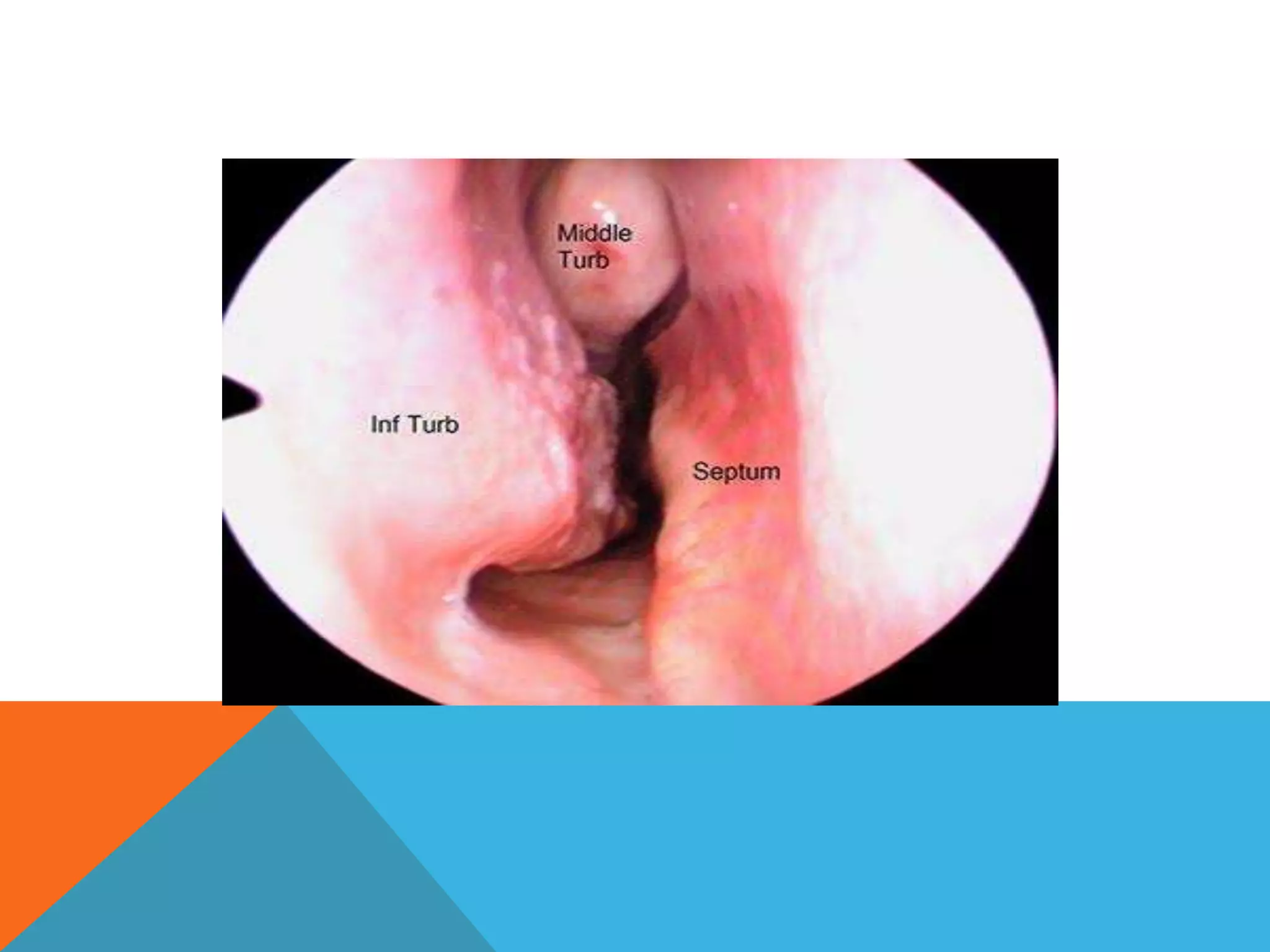
This document provides instructions for examining the nose and related structures. It describes examining the nose externally and internally using anterior and posterior rhinoscopy. Key parts of the nose that are examined include the nasal septum, turbinates, floor, roof and lateral walls. Functional tests like the spatula and cotton wisp tests evaluate nasal patency. The sense of smell is also tested. Related areas like the paranasal sinuses and cervical lymph nodes are inspected and palpated. The overall examination evaluates the nose, nasal passages and surrounding structures in detail.