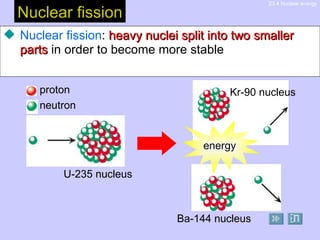
Nuclear fission occurs when heavy atomic nuclei split into lighter parts, releasing energy. In a nuclear reactor, uranium-235 nuclei are split in a controlled chain reaction to generate heat and produce steam to power turbines for electricity production. Nuclear reactors use fuel rods containing uranium-235 surrounded by water as a moderator. Control rods made of boron or cadmium absorb neutrons to control the fission rate. Nuclear power plants transfer heat from the reactor to steam, which powers the turbines to generate electricity via an electromagnetic generator. Radioactive waste from the plants requires careful long-term storage.