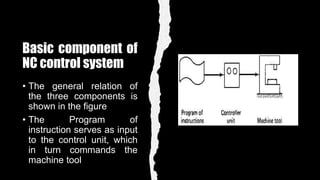
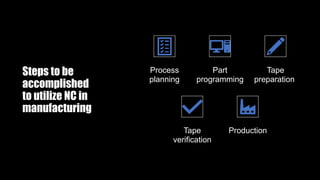
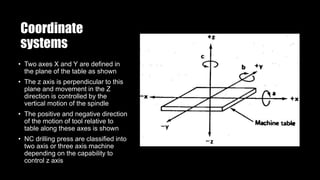
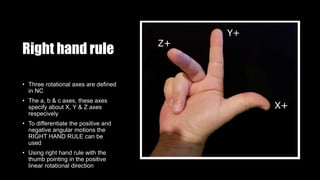
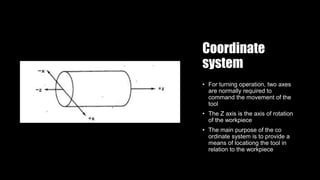
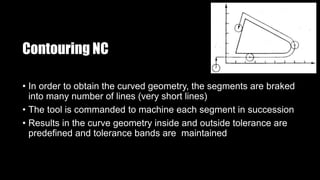
This document provides an overview of numerical control (NC) and CNC machine tools, detailing their essential components, input methods, and programming processes. It explains the structure of NC systems, including the control unit, input programs, and machine tools, while also discussing different motion control types and the associated advantages and limitations. Additionally, the document highlights various applications for NC technology in machining processes, emphasizing its role in enhancing manufacturing flexibility and accuracy.