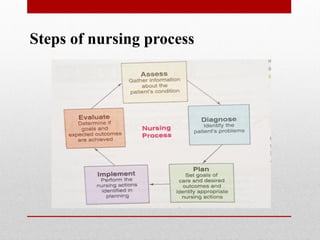
This document discusses the nursing process and its steps for caring for patients. It begins by defining the nursing process as the critical thinking process nurses use to provide evidence-based care and promote human health and well-being. The five steps of the nursing process are then described as assessment, nursing diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. Assessment involves collecting subjective and objective data. Nursing diagnosis involves determining the patient's response to their condition. Planning involves setting goals and determining interventions. Implementation involves applying the planned interventions. Evaluation involves assessing the effectiveness of the interventions. The document then provides details on each step, such as how to formulate nursing diagnoses and develop nursing care plans.