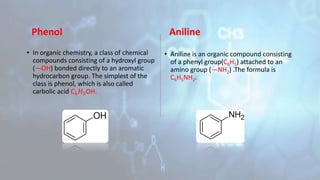
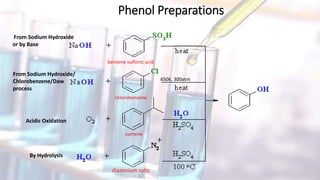
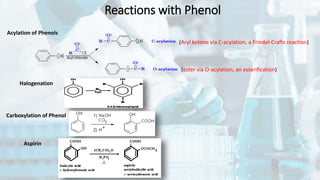
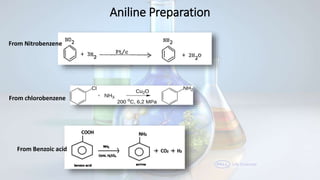
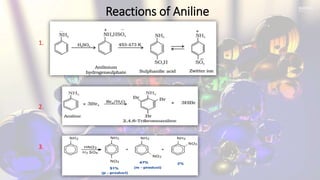
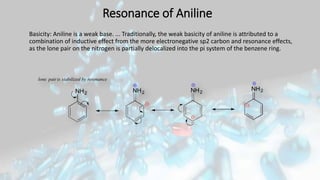
Phenol and aniline are organic compounds derived from benzene. Phenol, also known as carbolic acid, contains a hydroxyl group bonded to an aromatic hydrocarbon. It can be prepared through oxidation of benzene, cumene, chlorobenzene, or diazonium salts. Phenol undergoes acylation, halogenation, carboxylation, and other reactions. Its structure exhibits resonance. Aniline contains an amino group bonded to a phenyl group. It can be prepared from nitrobenzene, chlorobenzene, or benzoic acid. Aniline undergoes various substitution and addition reactions. Its structure also exhibits resonance, contributing to its weak basicity.