The document discusses different number base systems including binary, decimal, octal, and hexadecimal. It provides the following information:
- The binary system uses two digits, 0 and 1, and has a base of 2. Decimal is base 10 and uses digits 0-9.
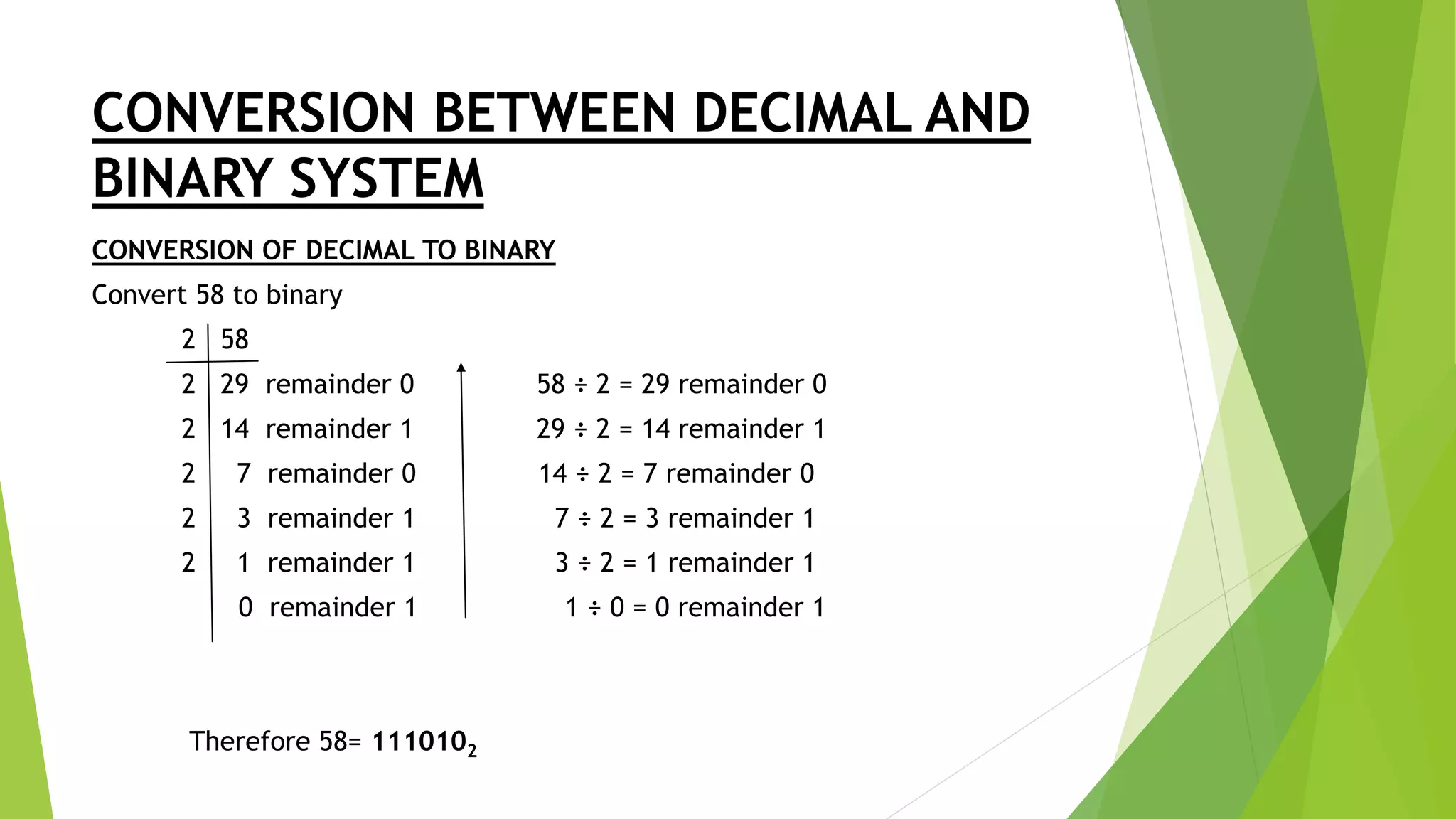
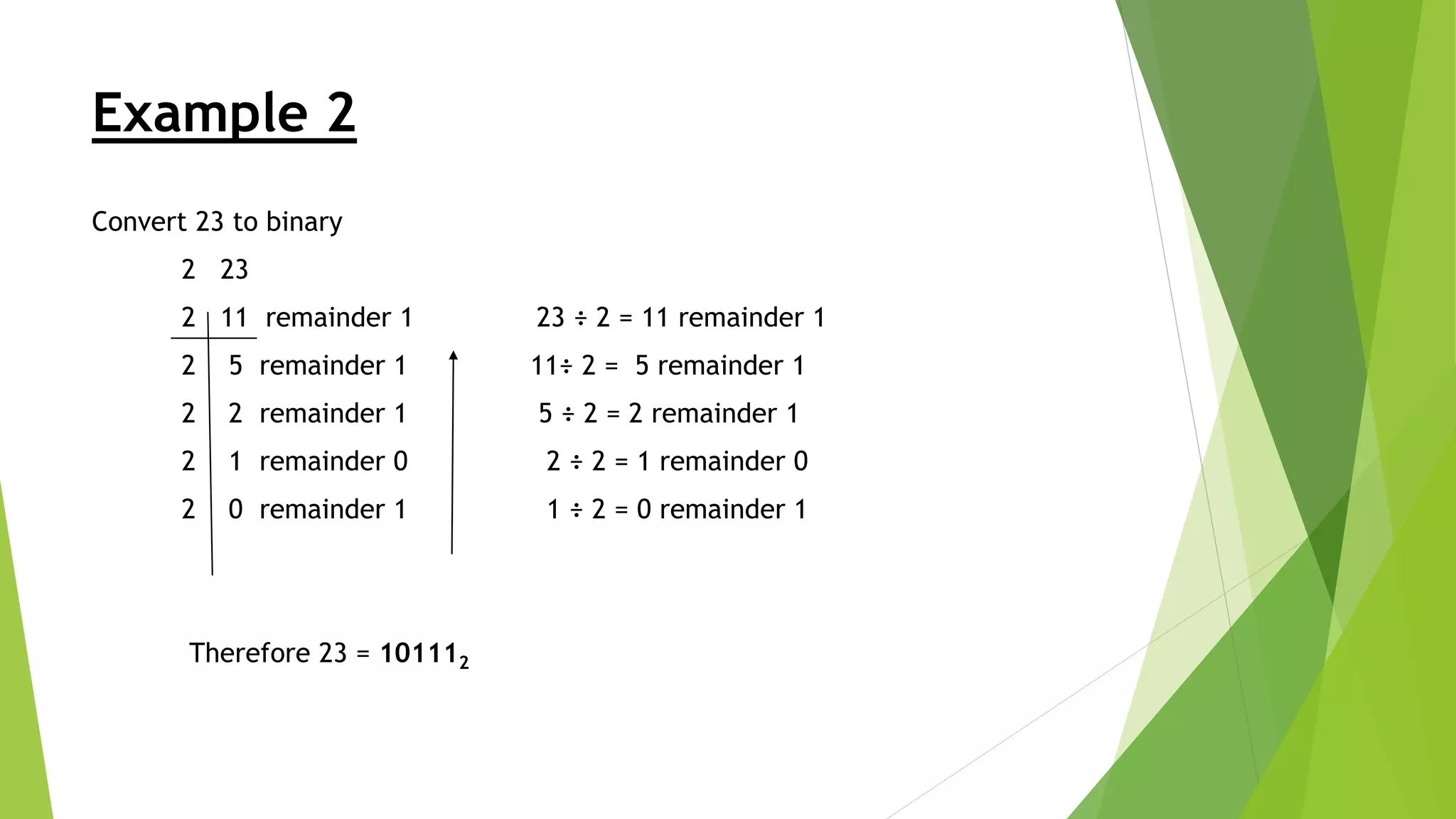
