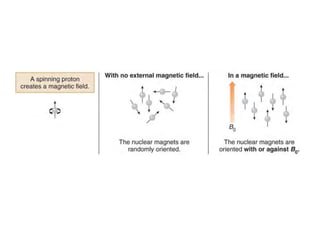
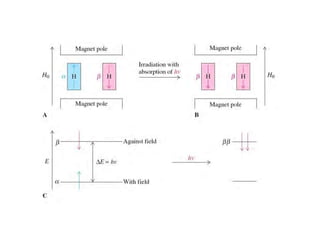
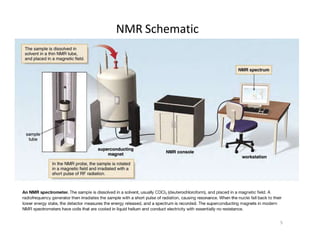
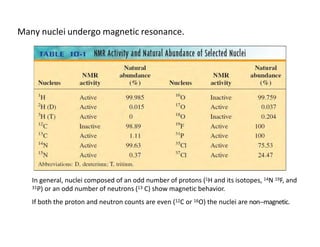
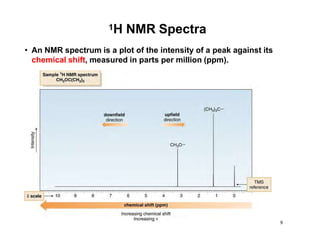
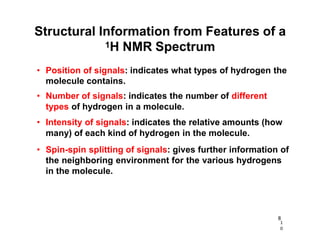
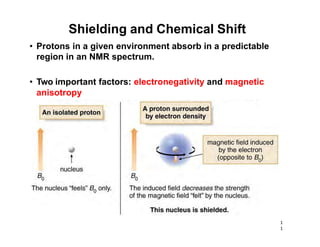
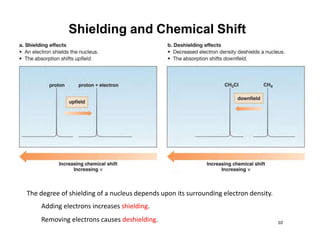
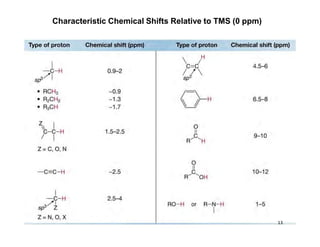
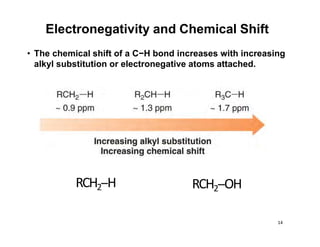
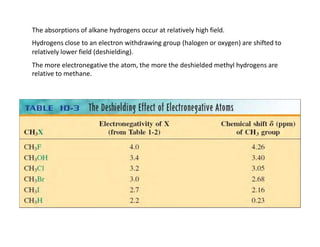
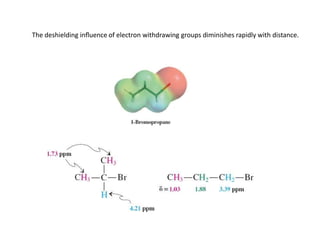
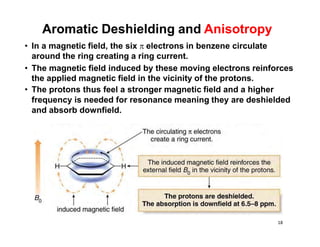
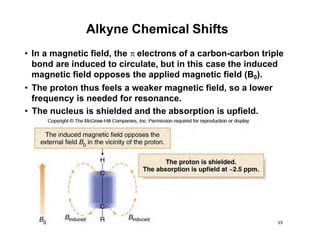
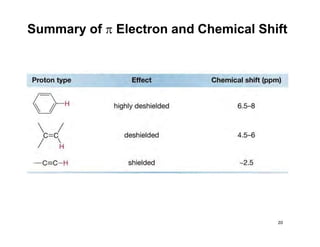
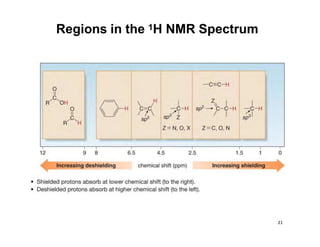
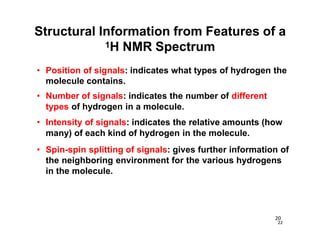
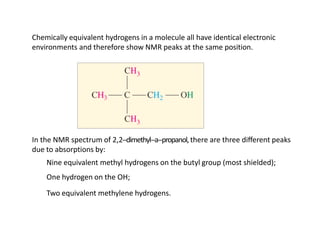
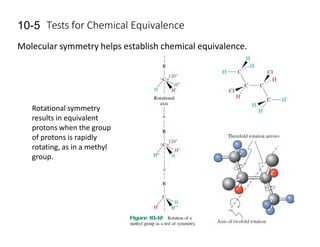
