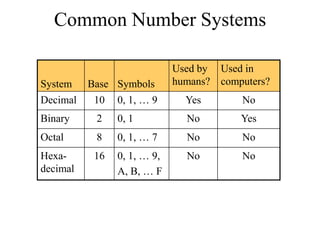
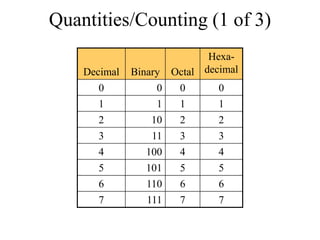
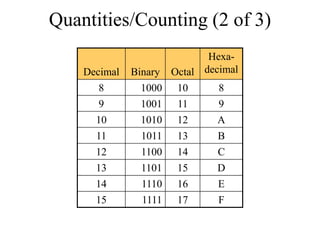
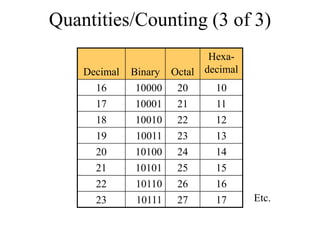
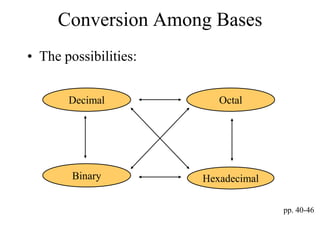
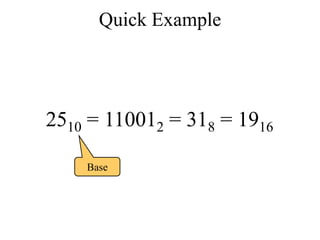
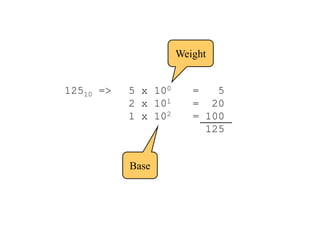
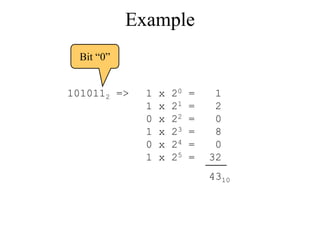
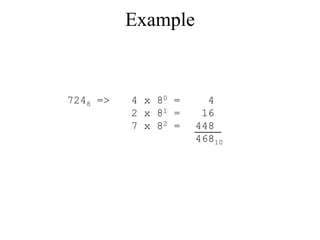
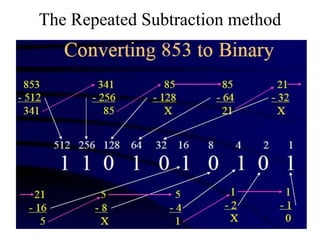
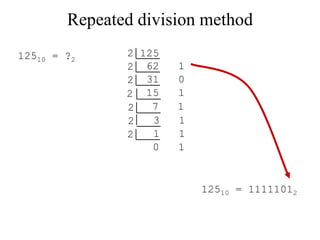
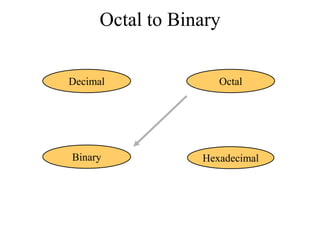
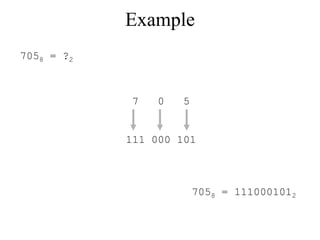
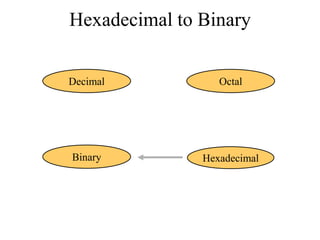
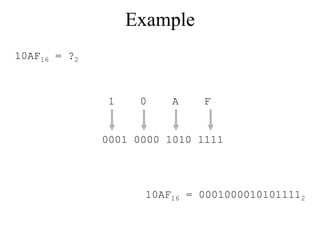
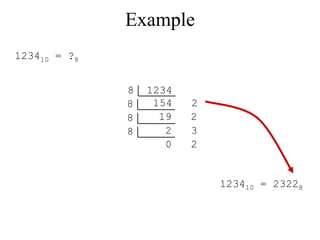
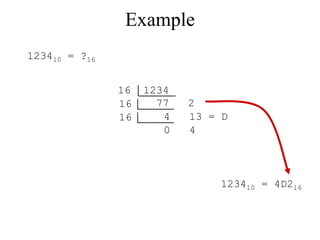
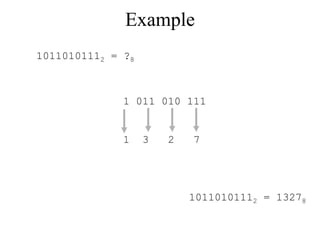
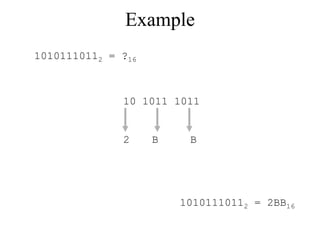
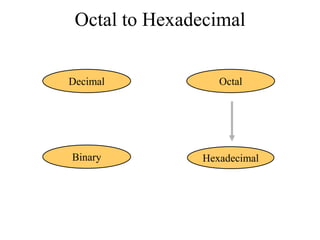
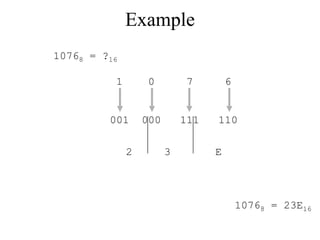
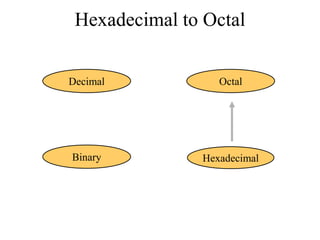
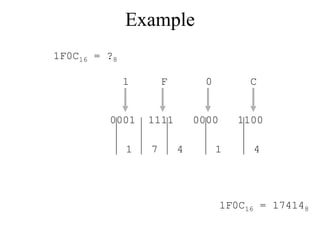
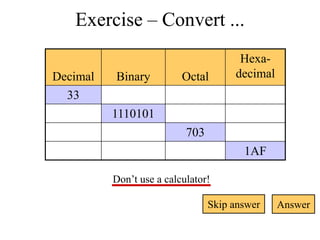
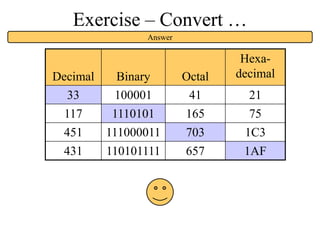
The document discusses different common number systems including decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal. It provides tables showing the base, symbols used, whether humans or computers use each system, and examples of counting in each system. The document also describes techniques for converting between the different number systems by multiplying or dividing place values and keeping track of remainders.