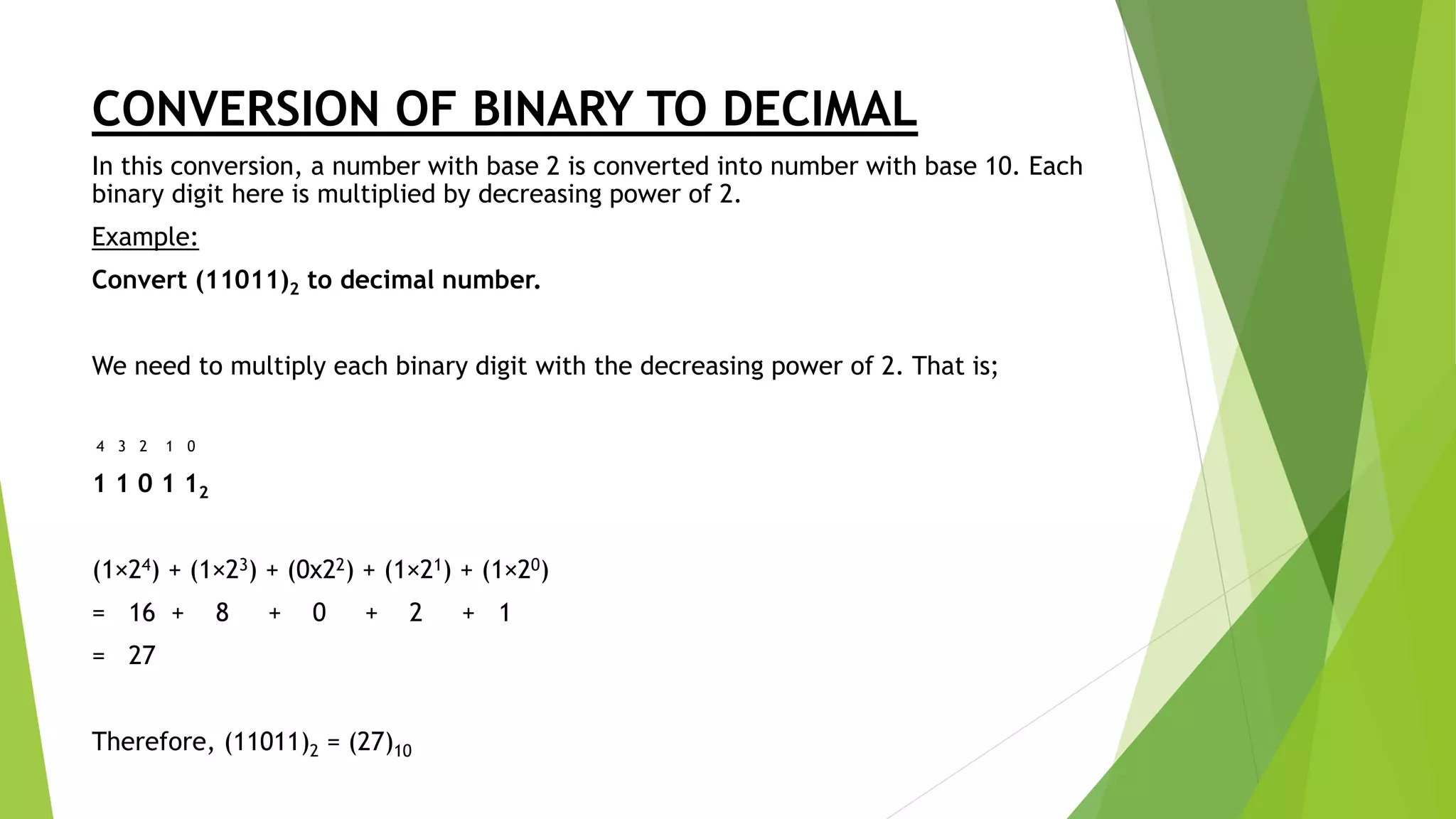
- Converting between decimal and binary involves repeatedly dividing the number by 2 and recording the remainders as binary digits.