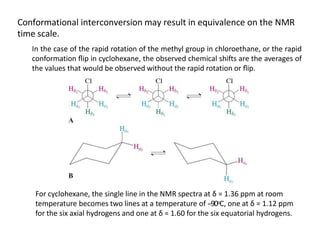
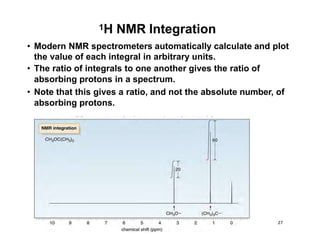
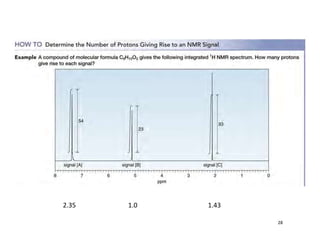
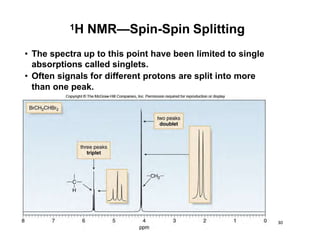
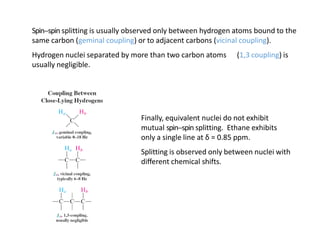
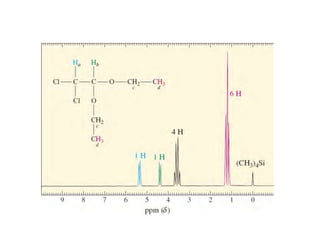
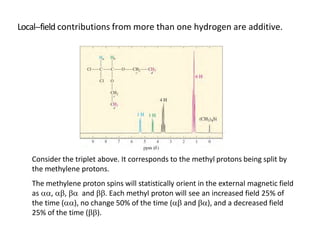
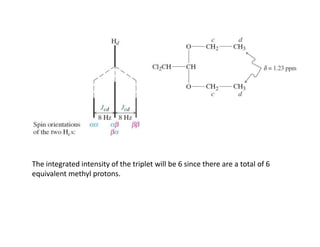
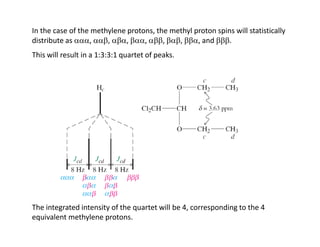
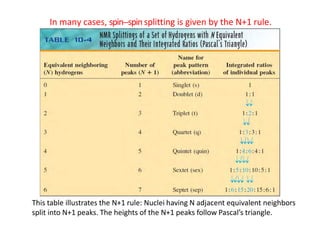
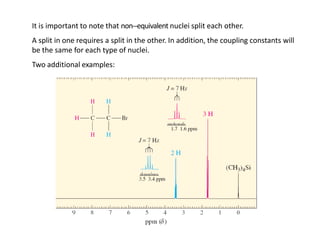
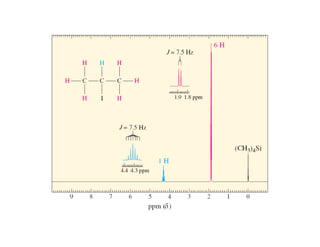
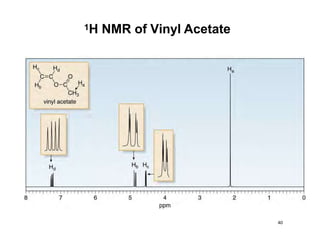
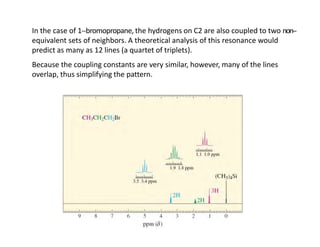
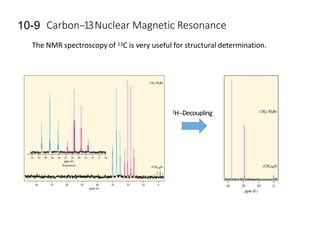
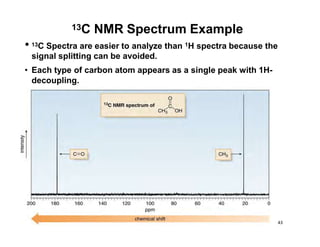
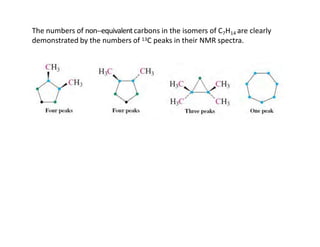
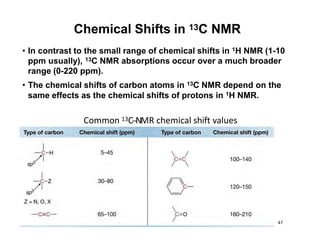
