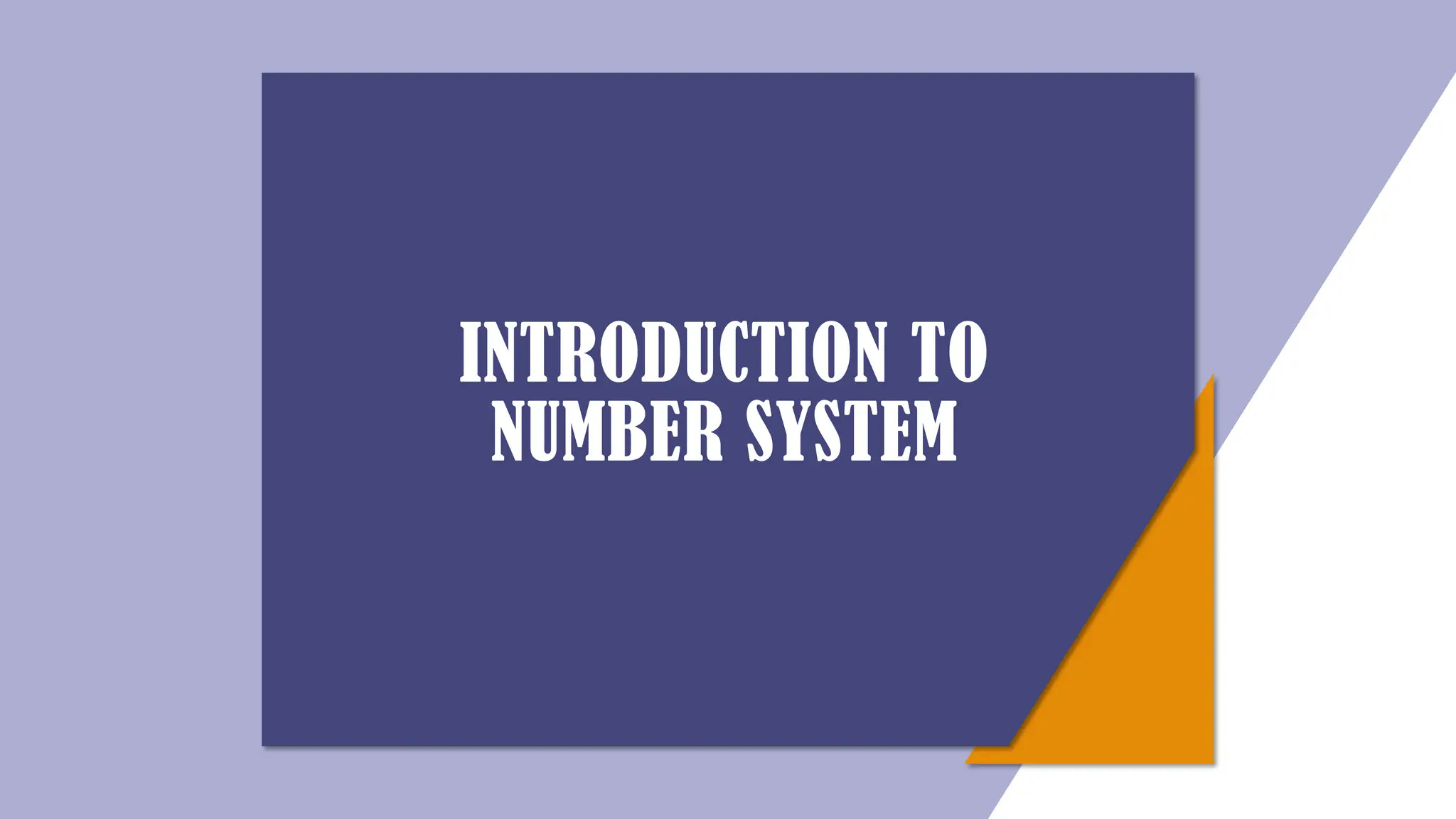
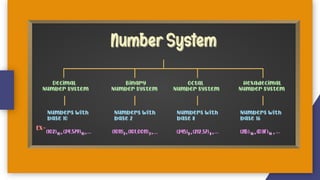
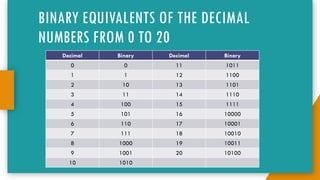
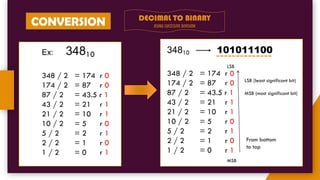
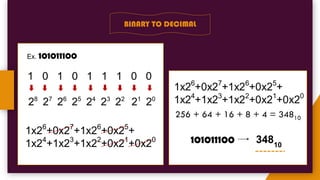
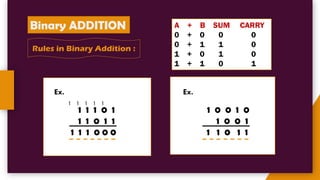
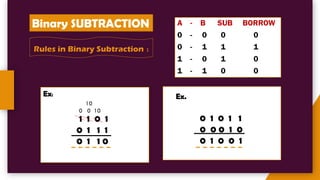
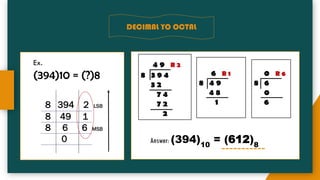
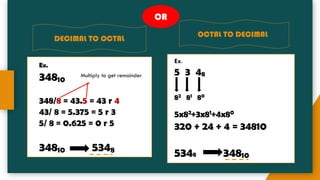
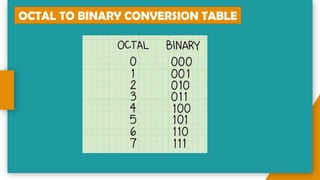
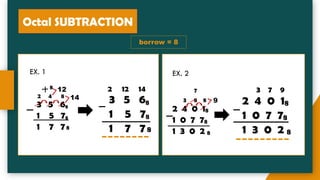
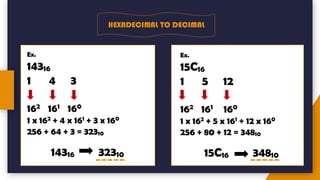
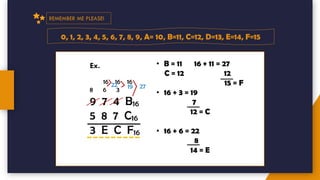
The document provides an introduction to number systems used in computing, detailing various types such as binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal systems. It explains how numbers are represented, including conversion methods between different bases and operations like addition and subtraction in these systems. Examples are given to illustrate concepts, particularly focusing on the binary and decimal systems.