- Octal is base 8 using digits 0-7. Hexadecimal is base 16 using digits 0-9 and A-F.
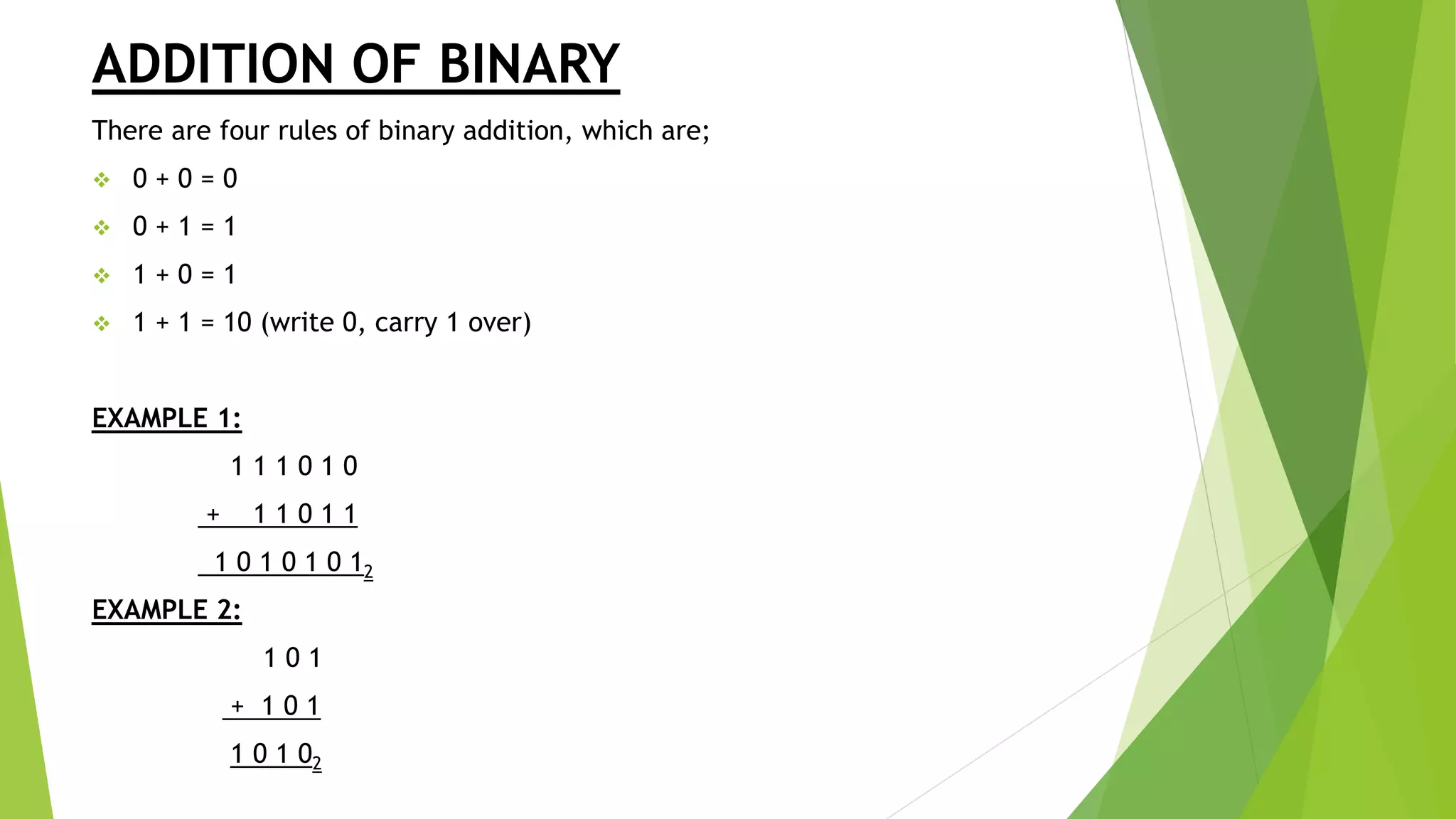