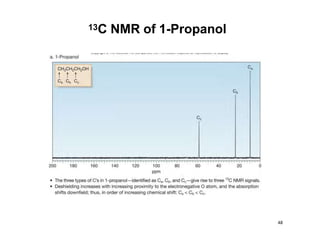
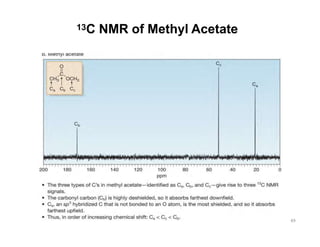
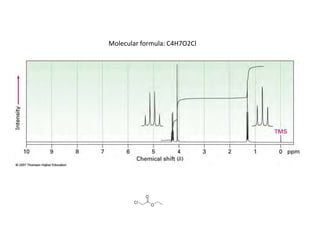
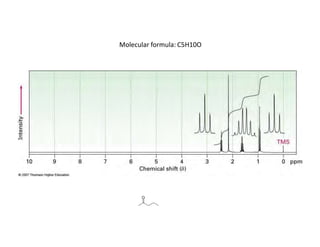
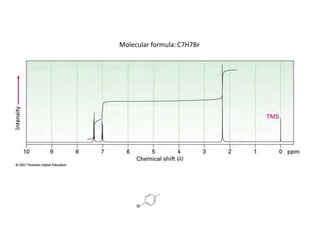
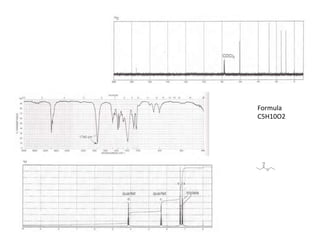
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a critical tool for organic chemists used for structural elucidation based on the absorption of radiofrequency by certain nuclei placed in magnetic fields. The technique provides key insights into molecular structure through signal patterns representing chemical shifts, which are influenced by the local electronic environment of nuclei. Factors such as electronegativity and molecular symmetry affect the observed spectra, enabling the determination of molecular formulas and structures.