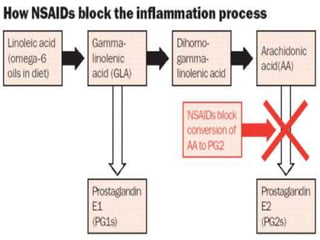
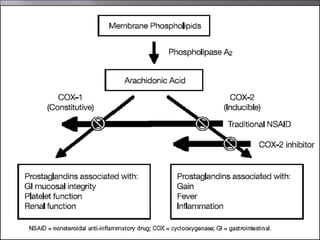
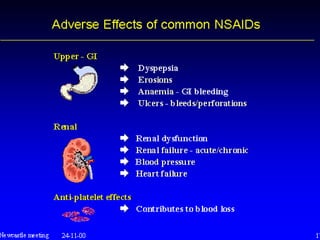
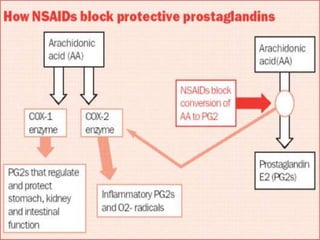
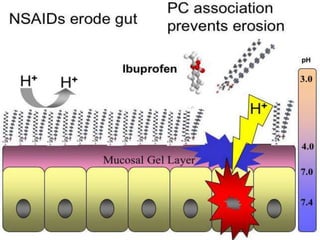
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) work by inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandins. There are several classes of NSAIDs including salicylates, para-aminophenol derivatives, pyrazolone derivatives, phenylpropionic acid derivatives, and oxicams. NSAIDs are well absorbed orally and highly protein bound. They are metabolized in the liver and excreted primarily in the bile. NSAIDs are indicated for reducing inflammation and pain in conditions like arthritis but can increase risks in pregnant women or those with gastrointestinal or liver issues. Common side effects include gastrointestinal distress and bleeding.