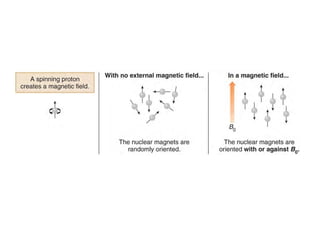
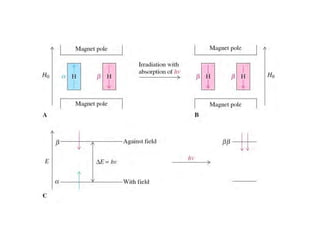
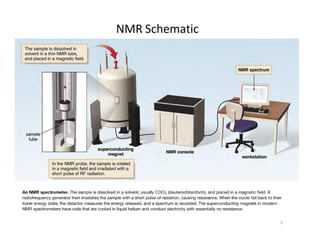
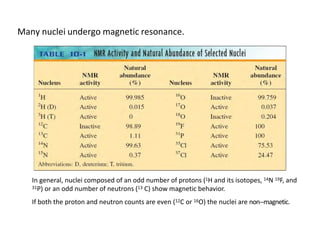
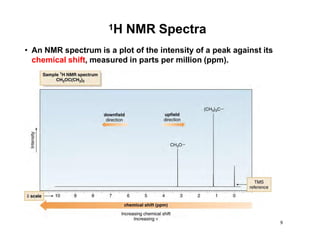
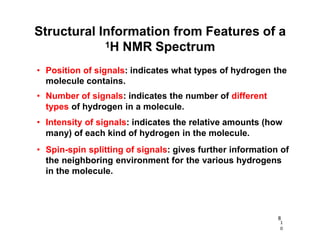
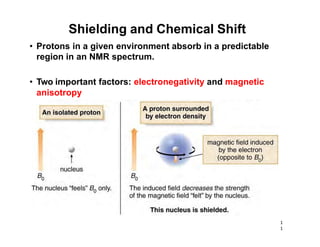
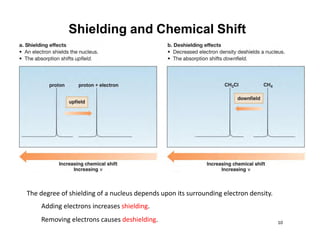
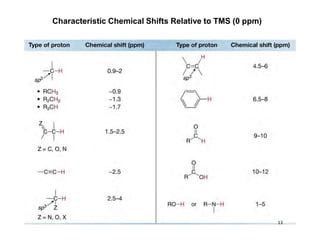
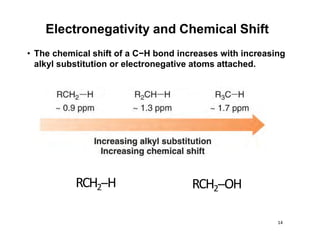
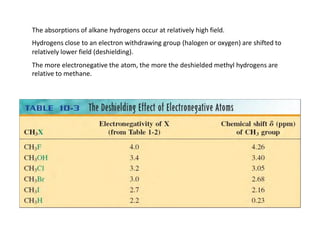
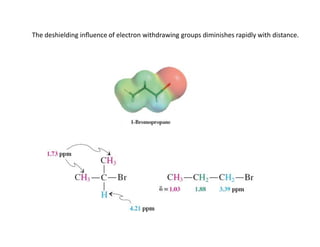
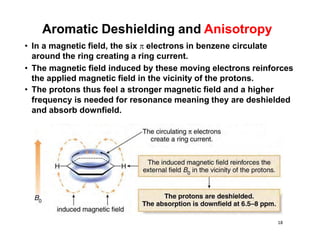
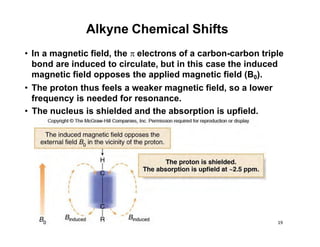
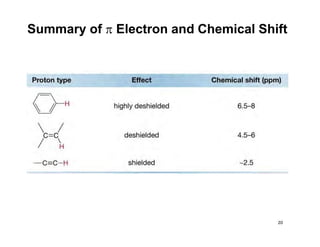
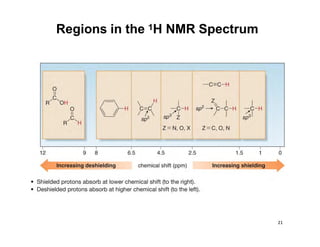
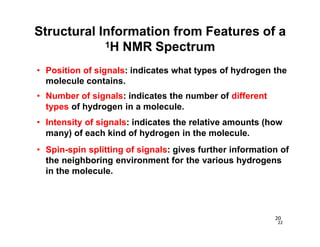
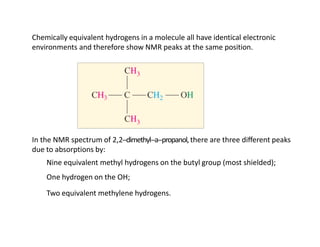
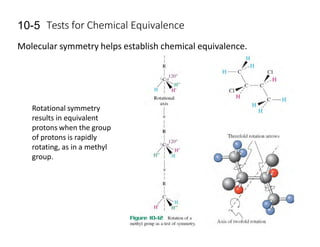