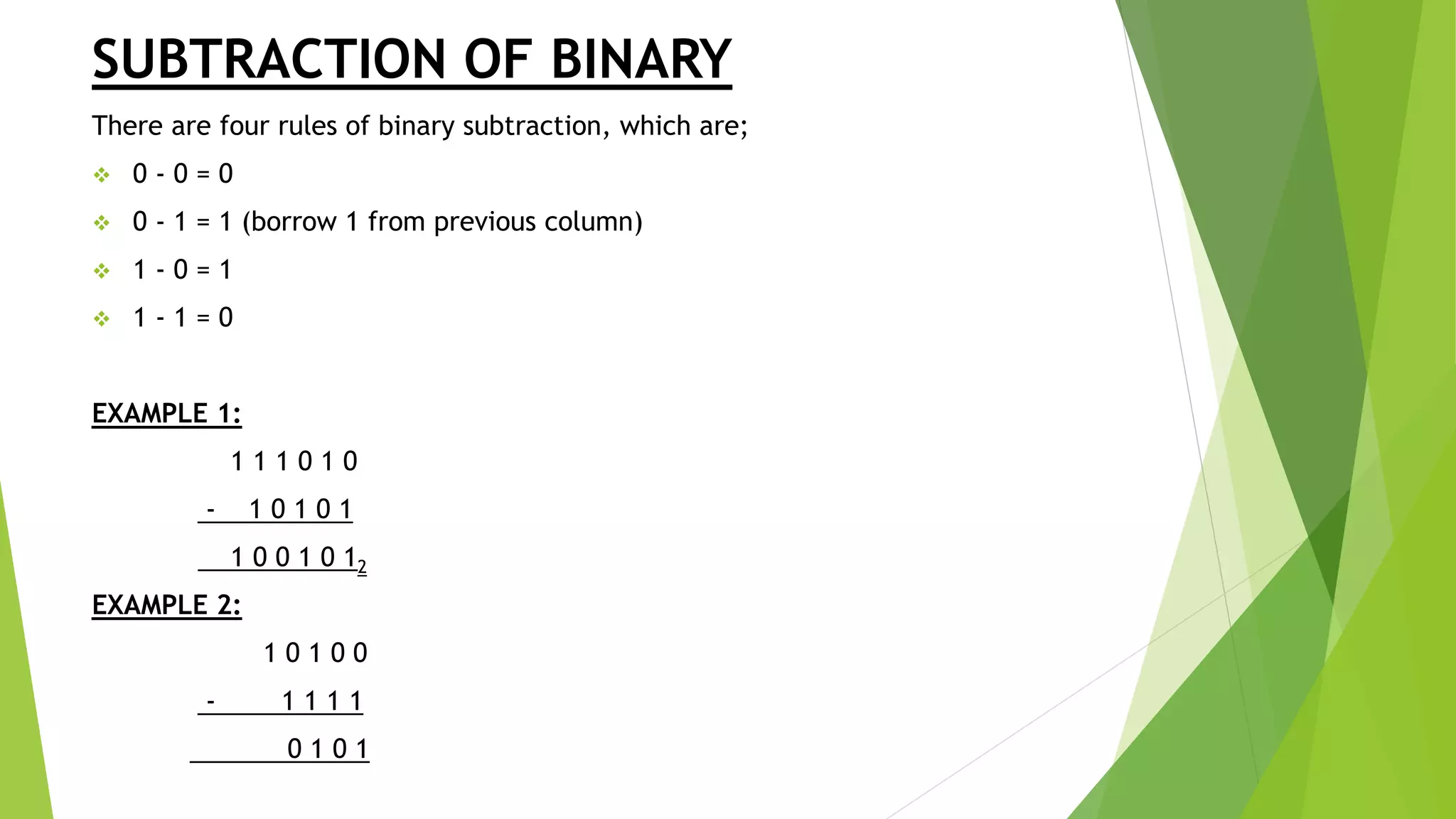
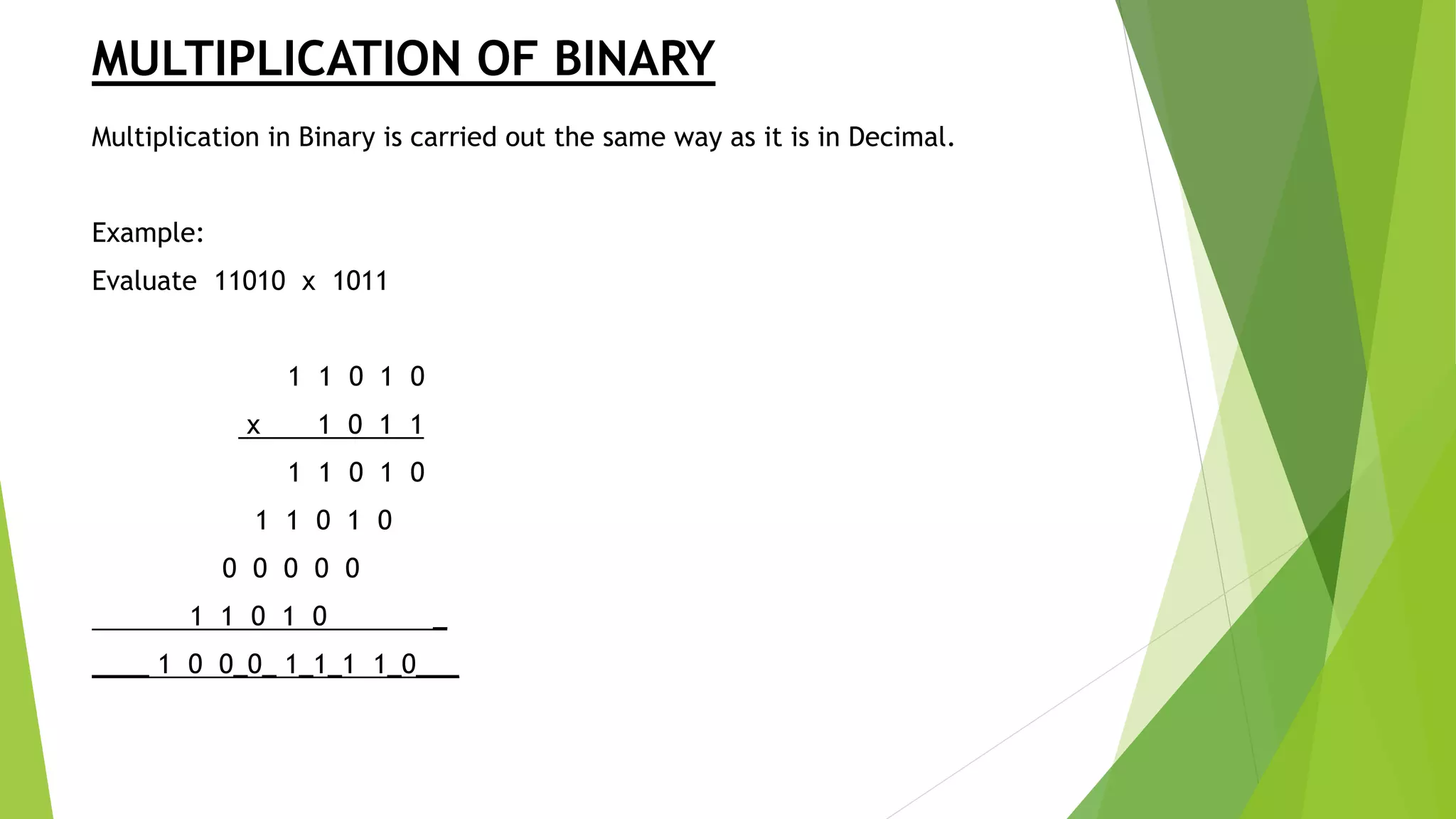
