronutrient are listed. The document clarifies myths about fats and recommends daily intake amounts of macronutrients based on lean body mass and total calories.