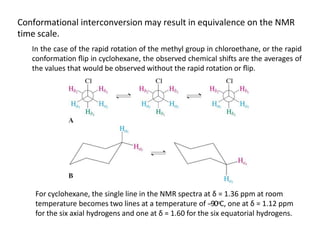
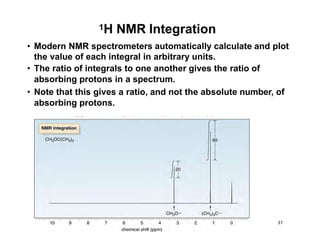
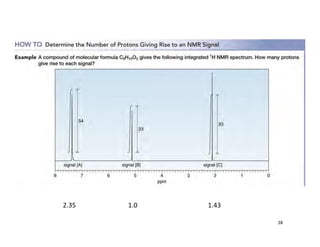
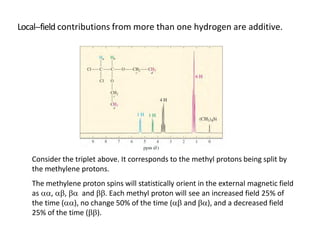
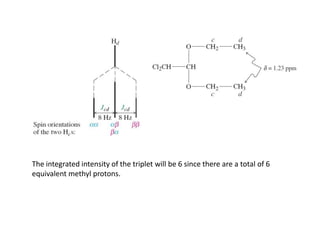
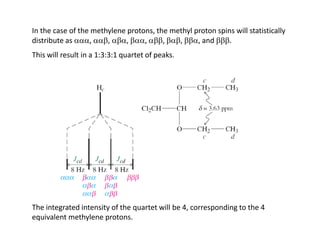
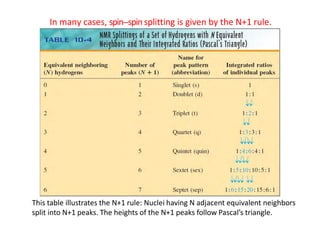
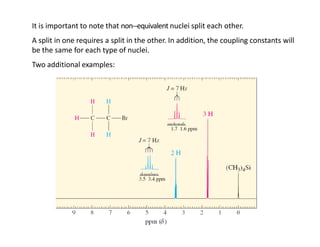
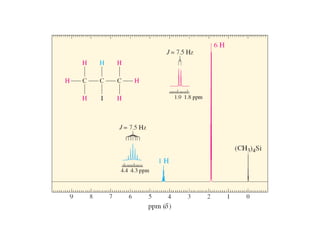
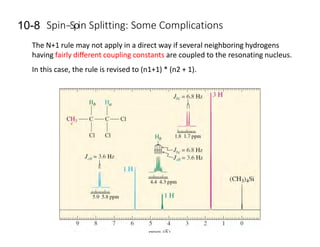
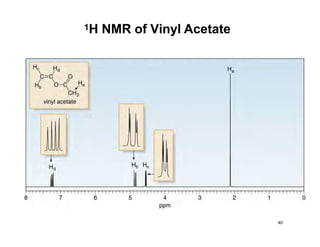
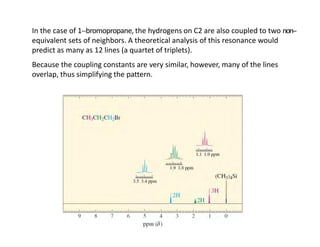
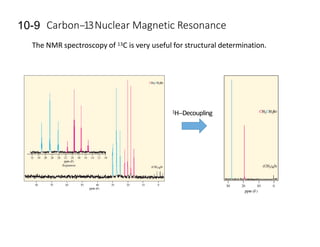
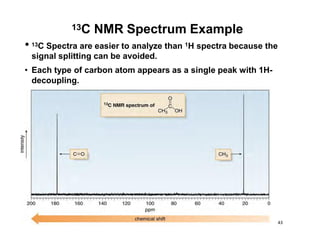
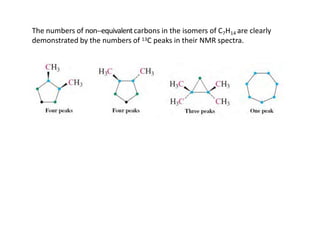
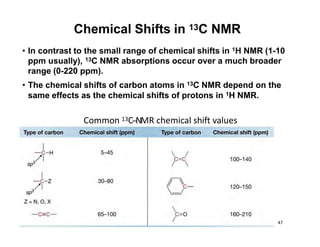
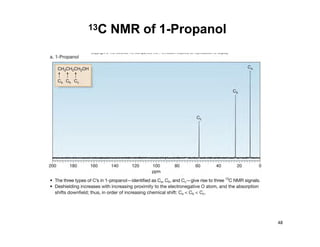
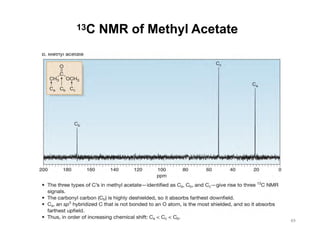
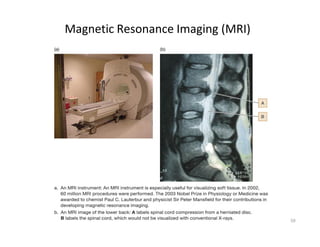