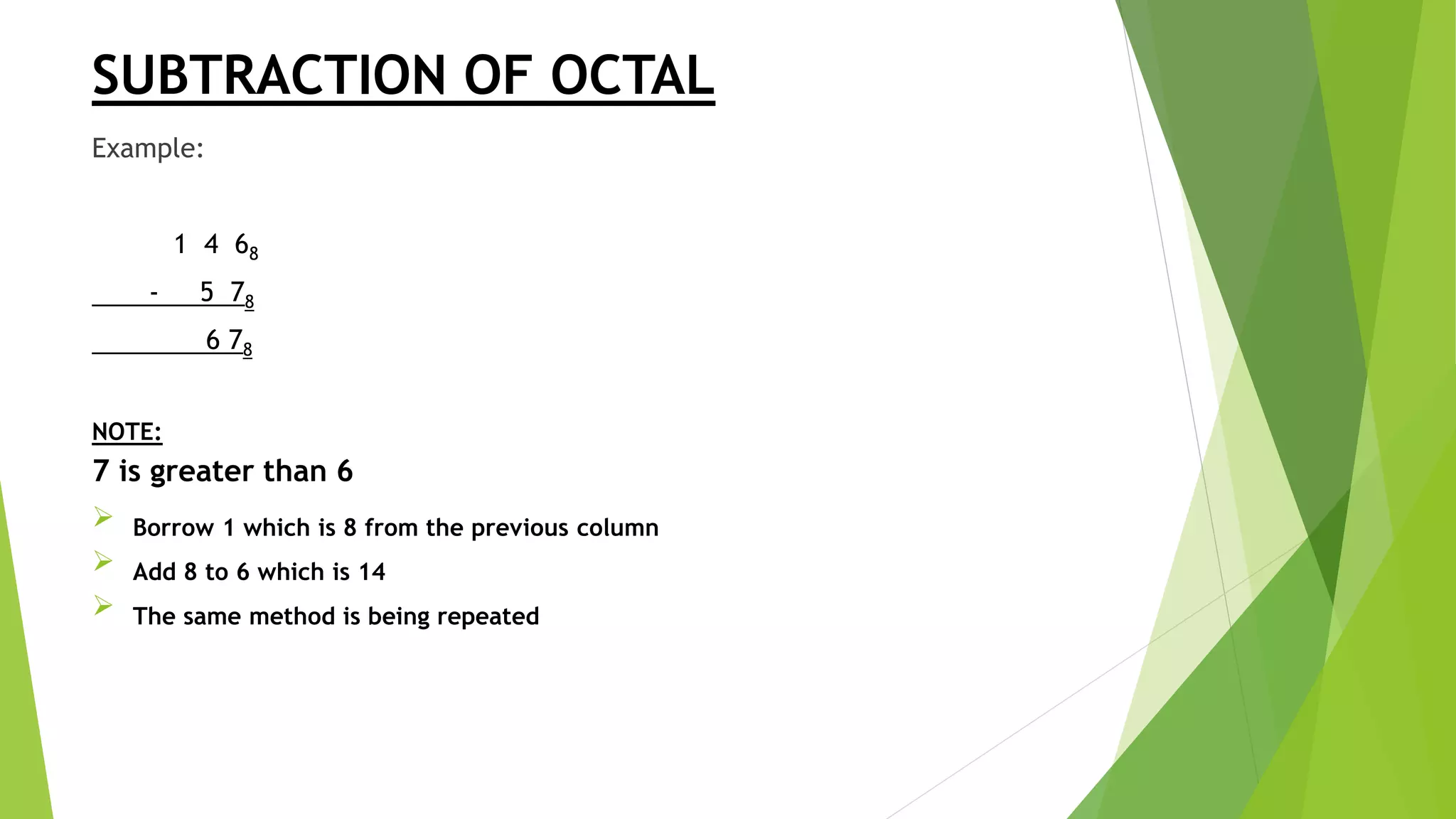
- Rules for addition, subtraction, and multiplication are provided for binary, octal, and hexadecimal number systems. Conversion between different bases and number systems is also covered.