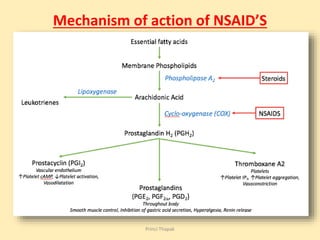
This document discusses non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including their classification, mechanisms of action, uses, and examples like aspirin and ibuprofen. NSAIDs are analgesics that reduce pain, fever, and inflammation by inhibiting cyclooxygenase enzymes. They are classified as non-selective, preferential, or selective inhibitors of COX-1 and COX-2. Common side effects include stomach ulcers, kidney problems, and platelet dysfunction. Aspirin and ibuprofen are two widely used NSAIDs; they work by blocking prostaglandin production and have analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory properties.



![A] Non selective COX Inhibitors
Salicylates – Aspirin(acetylsalicylic acid), Diflunisal,
Salicylic acid and its salt, Salsalate.
Pyrazolone derivatives – Phenyl butazone ,
Oxyphenbutazone .
Indole derivatives- Indomethacin, Sulindac
Propionic acid derivatives –
Ibuprofen,Dexibuprofen,Naproxen,Fenoprofen,
Ketoprofen,Dexketoprofen, Flurbiprofen,
Oxaprozin,Loxoprofen
By Princi Thapak](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nsaidspresentation-191212155308/85/Nsaids-presentation-4-320.jpg)
![A] Non selective COX Inhibitors
Anthranilic acid derivatives - Mefenamic acid
Meclofenamic acid, Flufenamic acid, Tolfenamic acid
Aryl acetic acid derivatives- Etodolac, Ketorolac,
Diclofenac
Oxicam derivatives- Pyroxicam, Tenoxicam
Pyrrolo- pyrrole derivatives- Ketorolac
By Princi Thapak](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nsaidspresentation-191212155308/85/Nsaids-presentation-5-320.jpg)
![B] Preferential COX 2 Inhibitors
Nemesulide
Meloxicam
Nabumetone
C] Selective COX 2 Inhibitors
Celecoxib
Rafecoxib
Valdecoxib
D] Analgesic anti pyretic and poor inflammatory drugs
Para aminophenol derivative- Paracetamol
Pyrazolone derivatives - metamizol, propiphenazone
Benzoxazocine derivatives- Nefopam
By Princi Thapak](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nsaidspresentation-191212155308/85/Nsaids-presentation-6-320.jpg)