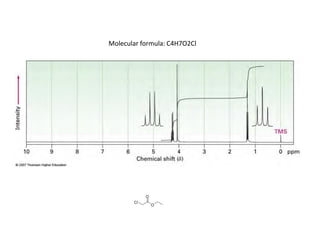
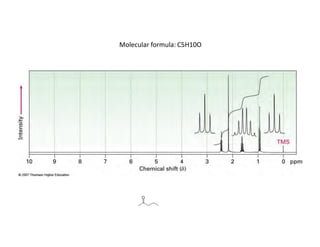
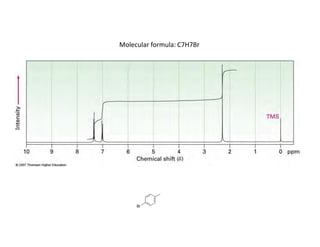
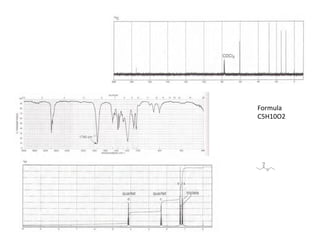
NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) spectroscopy is a powerful technique used for elucidating the structures of organic compounds by analyzing transitions between nuclear spin states in a strong magnetic field. The 1H NMR spectrum provides information on the types and numbers of hydrogen atoms in a molecule, their environments, and allows for the determination of chemical equivalence and coupling patterns between nuclei. 13C NMR complements this by providing insights on carbon structures, with broader chemical shift ranges and simplified signal patterns through 1H-decoupling.