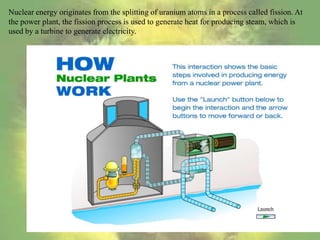
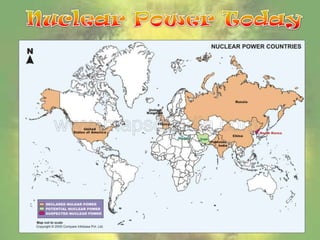
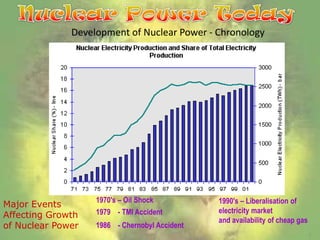
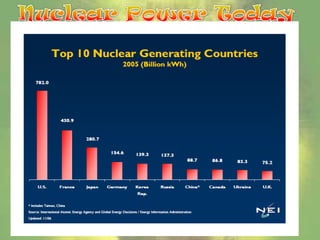
Nuclear energy originates from splitting uranium atoms through fission. At nuclear power plants, fission is used to generate heat and produce steam to power turbines and generate electricity. Construction costs for plants are very high but operating costs have decreased over time. Nuclear power produces radioactive waste that remains dangerous for hundreds of thousands of years, and accidents like Chernobyl show the risks of contamination. There are also concerns about nuclear materials being used for weapons.